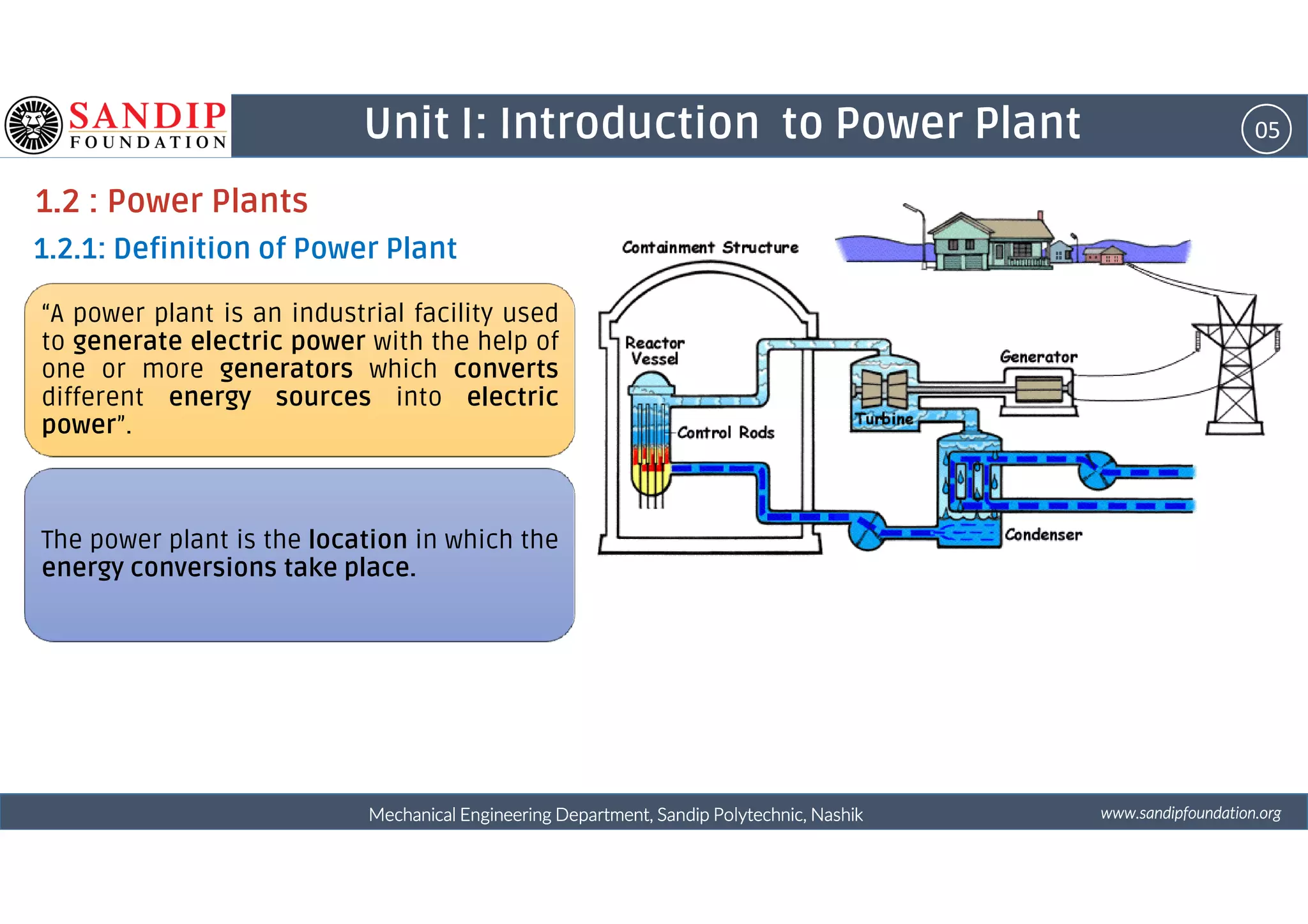
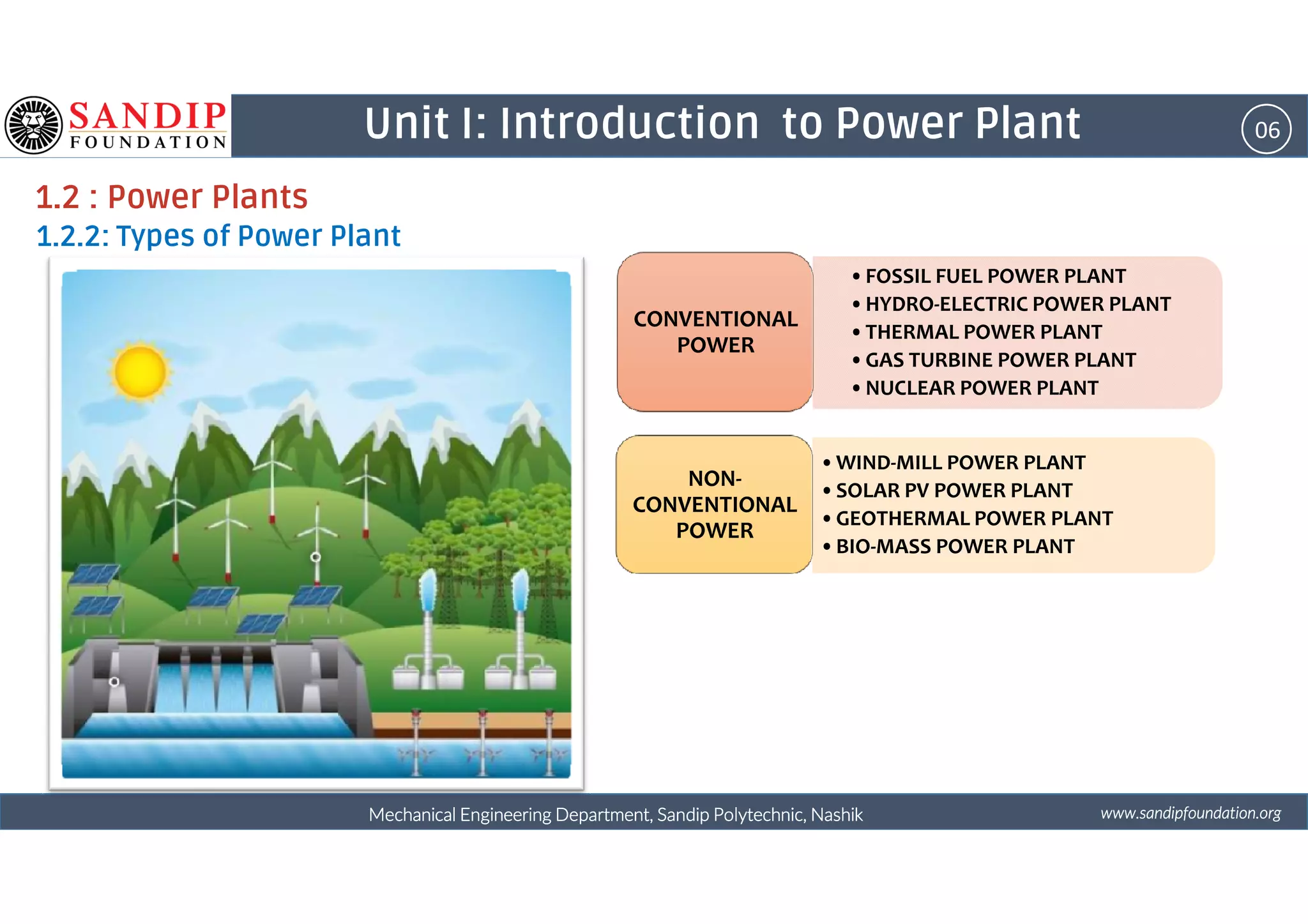
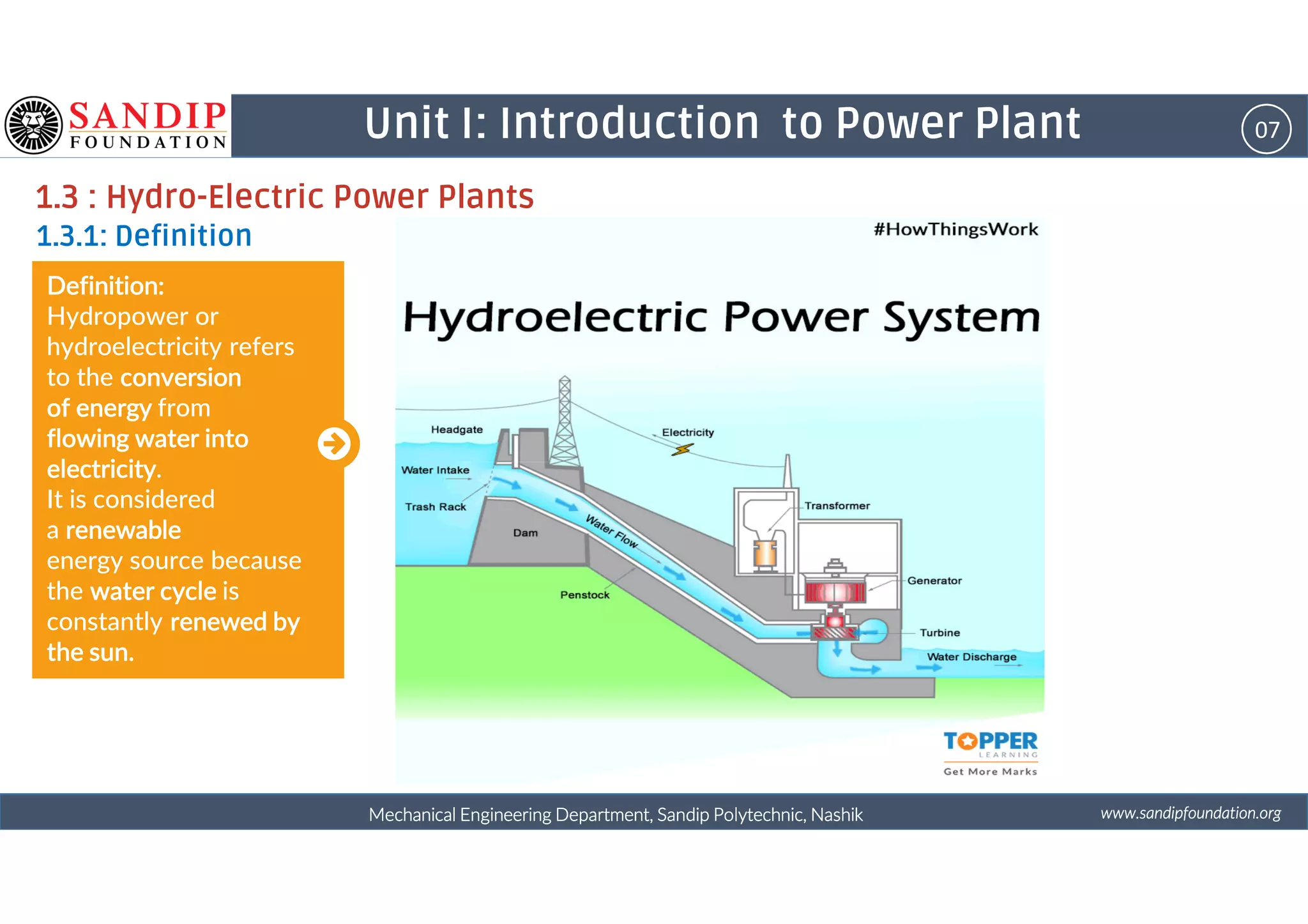
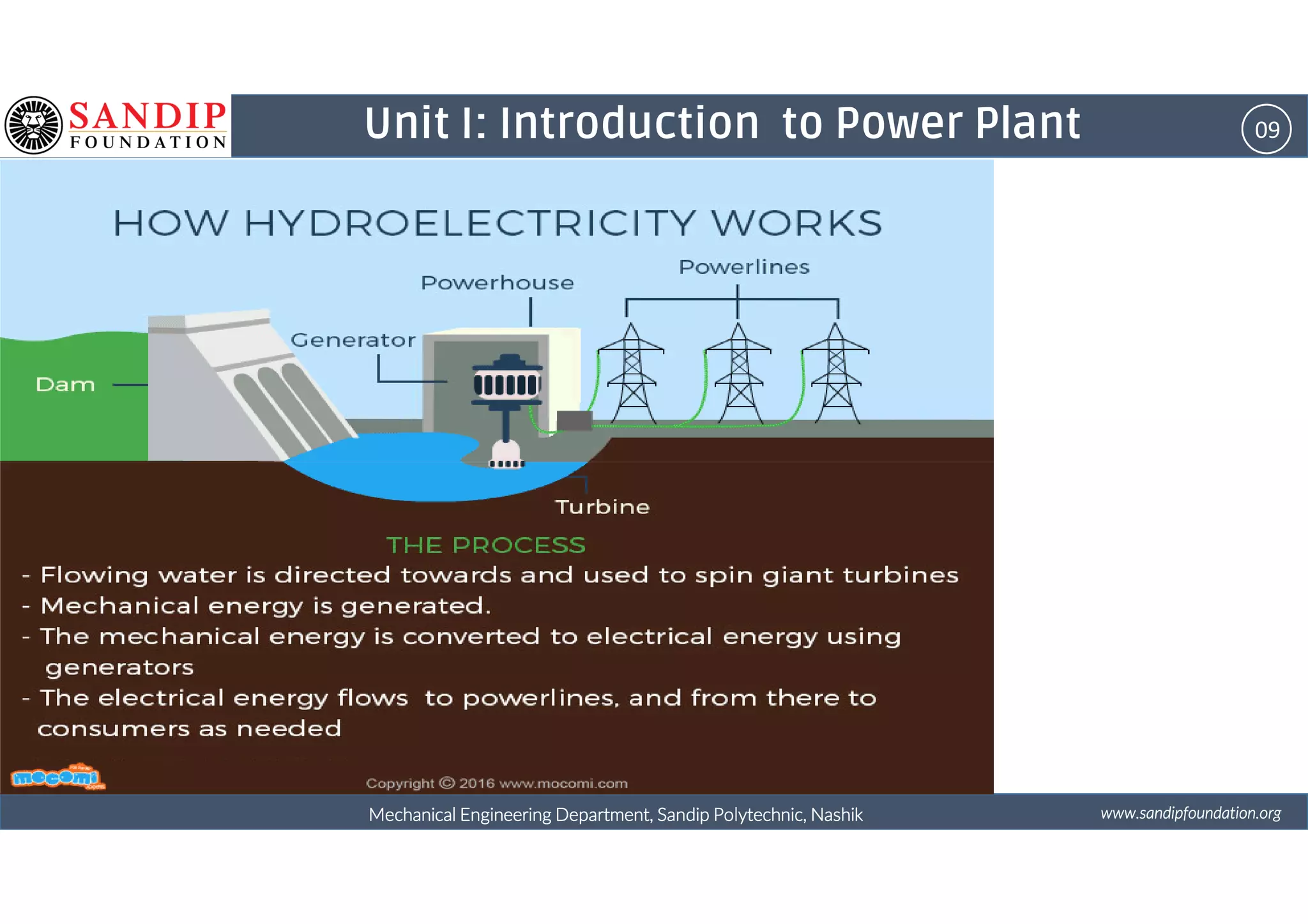
