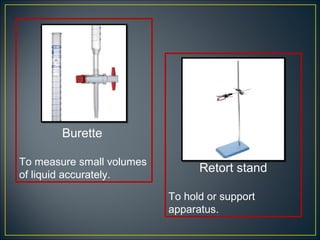
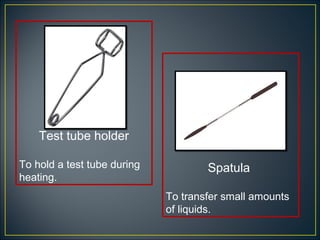
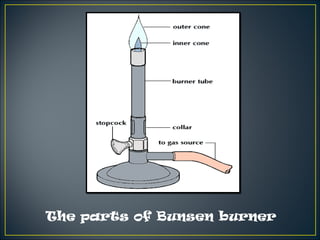
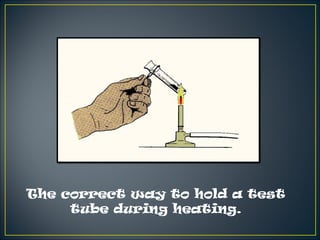
Science is the systematic study of nature and how it affects us. It provides explanations for natural phenomena through observations and experiments. Scientific knowledge develops as new discoveries are made daily, and is applied through technology to invent useful devices. Science plays an important role in our lives by helping us understand ourselves and our environment, and making life more comfortable through machines and modern conveniences. Laboratories are where scientists conduct investigations, using various apparatus carefully and following safety rules.