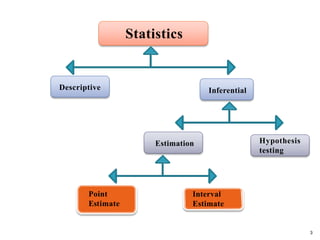
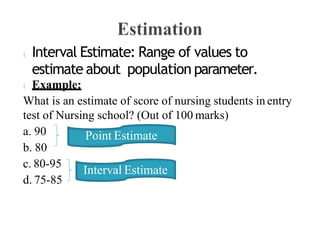
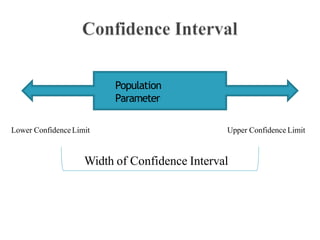
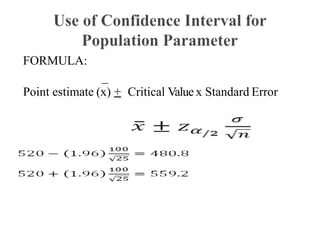
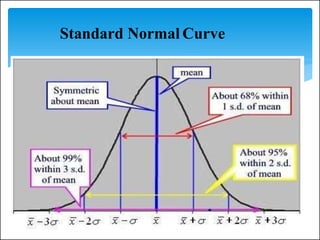
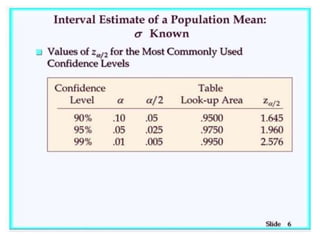
The document outlines the fundamentals of inferential statistics, specifically focusing on point and interval estimation techniques. It emphasizes the importance of these statistical tools in estimating population parameters based on sample data, highlighting concepts such as confidence intervals and margin of error. Additionally, it provides examples and formulas to demonstrate how point estimates and confidence intervals can be calculated and interpreted.