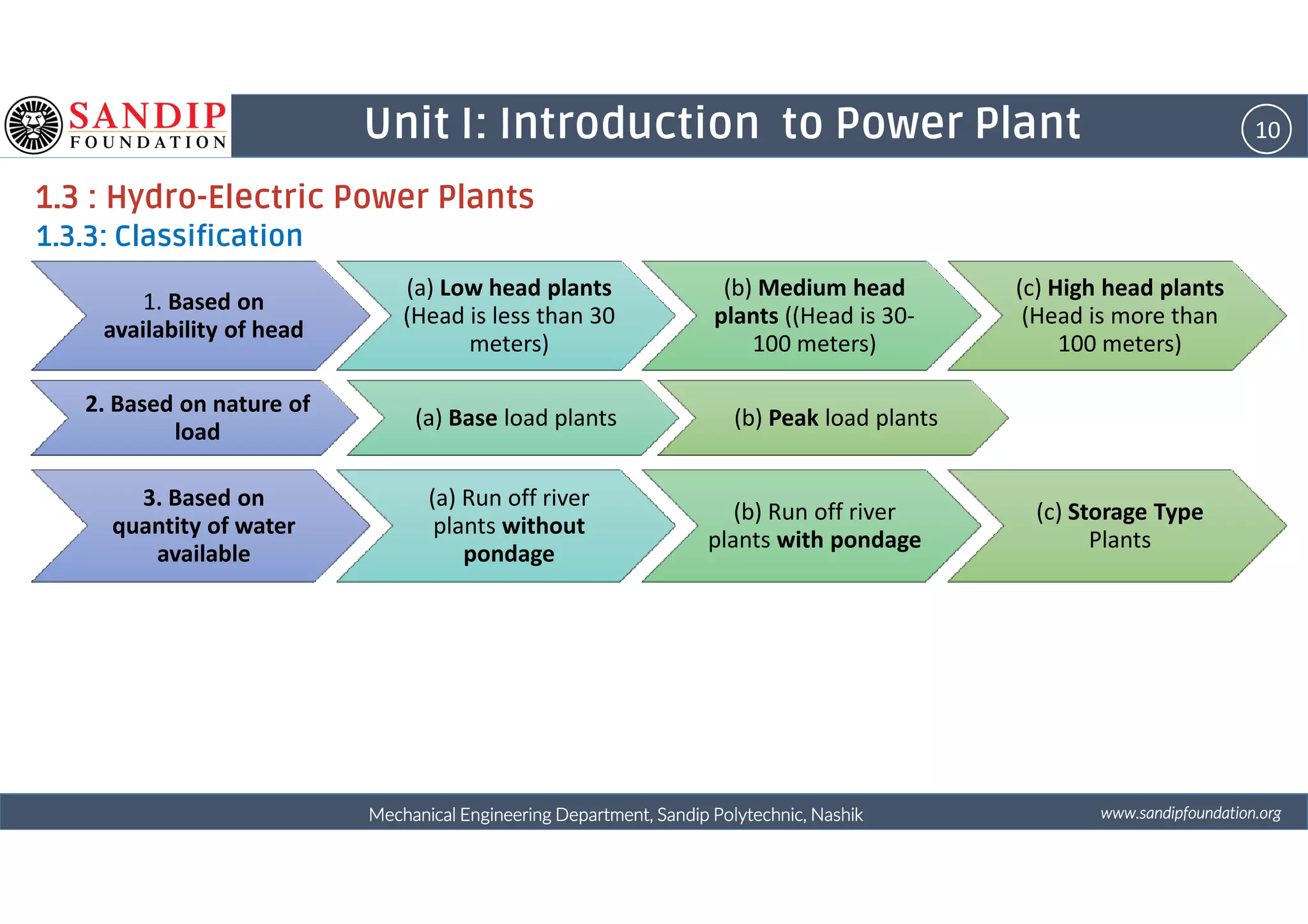
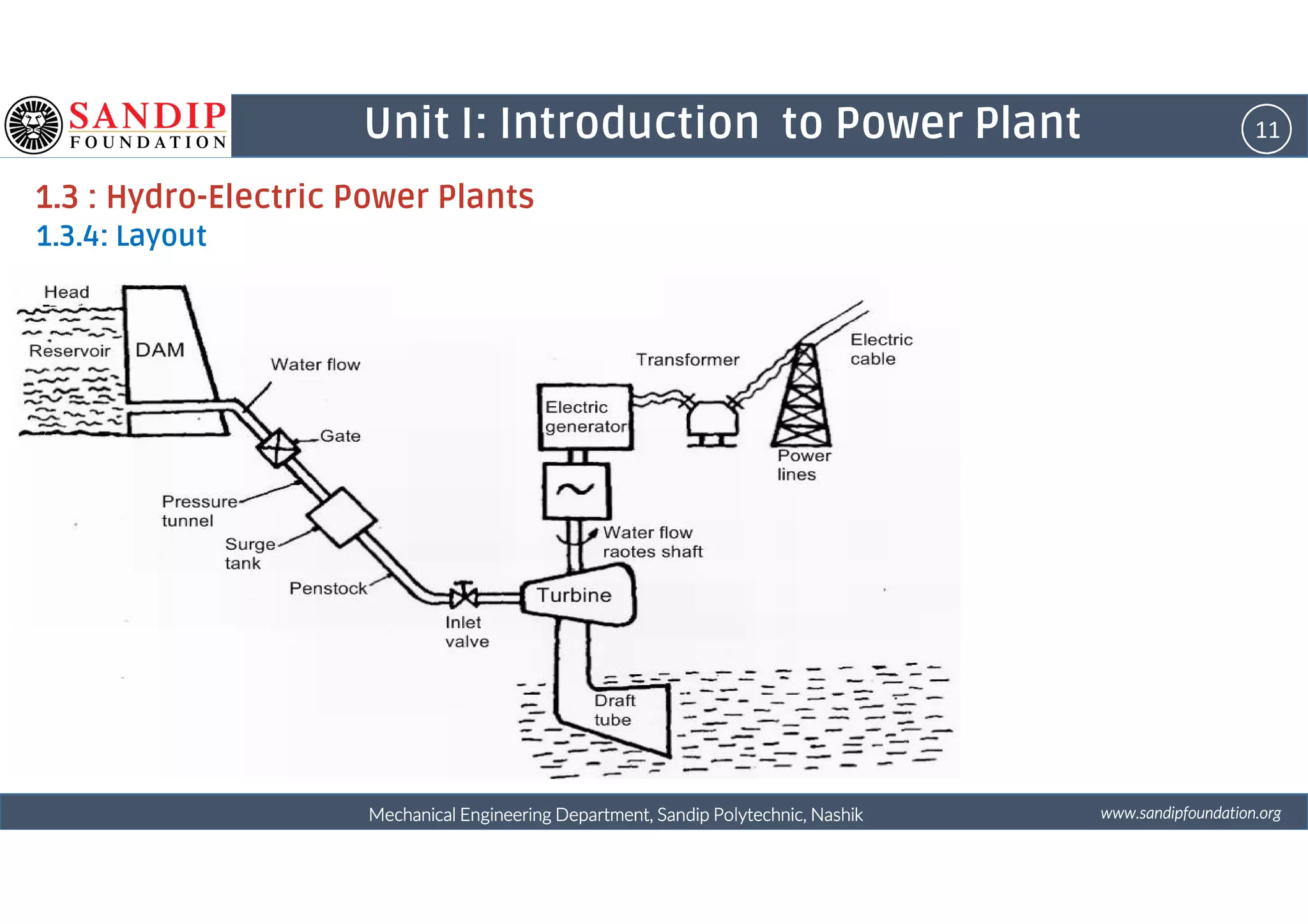
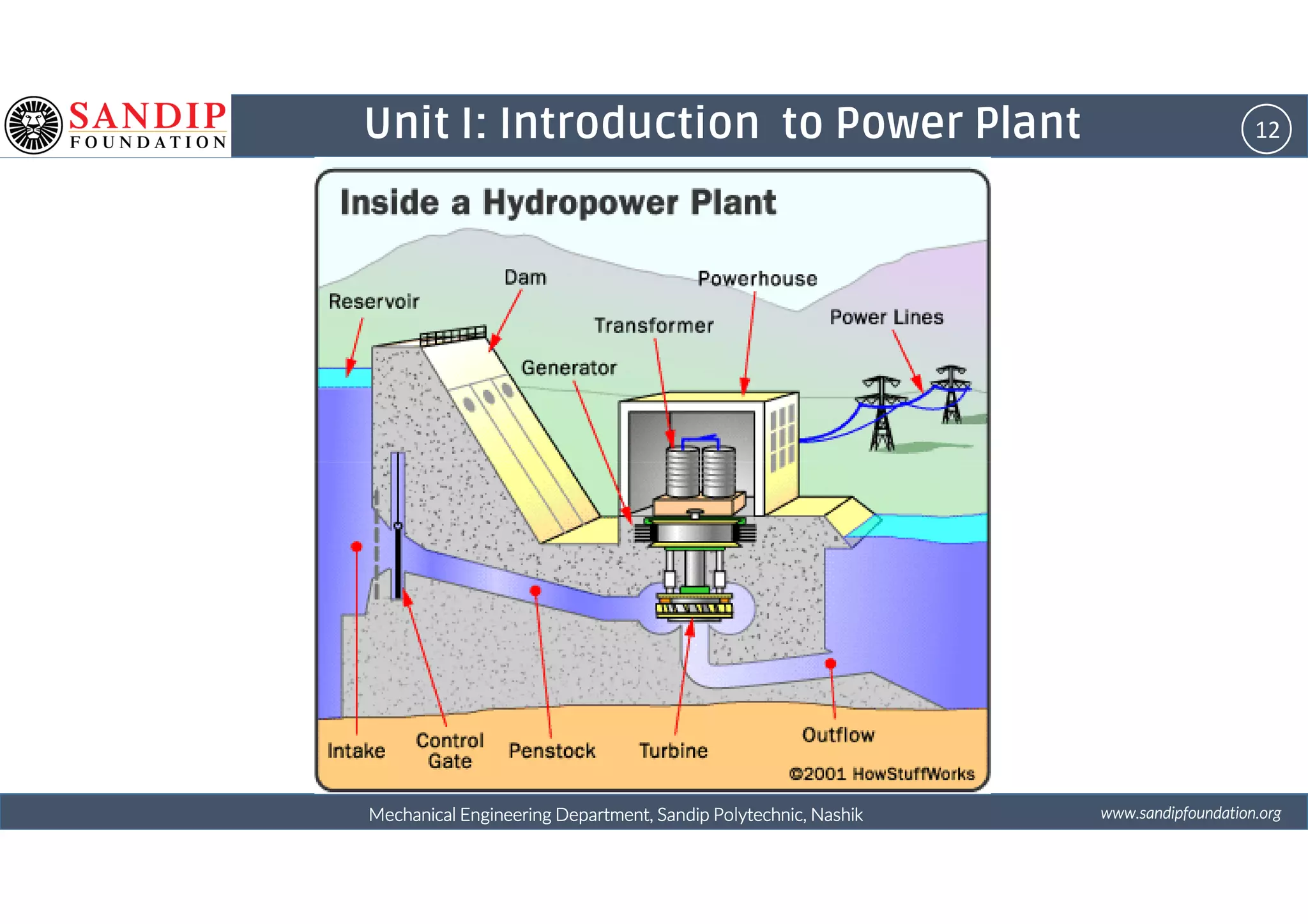
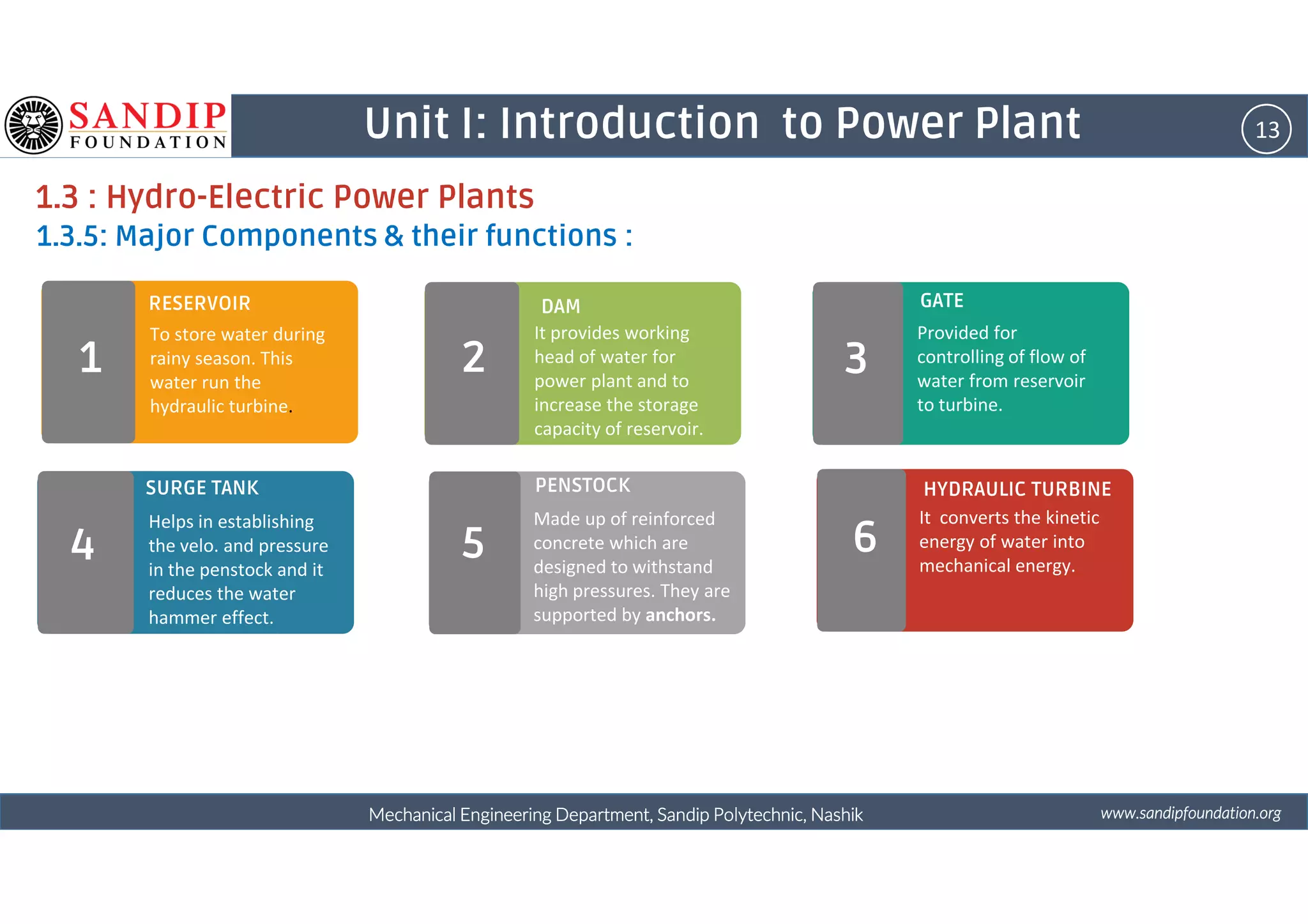
