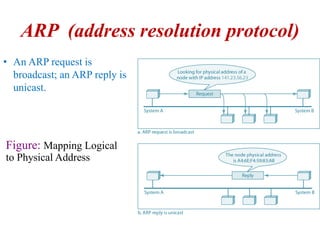
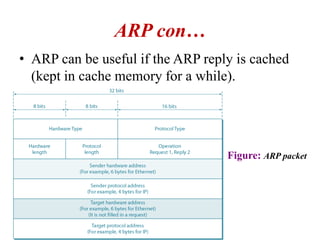
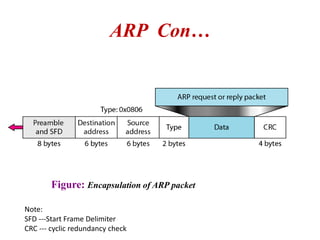
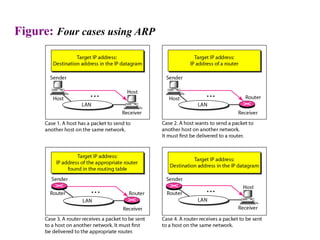
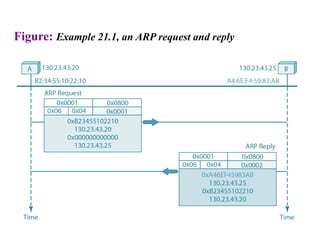
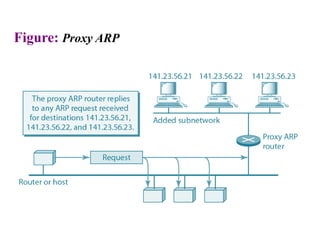
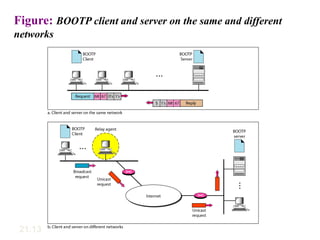
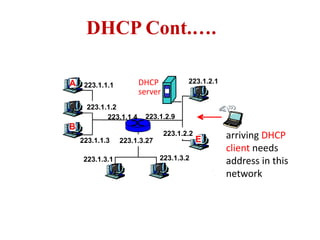
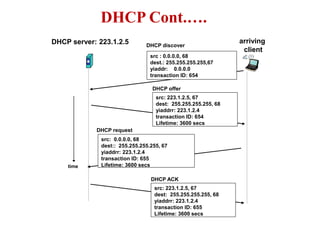
The document covers address mapping in networking, specifically the process of translating logical addresses to physical addresses using techniques like ARP, RARP, BOOTP, and DHCP. It explains how ARP is used for broadcasting requests and receiving replies to facilitate this mapping, while DHCP provides dynamic address allocation when hosts join a network. The document includes examples and figures illustrating ARP requests, replies, and the DHCP process.