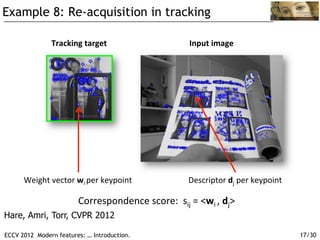
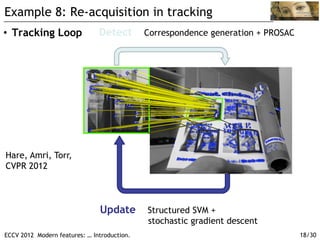
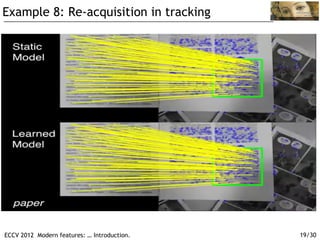
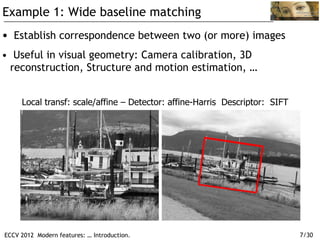
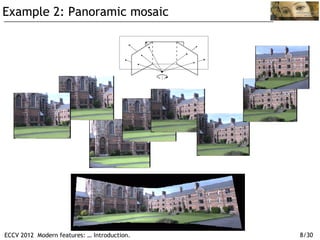
The document discusses modern feature detection techniques. It provides an introduction and agenda for a talk on advances in feature detectors and descriptors, including improvements since a 2005 paper. It also discusses software suites and benchmarks for feature detection. Several application domains are described, such as wide baseline matching, panoramic image stitching, 3D reconstruction, image search, location recognition, and object tracking.







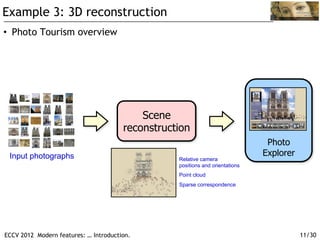
![Example 3: 3D reconstruction
57,845 downloaded images, 11,868 registered images. This video: 4,619 images.
The Old City of Dubrovnik Building Rome in a Day, Agarwal, Snavely, Simon, Seitz,
Szeliski, ICCV 2009
See also [Havlena, Torrii, Knop pand Pajdla, CVPR 2009].
ECCV 2012 Modern features: … Introduction. 12/30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modern-features-part-0-intro-121214032008-phpapp02/85/Modern-features-part-0-intro-12-320.jpg)

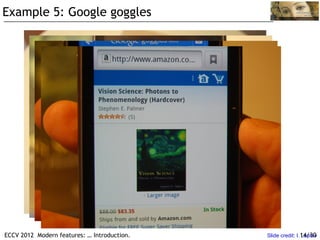
![Example 6: Where am I?
• Place recognition - retrieval in a structured (on a map) database
Query Image database Best match
Image indexing
with spatial
verification
Query
Expansion
(Panoramio,
Flickr, … )
Confuser
Suppression
Only negative
training data
(from geotags)
[Knopp, Sivic, features: … Introduction. http://www.di.ens.fr/willow/research/confusers/
ECCV 2012 Modern Pajdla, ECCV 2010] 16/30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modern-features-part-0-intro-121214032008-phpapp02/85/Modern-features-part-0-intro-16-320.jpg)