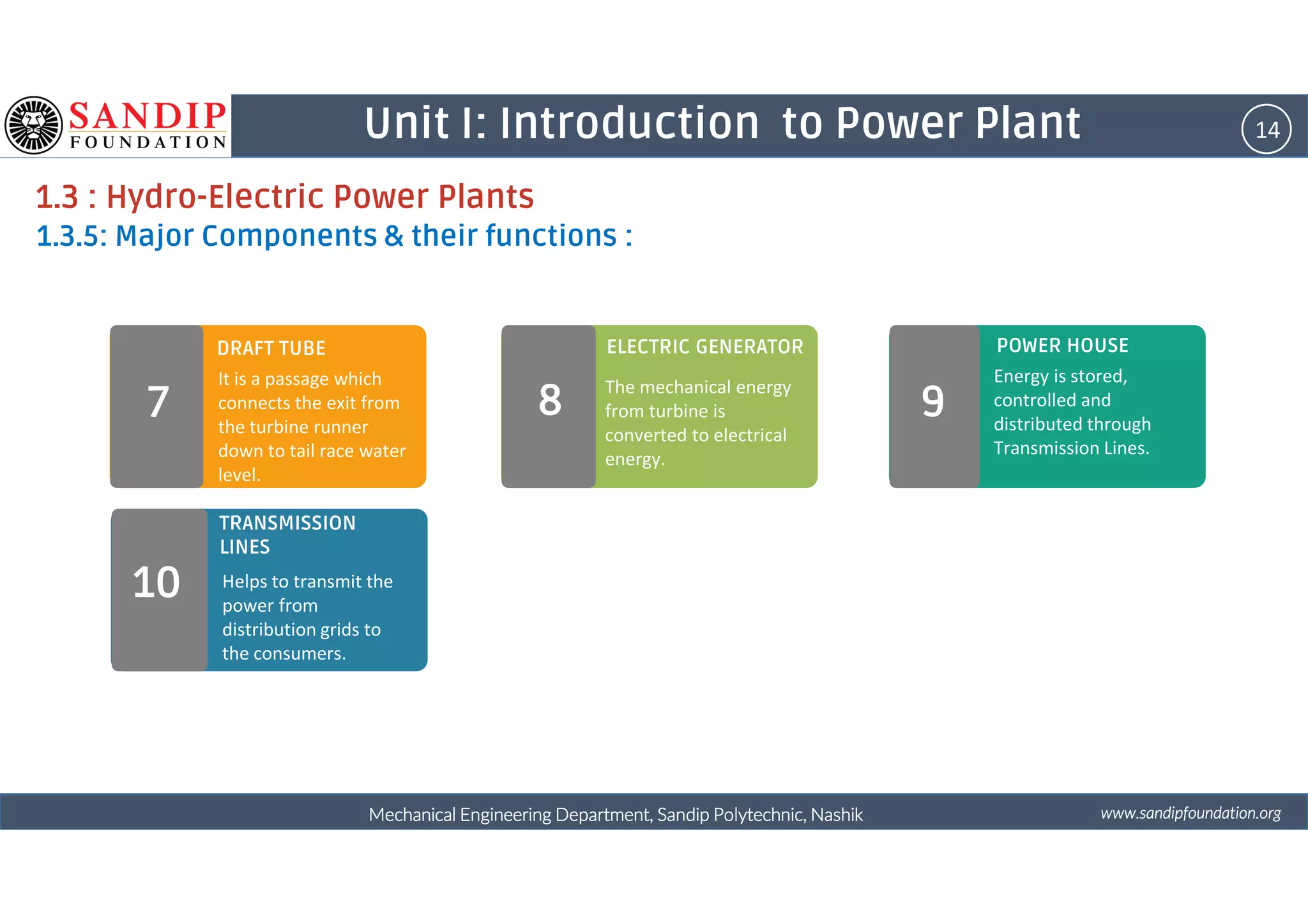
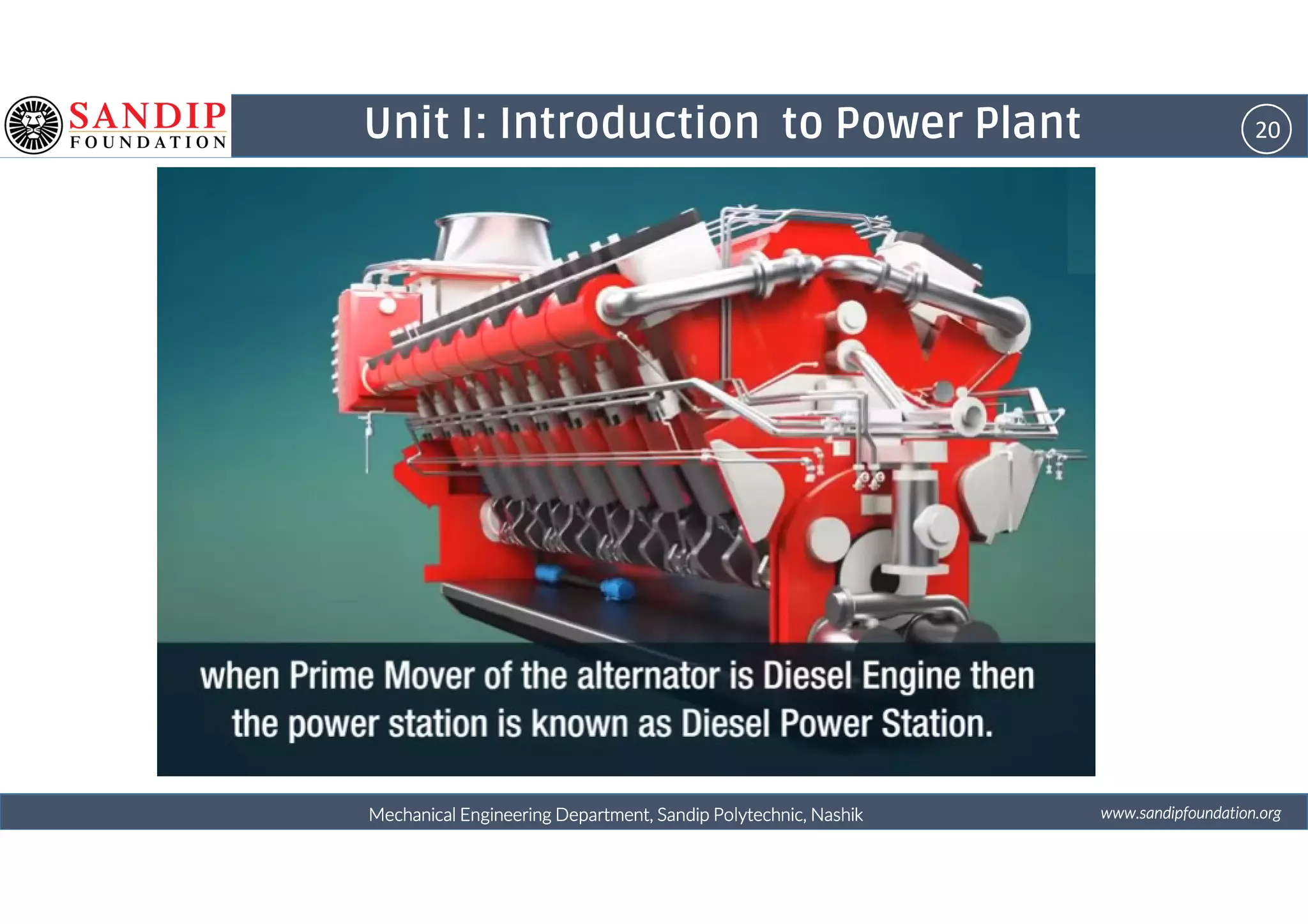
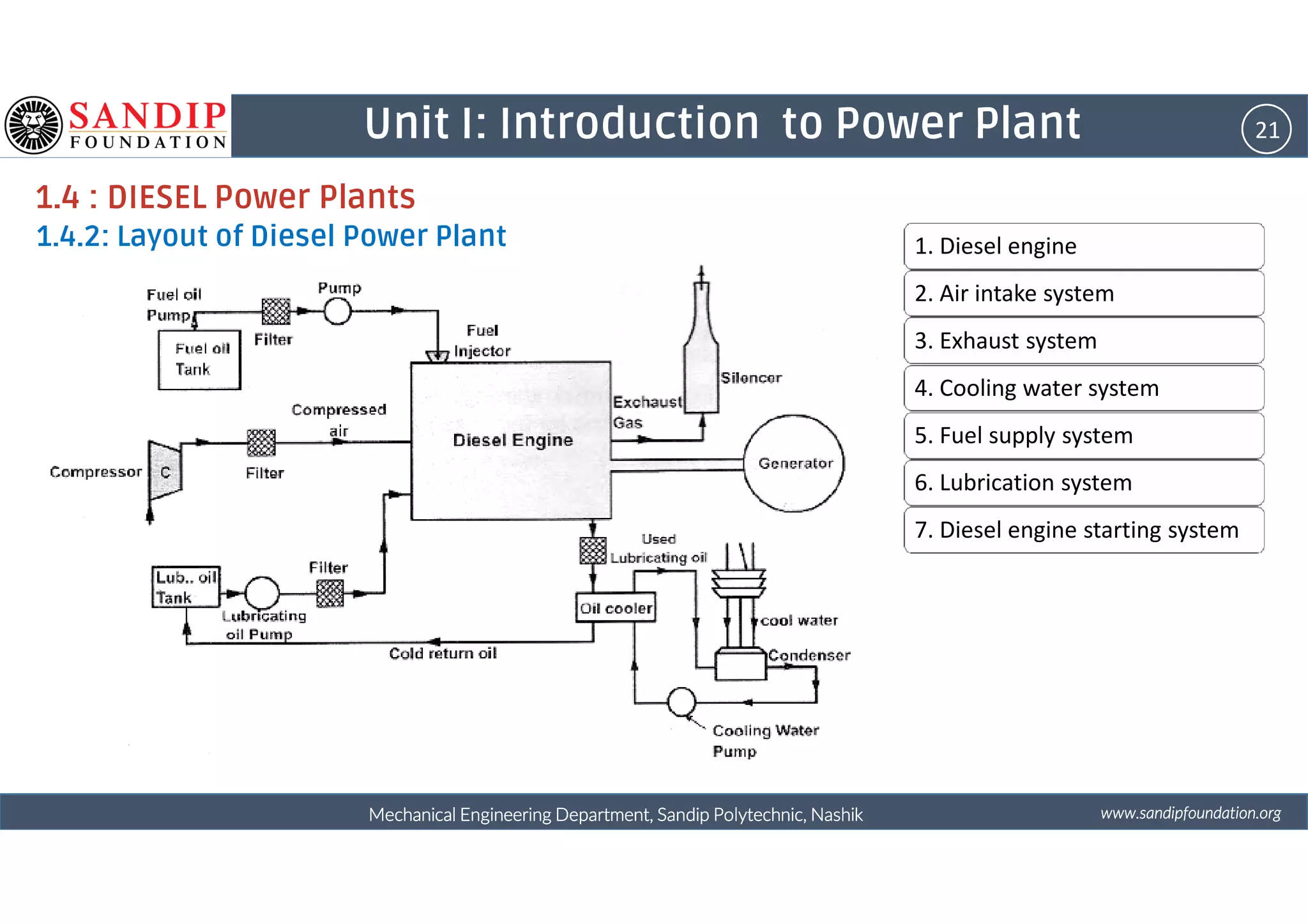
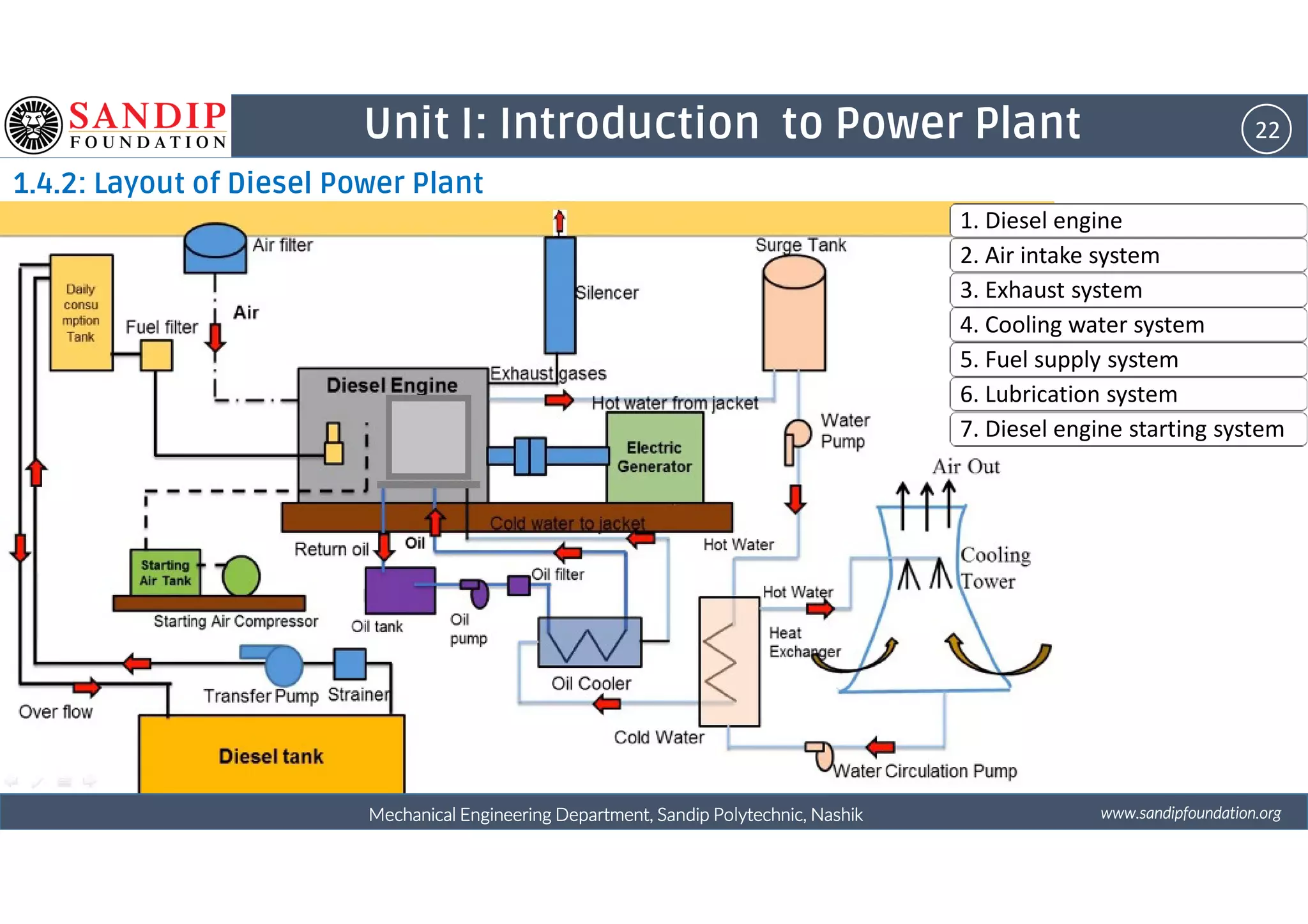
