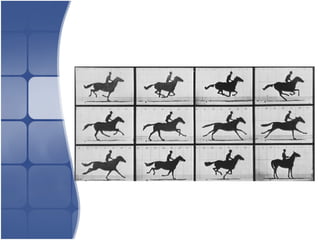
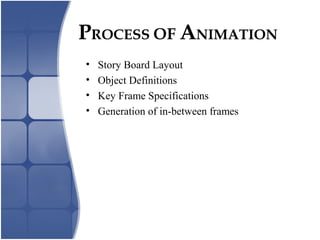
Animation involves creating the illusion of movement by displaying a sequence of slightly different images in rapid succession. It can be created through traditional techniques like cel animation using hand-drawn images or computer animation using 3D modeling software. Common types include key frame animation where frames in between key poses are automated, stop motion using physical objects manipulated frame-by-frame, and morphing where one image transforms smoothly into another. Rendering and file compression are important parts of the animation process.