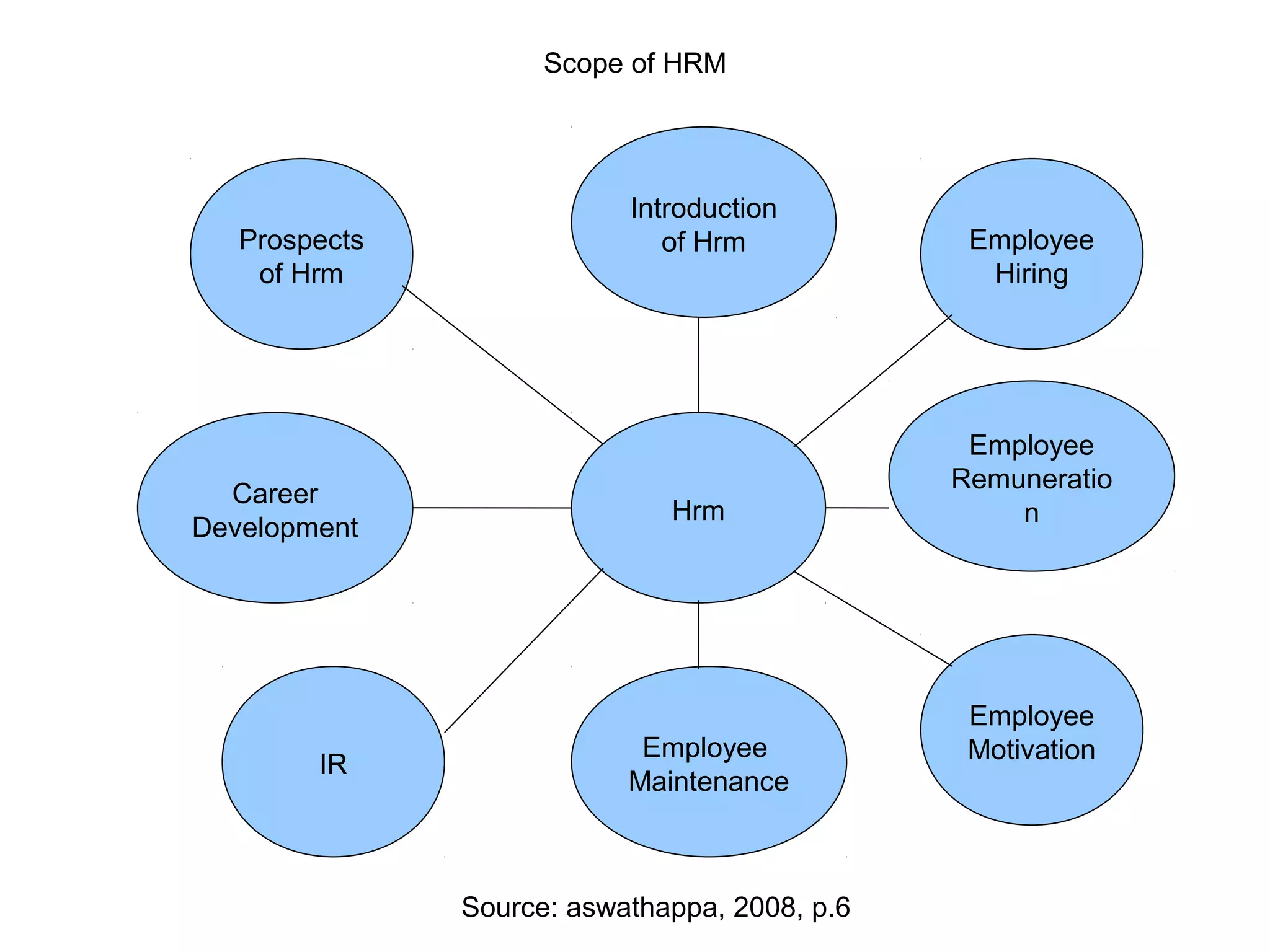
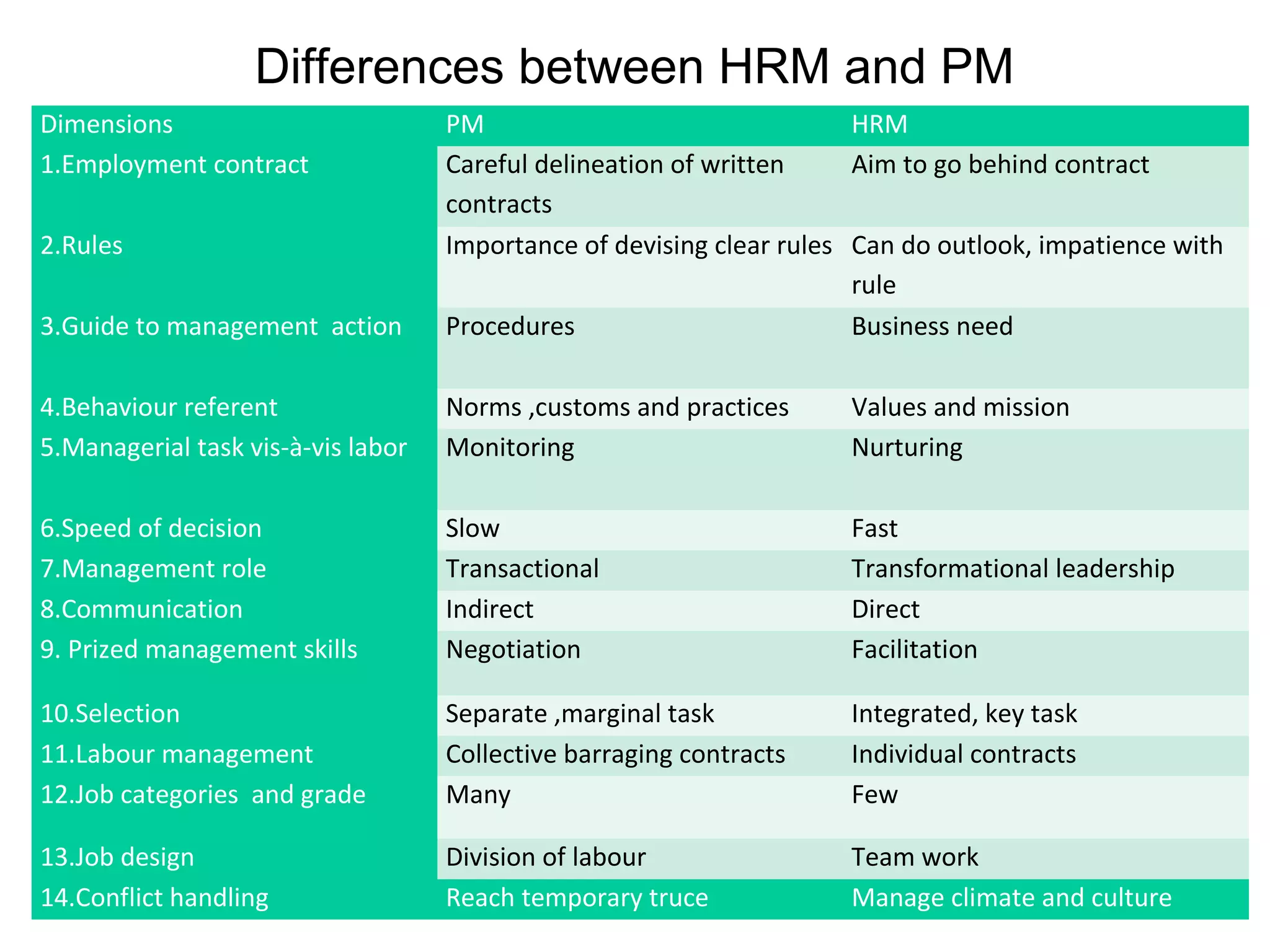
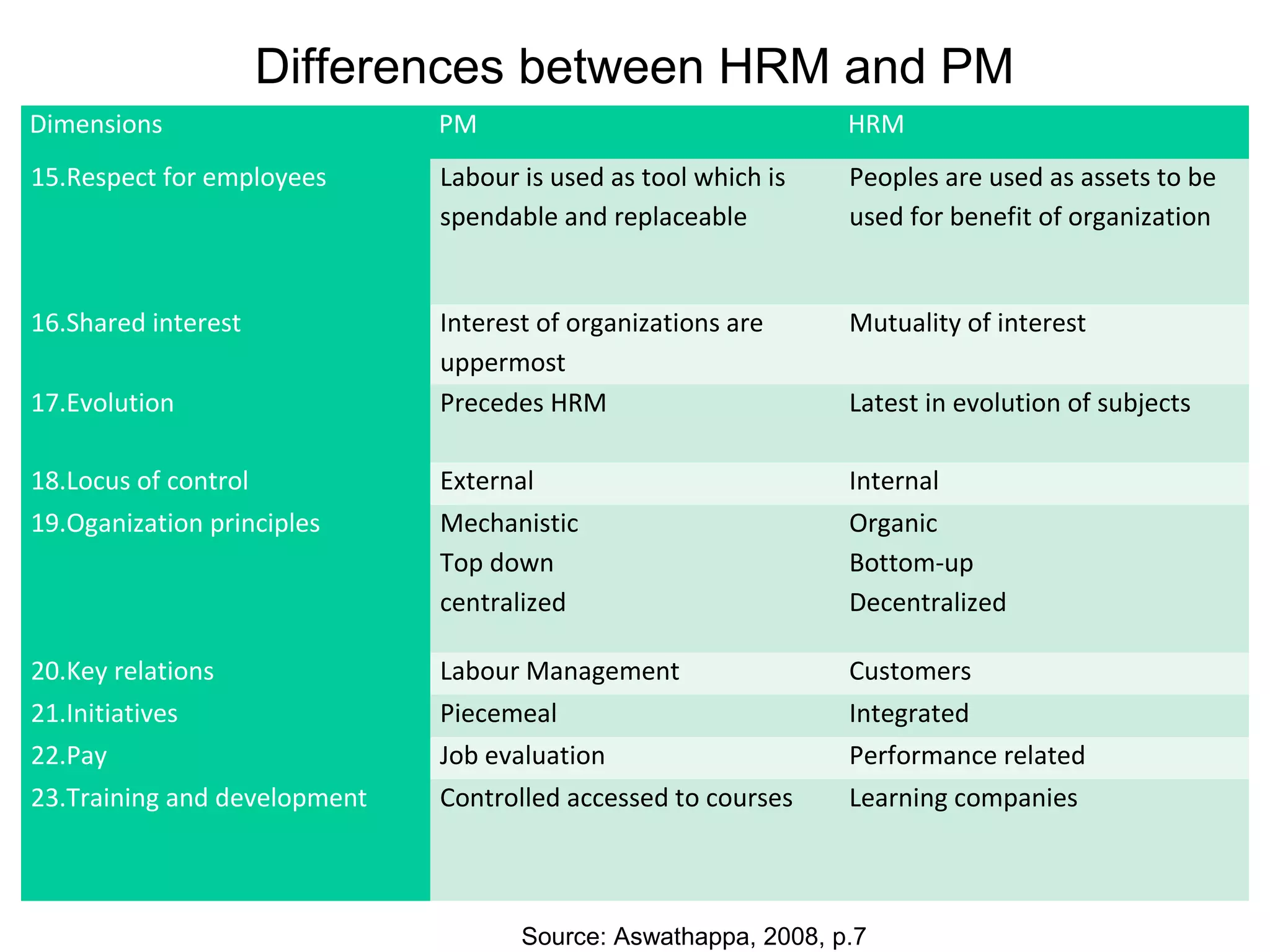
