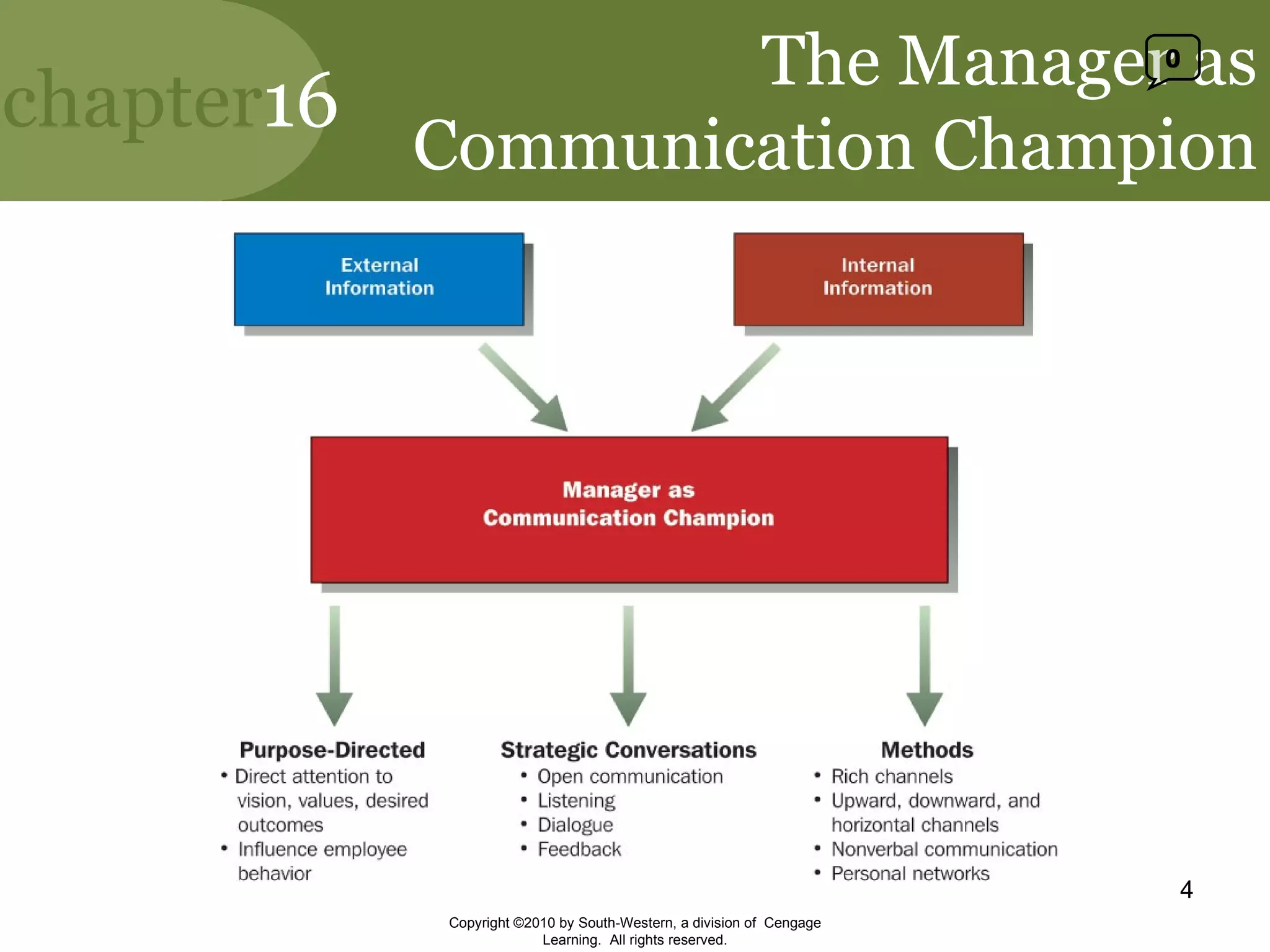
