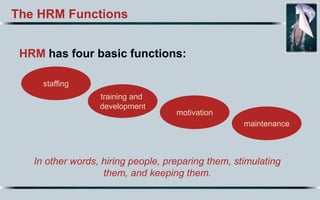
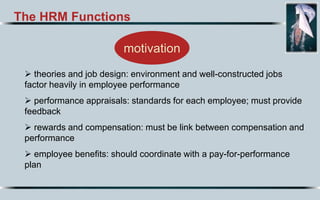
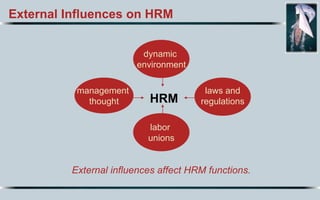
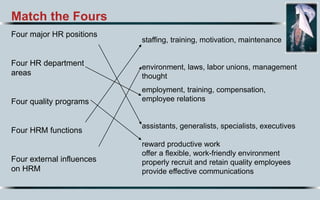
Here is my suggested order of priority for the most important characteristics of a superstar HR manager in the 21st century:
1. E. Understands the business/industry
2. C. Has a strategic mindset
3. A. Good with people
4. D. Knows HR content
5. B. Operationally efficient
6. G. Compassionate
7. F. Compliance Expert
Understanding the business and having a strategic mindset are most critical so the HR function can effectively support business goals and strategy. Strong interpersonal skills and HR expertise are also very important. Operational efficiency, compliance, and compassion are still valuable but less central to being a true strategic partner and driving