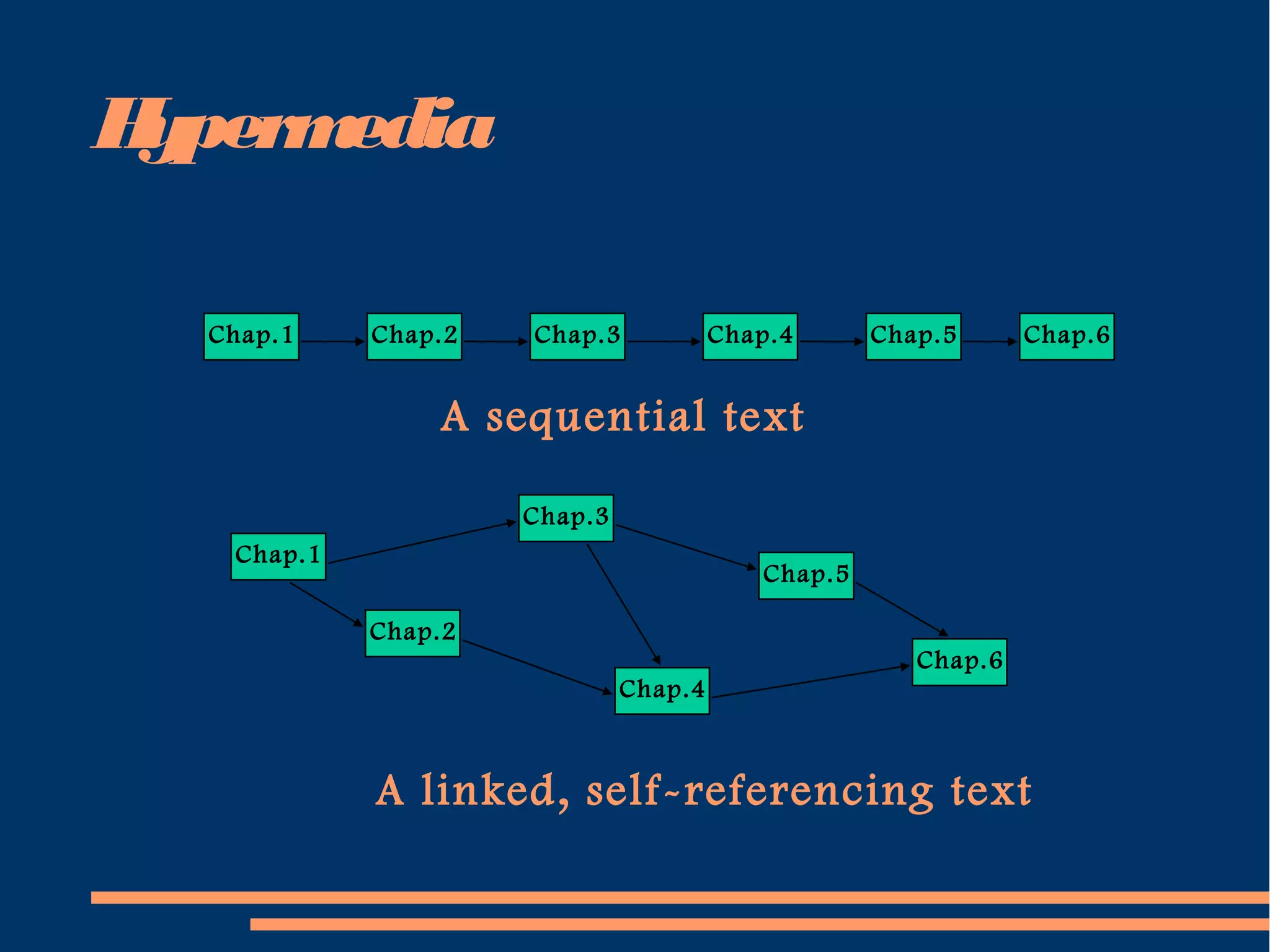
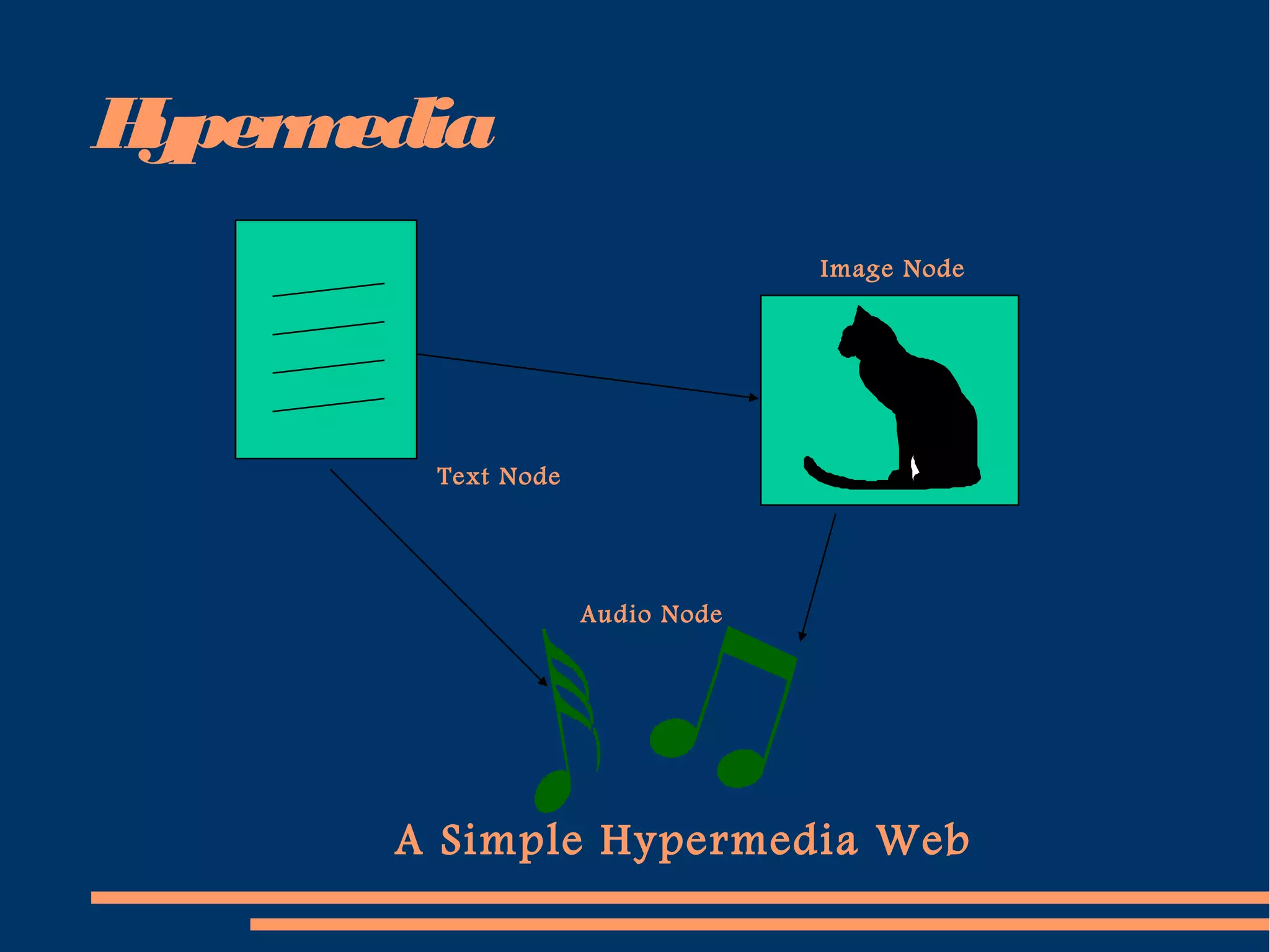
1. The document introduces multimedia systems, defining them as computer applications that incorporate various media like text, graphics, video, and sound for disseminating and presenting information.
2. Multimedia systems are characterized by integrated production, manipulation, presentation, storage, and communication of discrete and continuous media in a computer-controlled environment.
3. The history of multimedia is traced from early games and devices in the 1970s through developments in personal computers, the internet, and authoring tools that enabled the growth of multimedia applications.