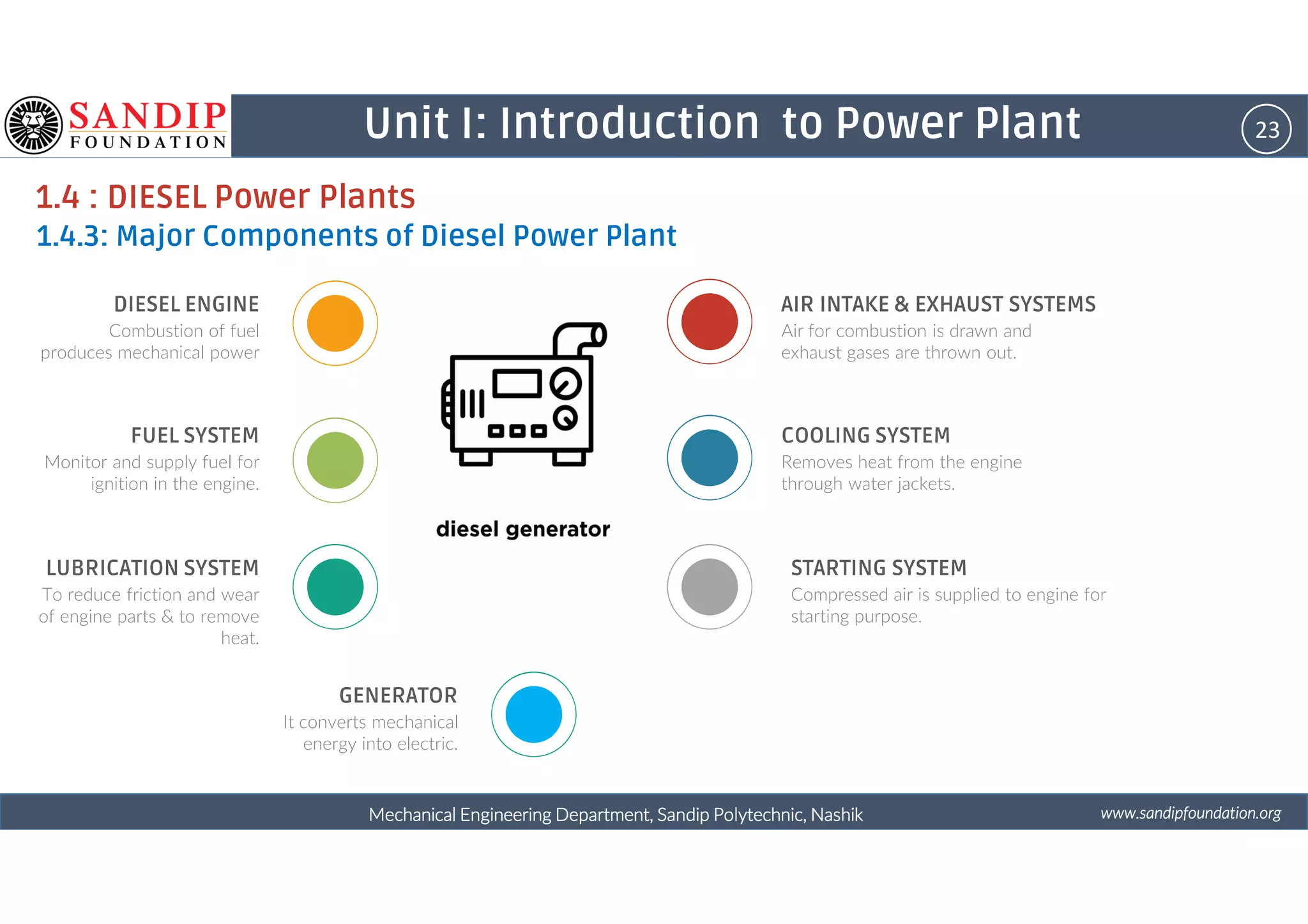
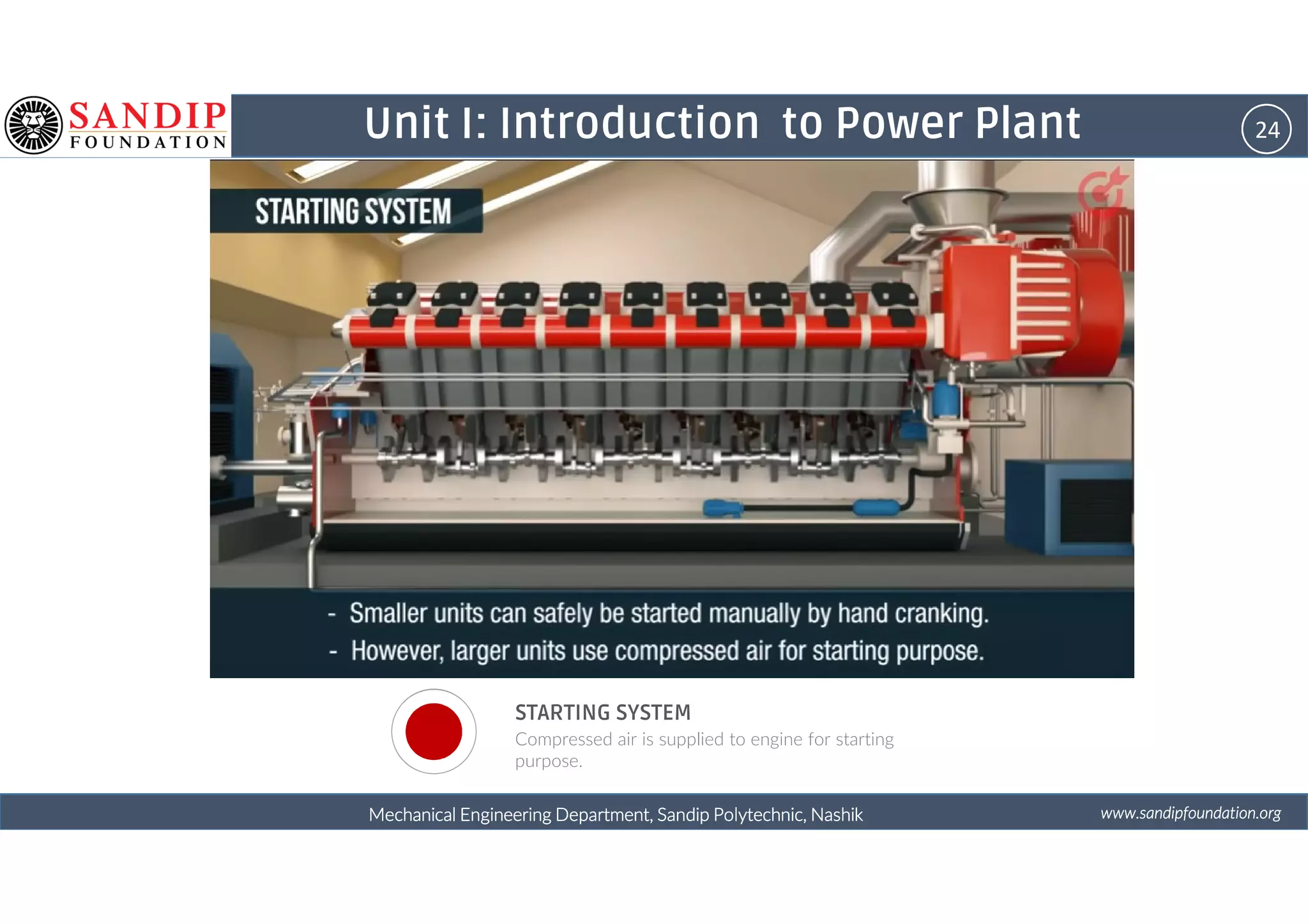
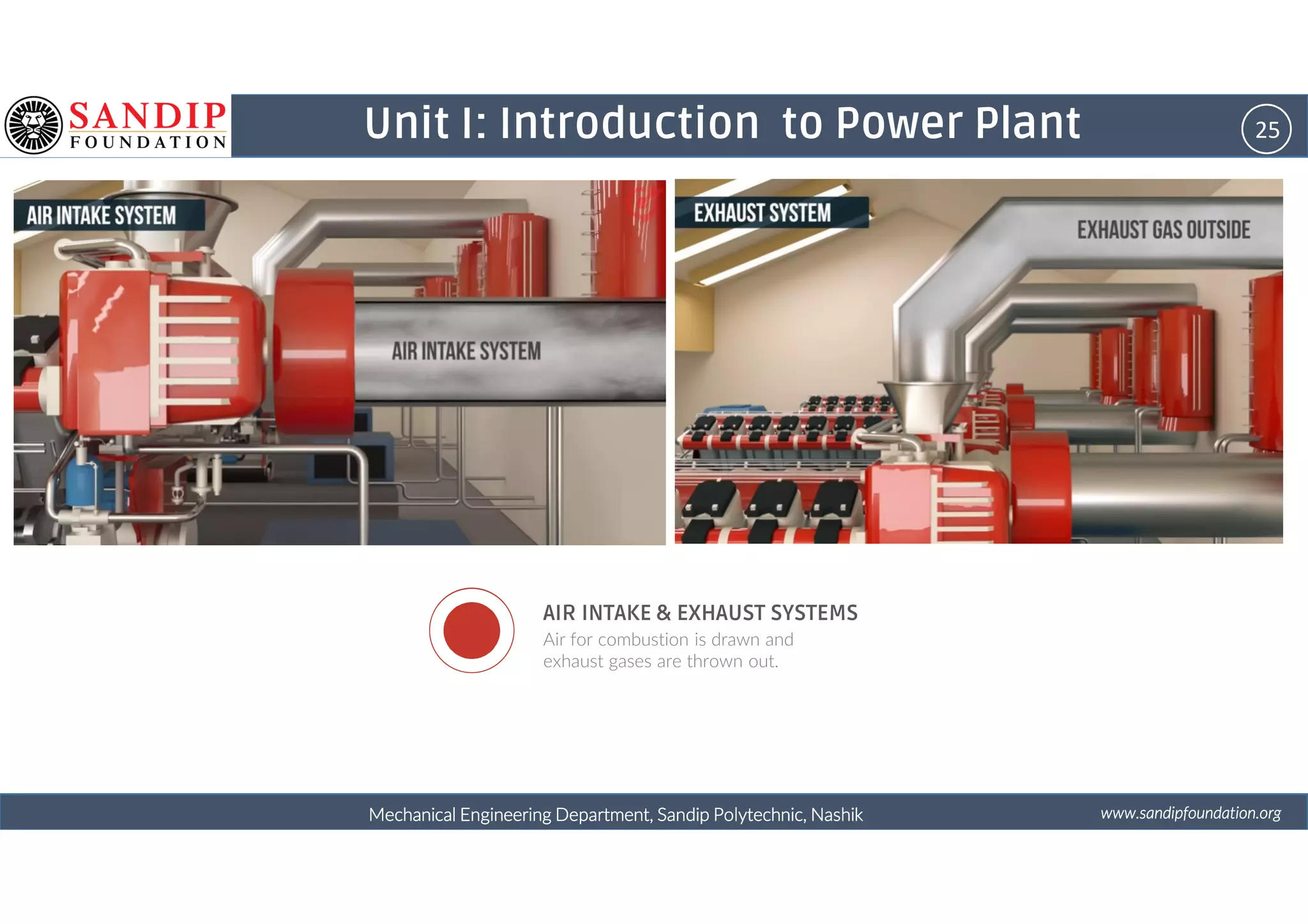
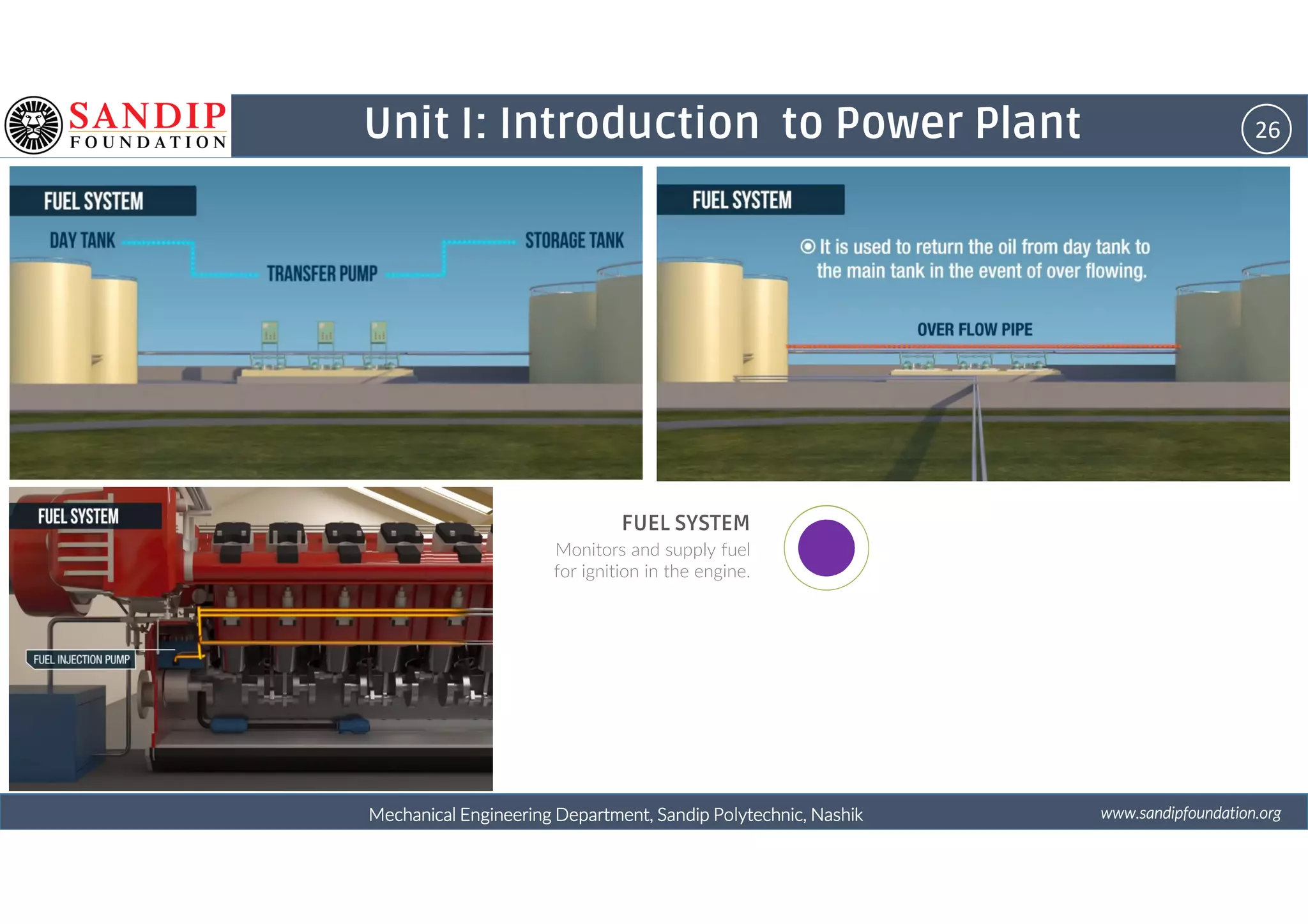
