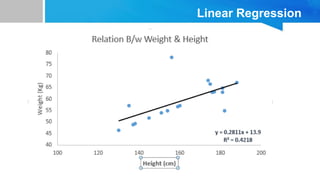
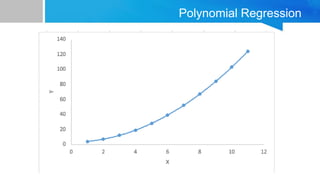
La regresión es una técnica de modelado predictivo que investiga la relación entre variables dependientes e independientes, utilizada para pronósticos y análisis causal. Existen diferentes modelos de regresión, siendo la regresión lineal el más sencillo, pero también se pueden utilizar las regresiones polinómicas para datos complejos. Las aplicaciones incluyen análisis predictivo para optimizar procesos empresariales y tomar decisiones informadas basadas en datos.