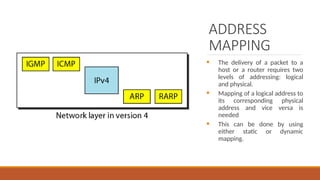
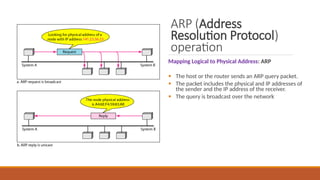
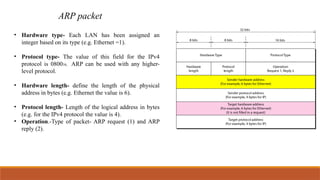
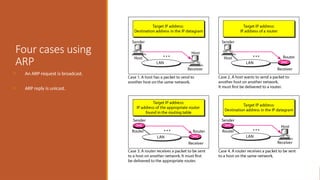
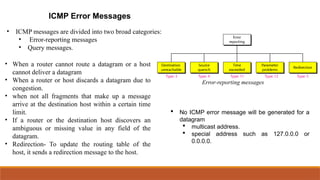
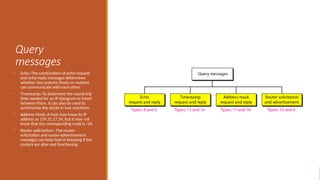
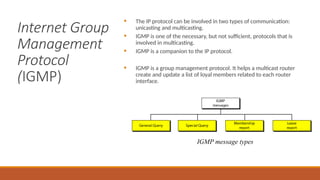
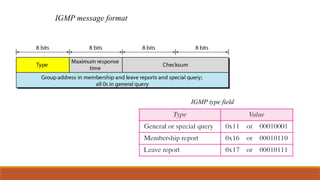
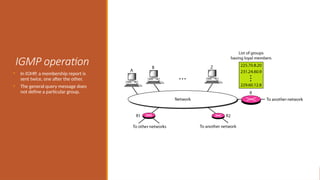
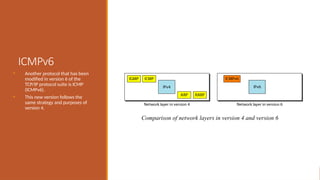
This explains the address mapping includes Arp, RARP and ICMP messages. Arp Header format, ICMP header format and the ICMP query messages. It explains that the ICMP add the reliability functionality in the IPV4. ICMP explains all the kind of the query messages.