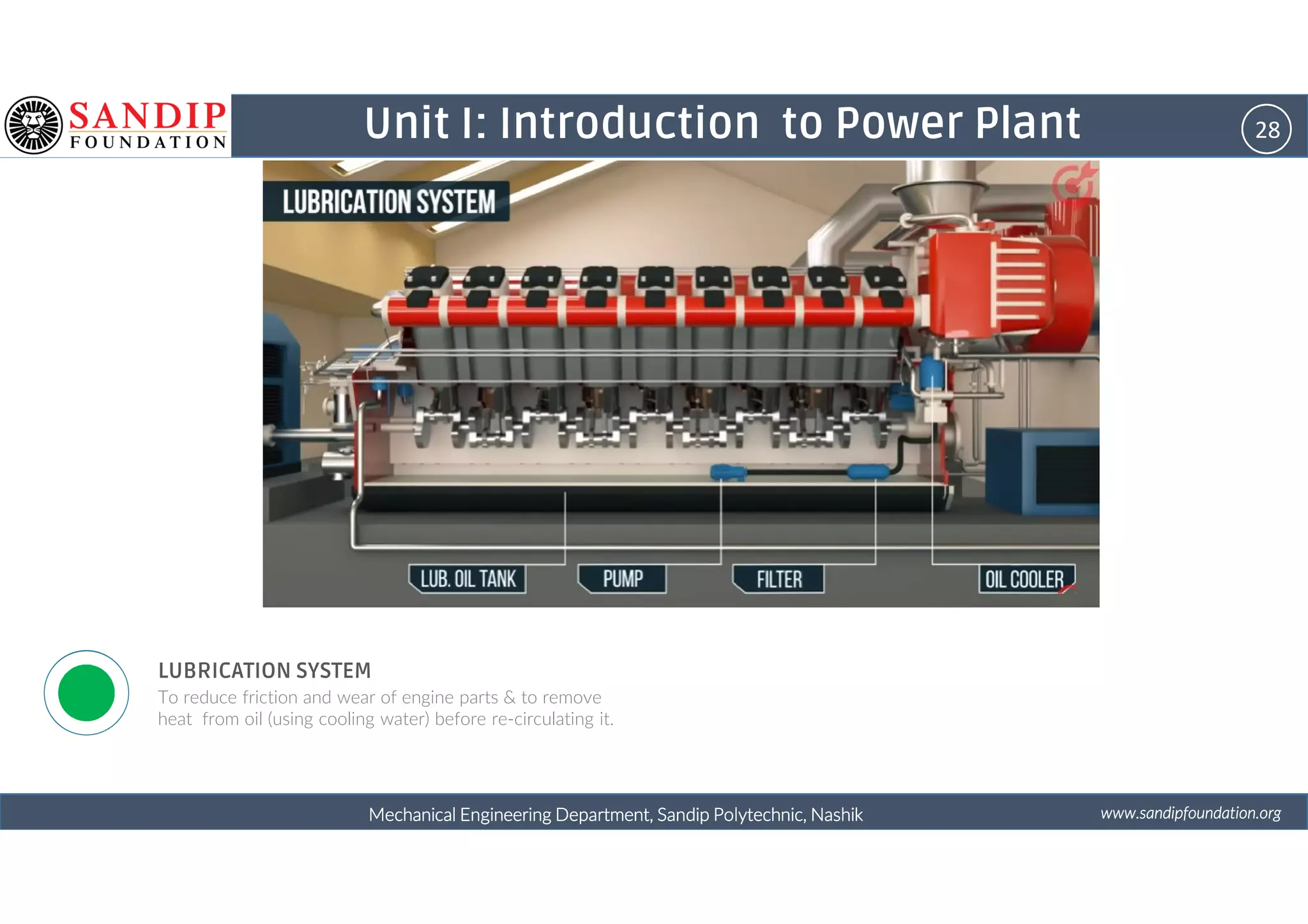
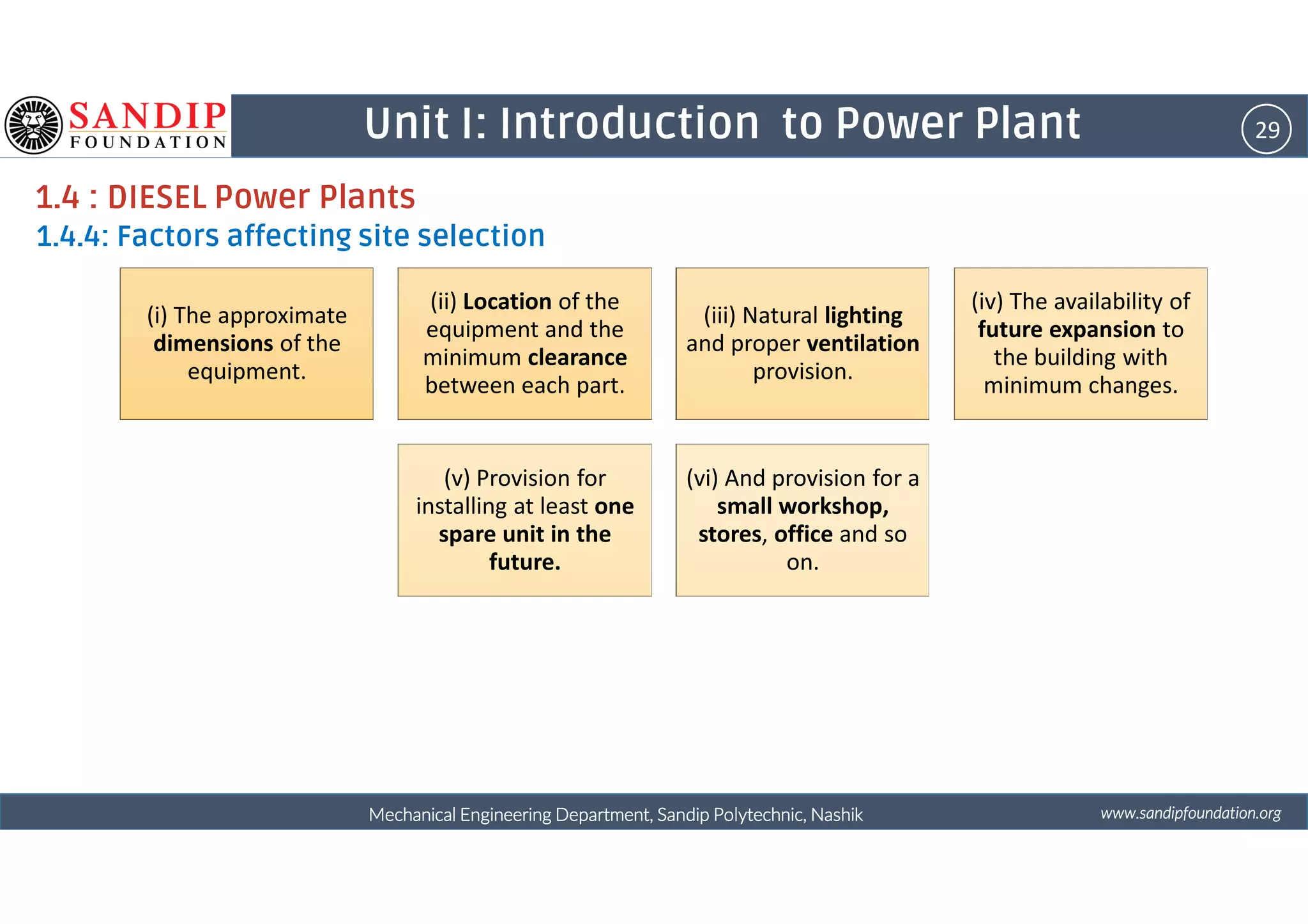
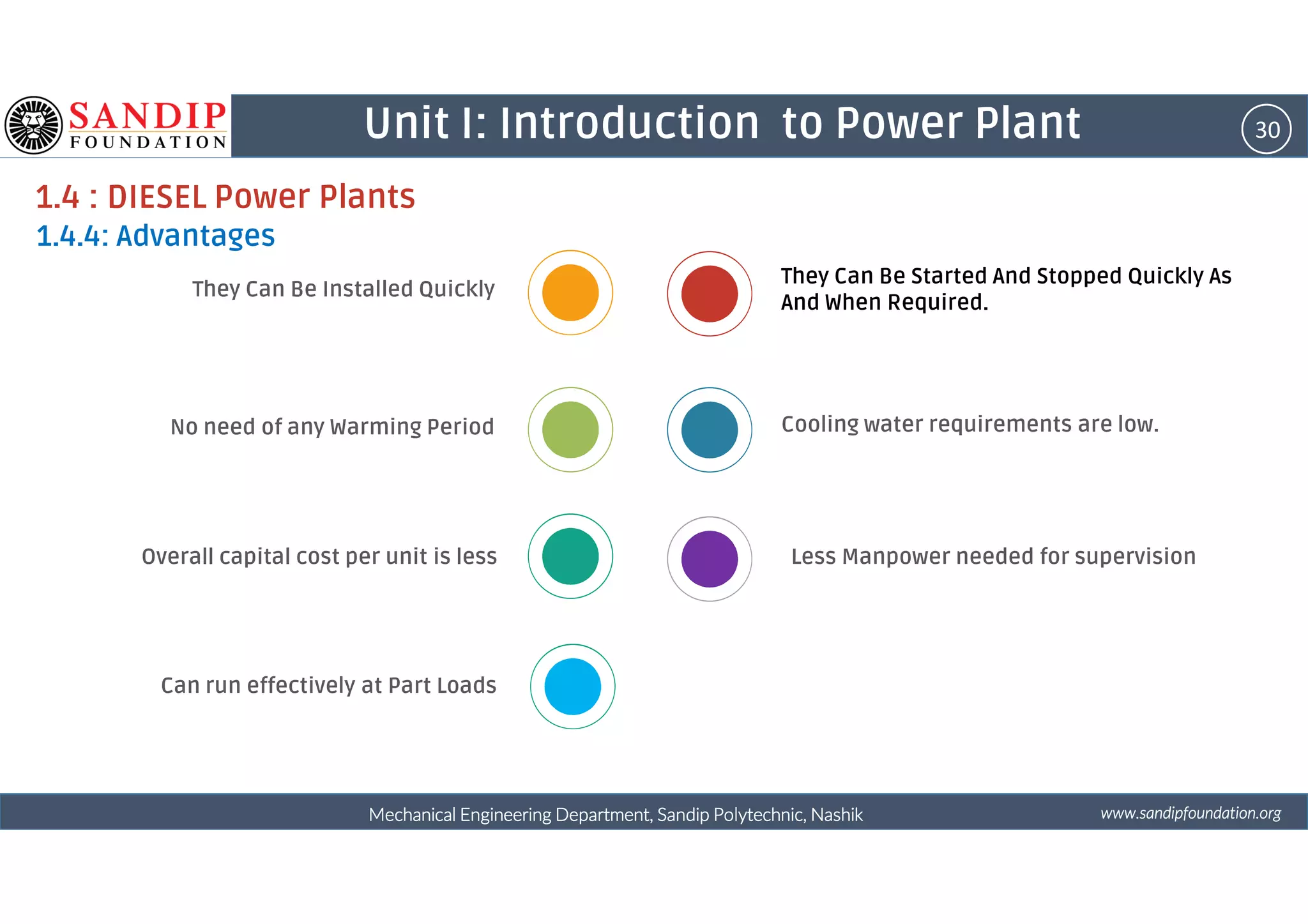
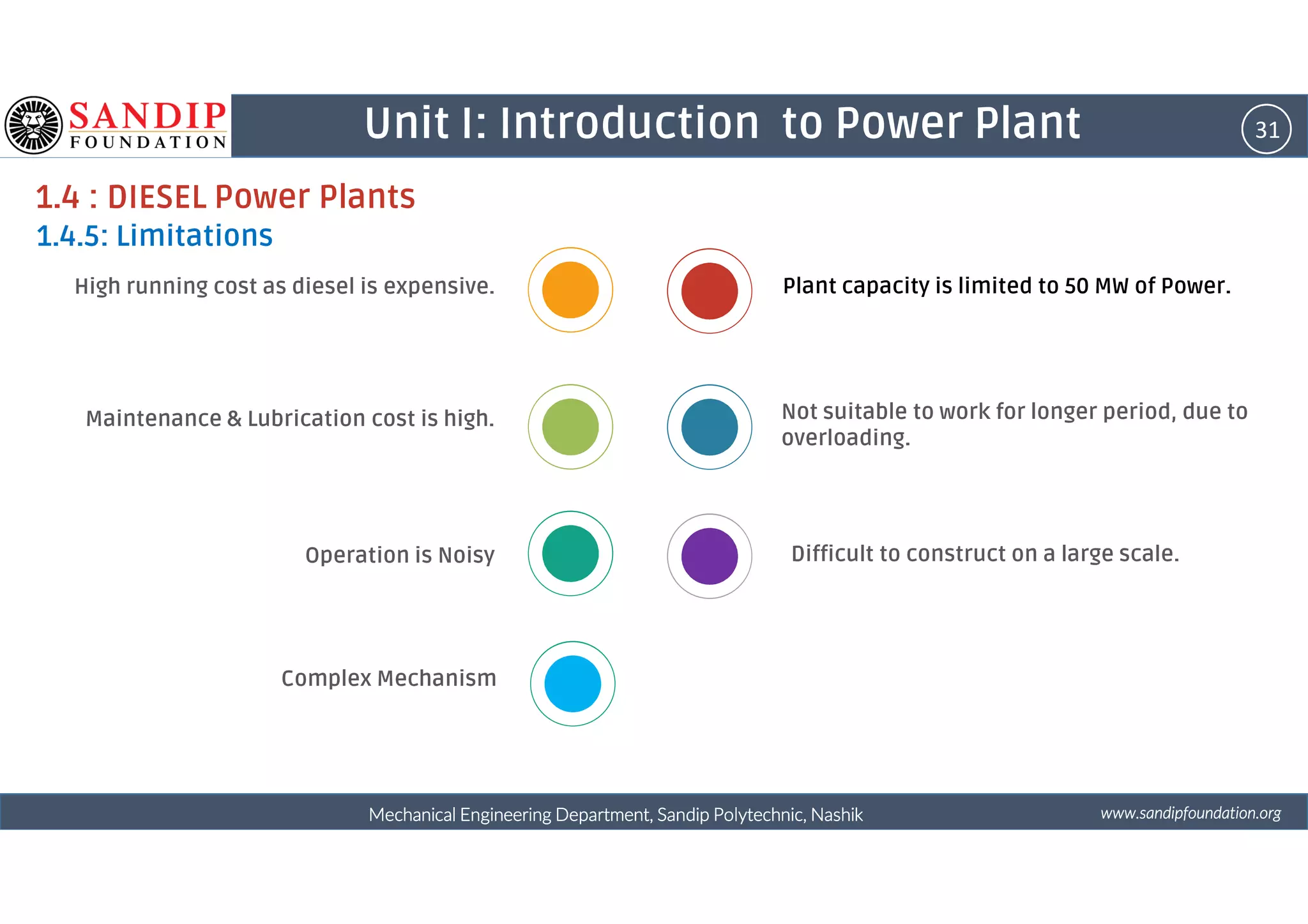
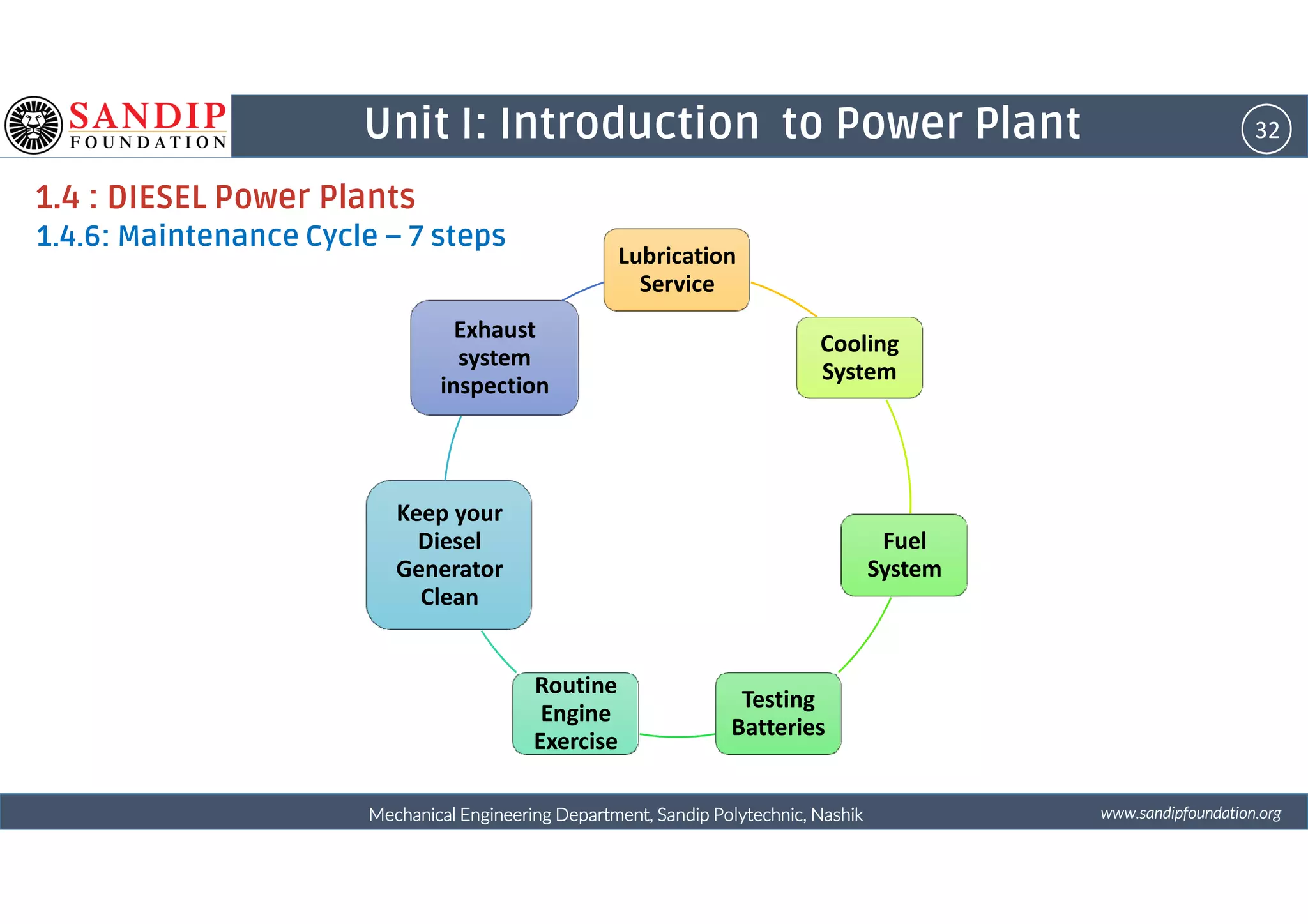