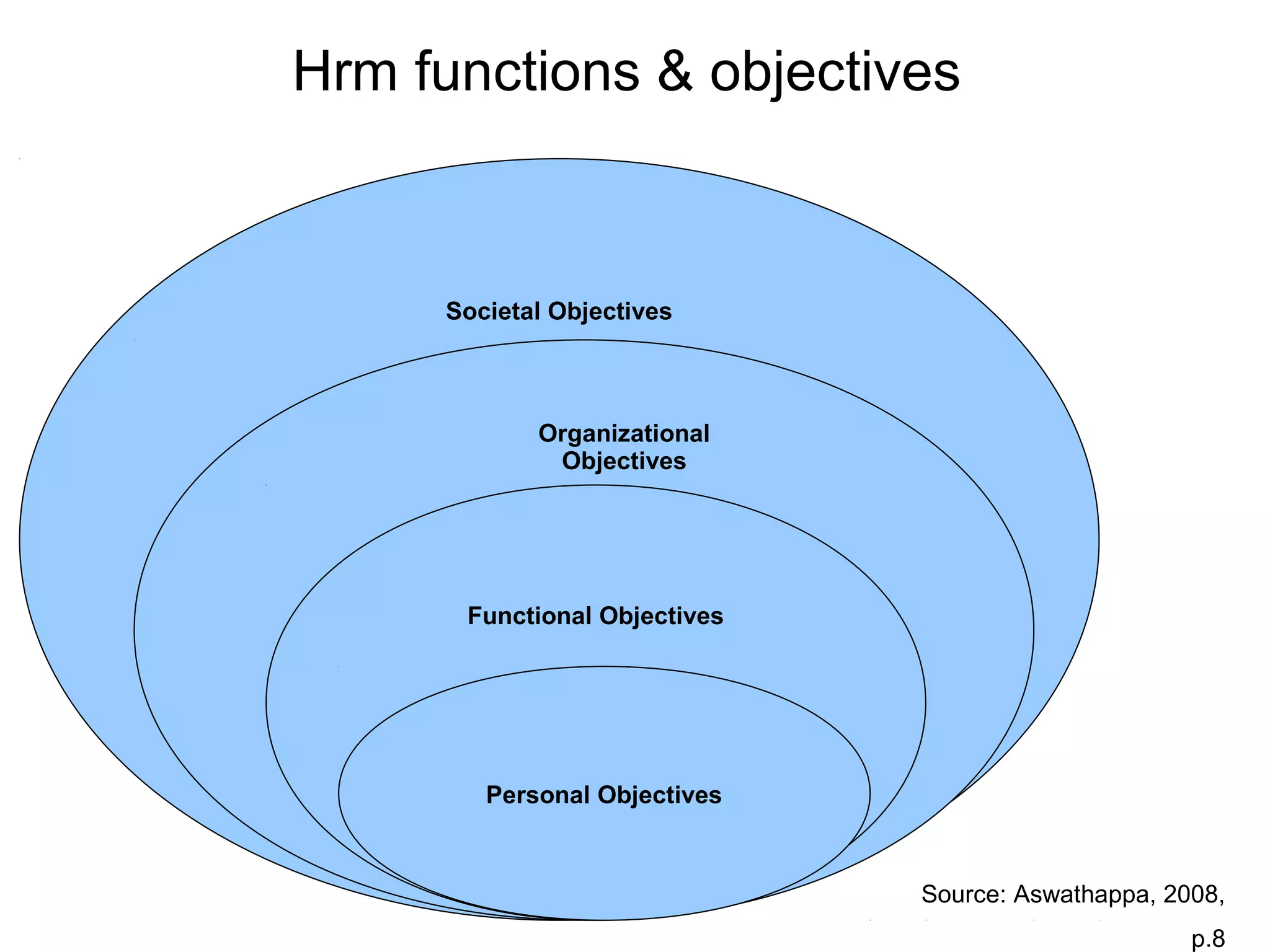
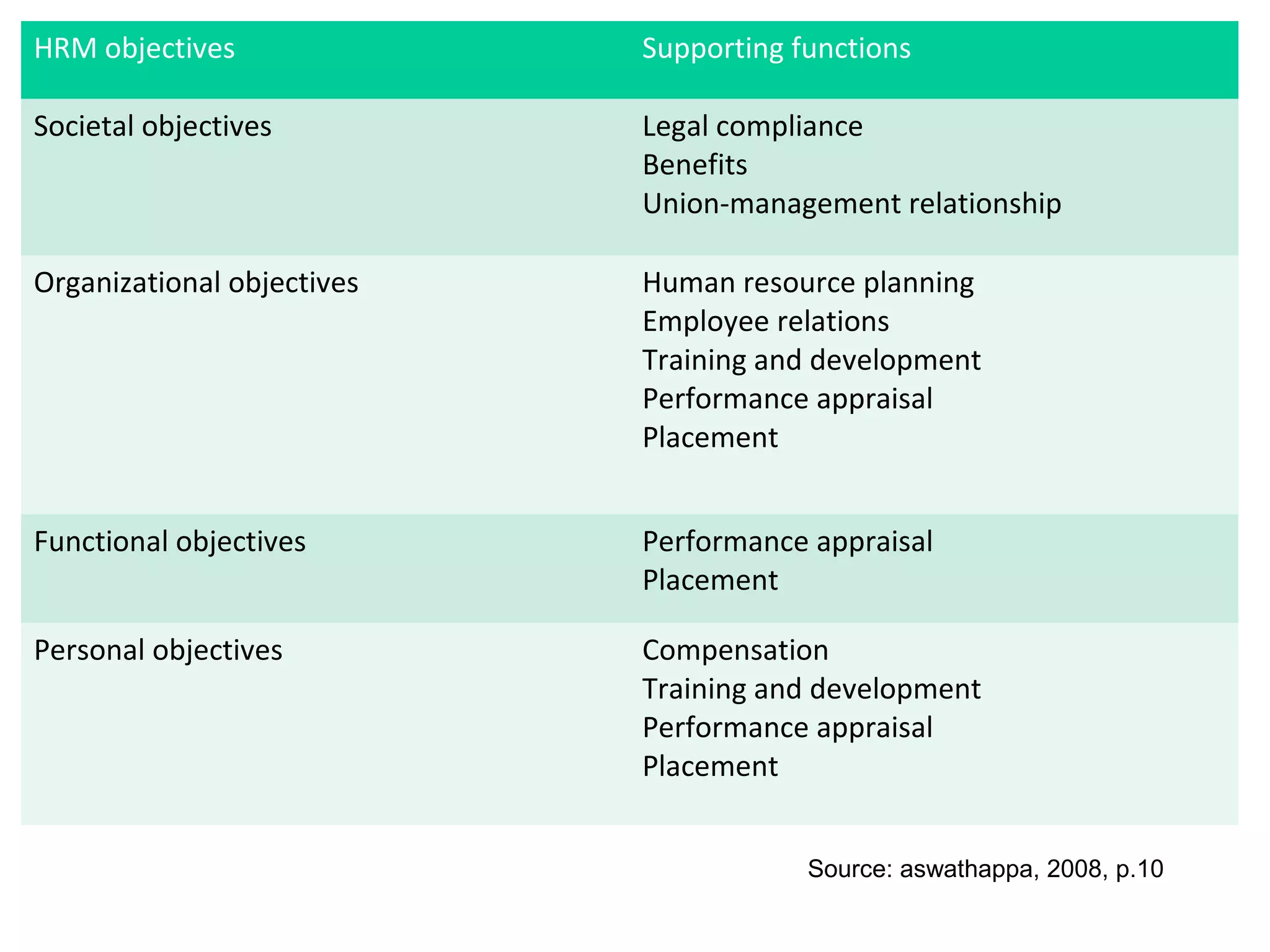
