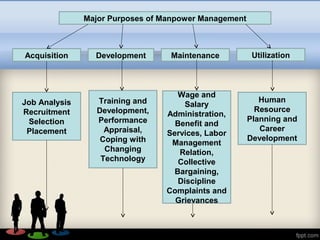
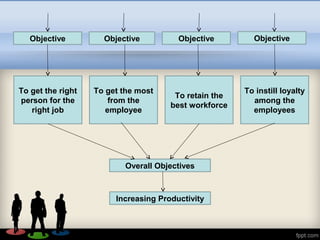
Human Resource Management (HRM) focuses on hiring and developing employees to achieve organizational goals, integrating various perspectives such as normative, critical, behavioral, and systems views. It encompasses personnel management, employee welfare, and industrial relations, with objectives including recruitment, employee benefits, and legal compliance. Effective HRM practices significantly contribute to professional growth, better employee relations, and overall organizational productivity.