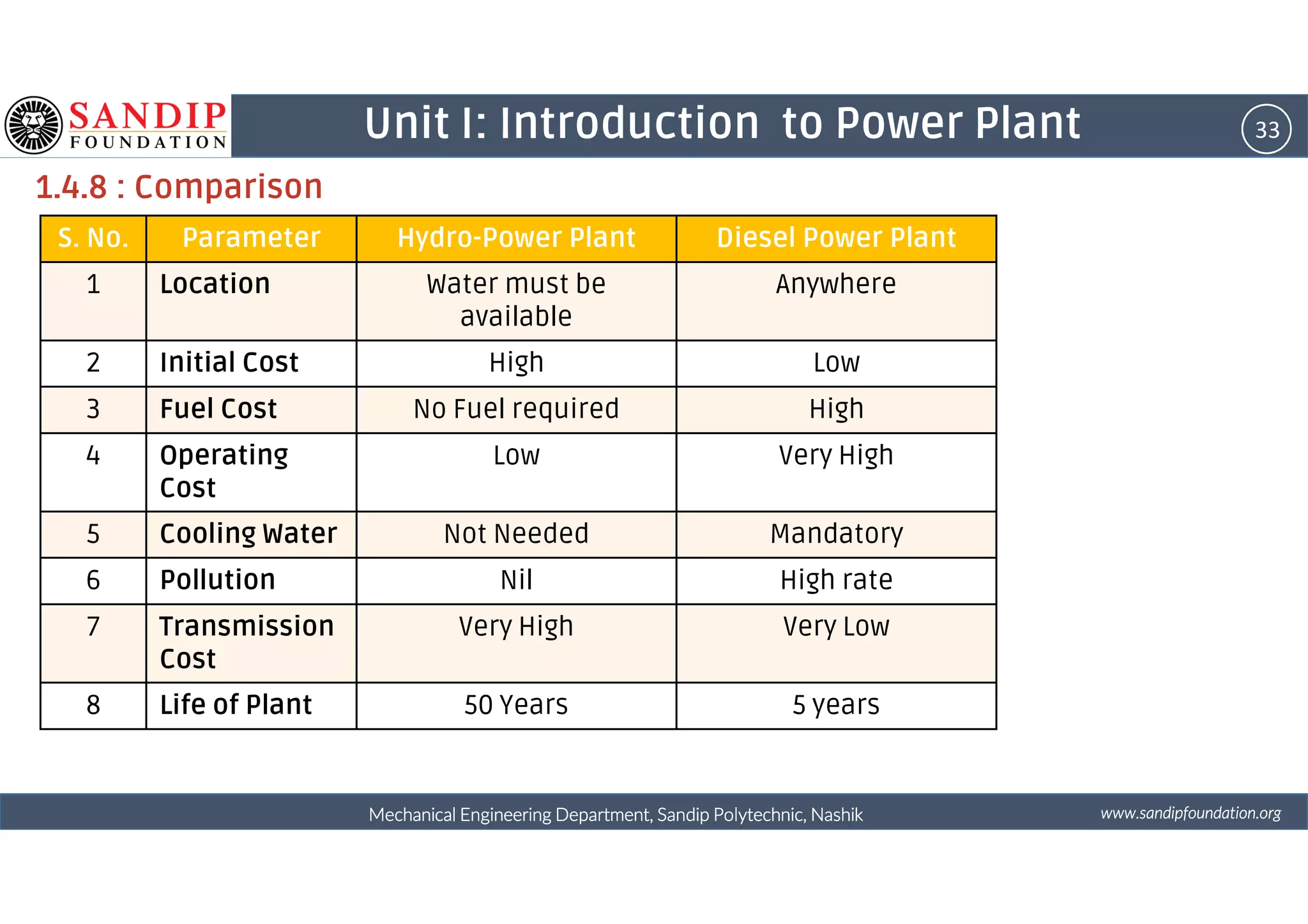
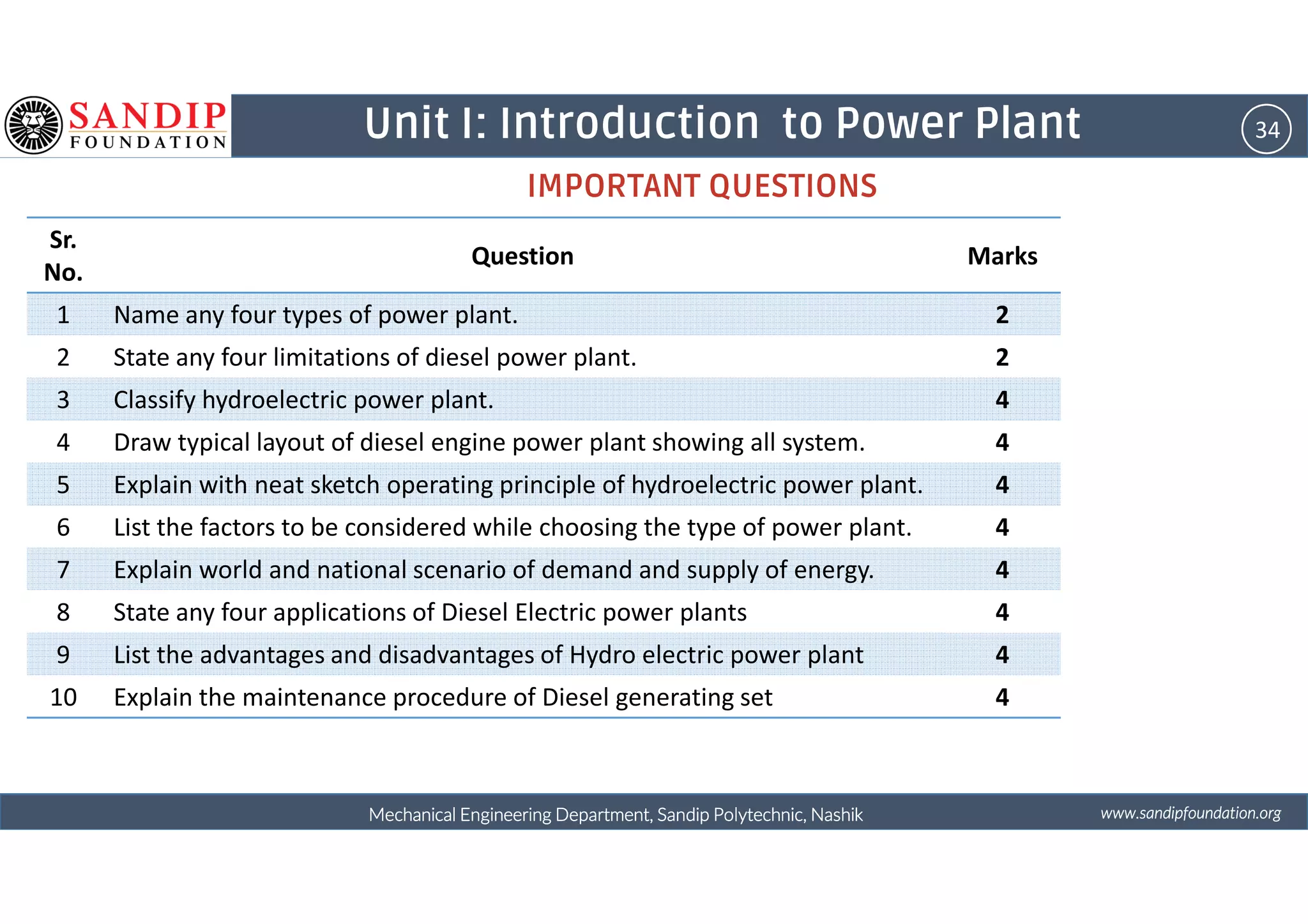
The document outlines a course on power plant engineering for mechanical diploma students at Sandip Polytechnic, Nashik. It covers various topics including the introduction to power plants, their types, and details on hydroelectric and diesel power plants along with maintenance procedures. The document also introduces unit outcomes related to energy conversion and preventive maintenance in power plants.