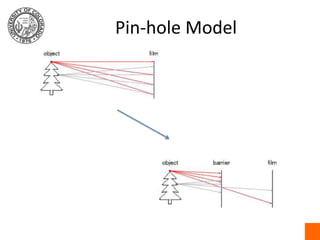
This document discusses various computer vision techniques for obtaining range and depth information from images, including depth from focus, depth from stereo, and optical filters. It introduces the pinhole camera model and explains how depth can be estimated from a single image by analyzing focus versus from multiple images using stereo vision. Examples of image processing techniques like convolution and morphological operations are also provided. The challenges of object recognition are discussed, noting that perception depends on assumptions about lighting, geometry, frequency, color and other factors that can be ambiguous.