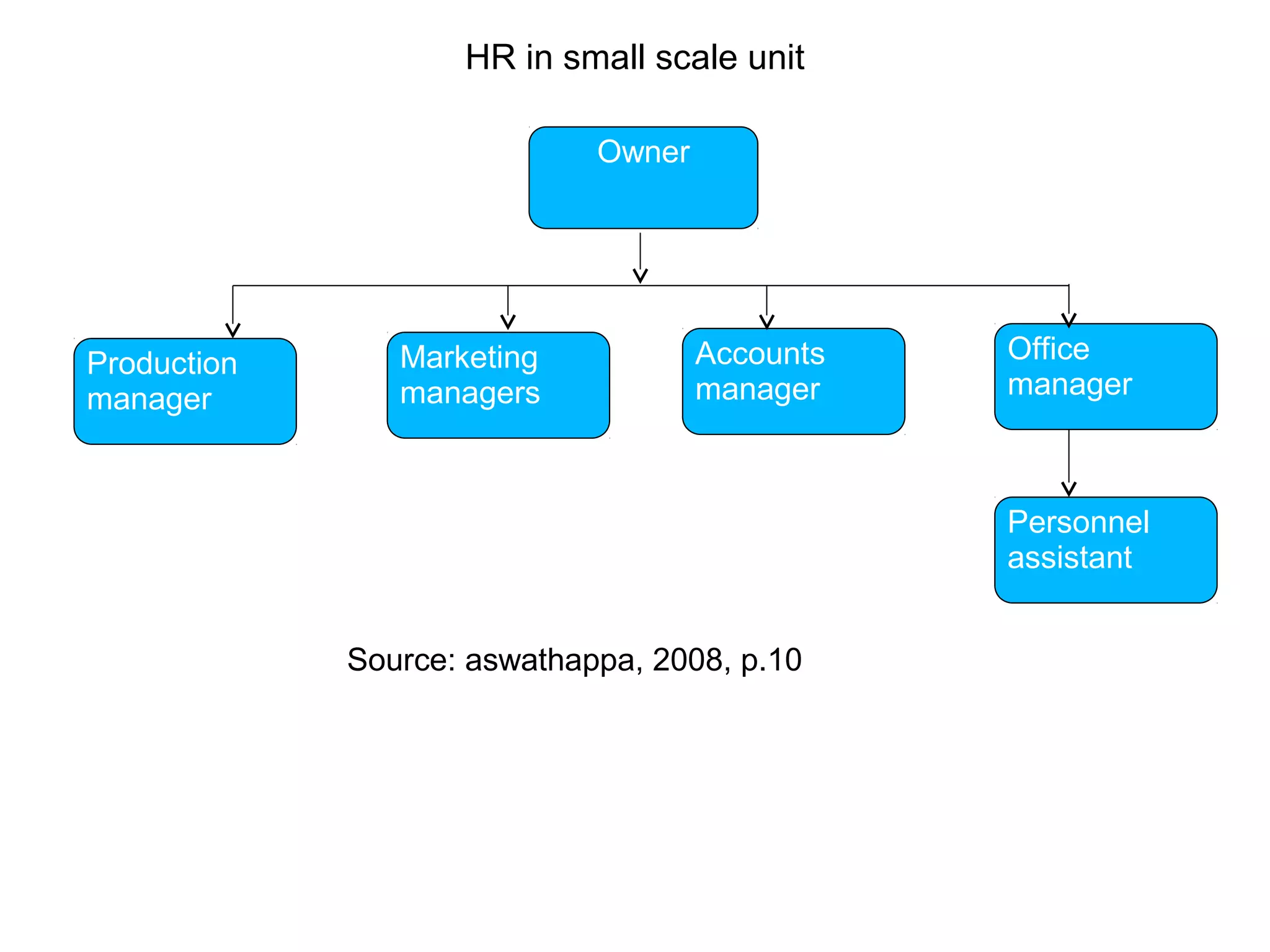
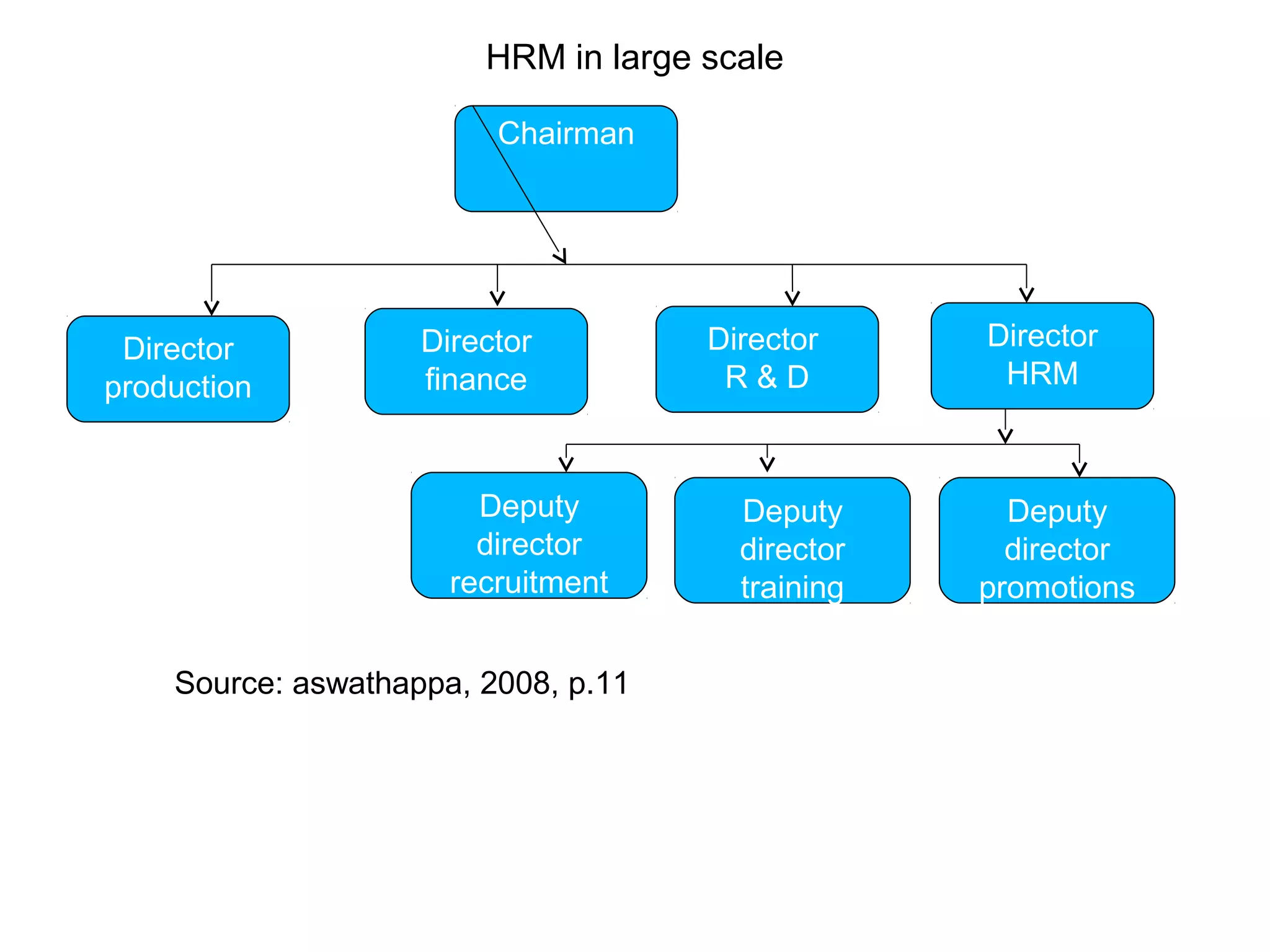
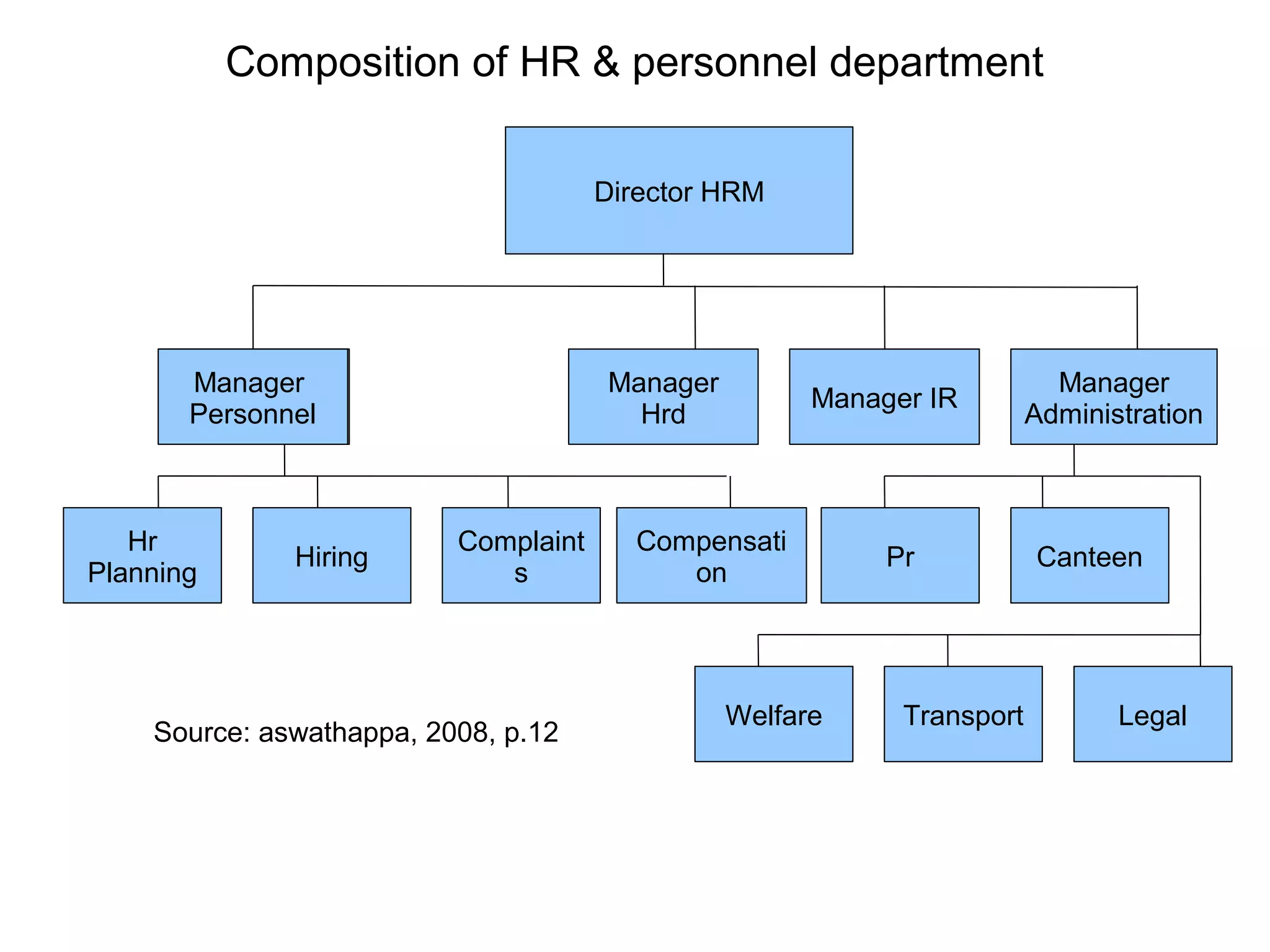
This document provides an overview of key concepts in human resource management (HRM) including: the nature and scope of HRM; HRM functions such as recruitment, selection, performance appraisal, compensation; and differences between HRM and personnel management. It discusses HRM objectives at the societal, organizational, functional, and personal levels. Finally, it describes the organization of HRM departments in small versus large organizations and options for outsourcing some HRM activities.