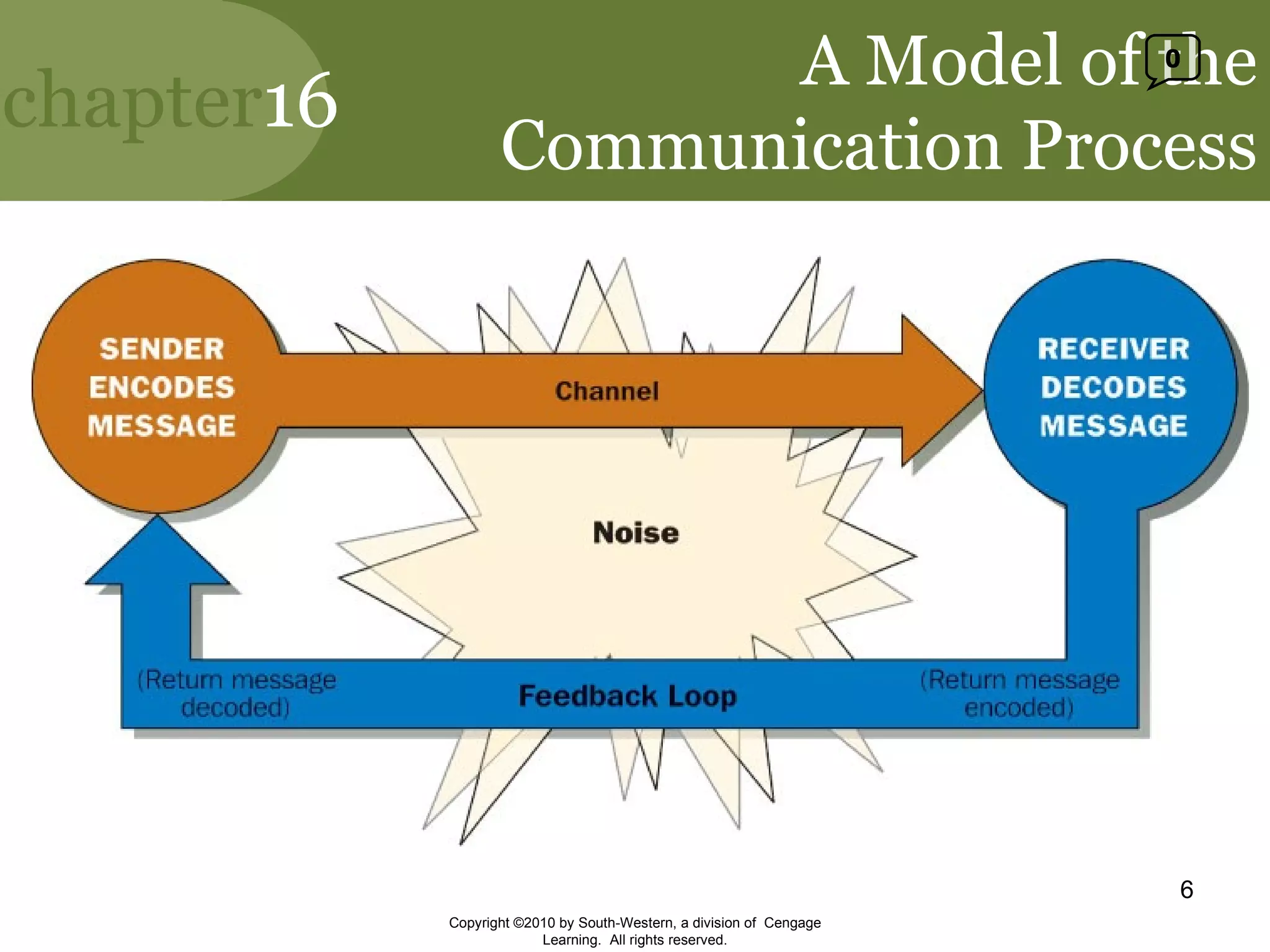
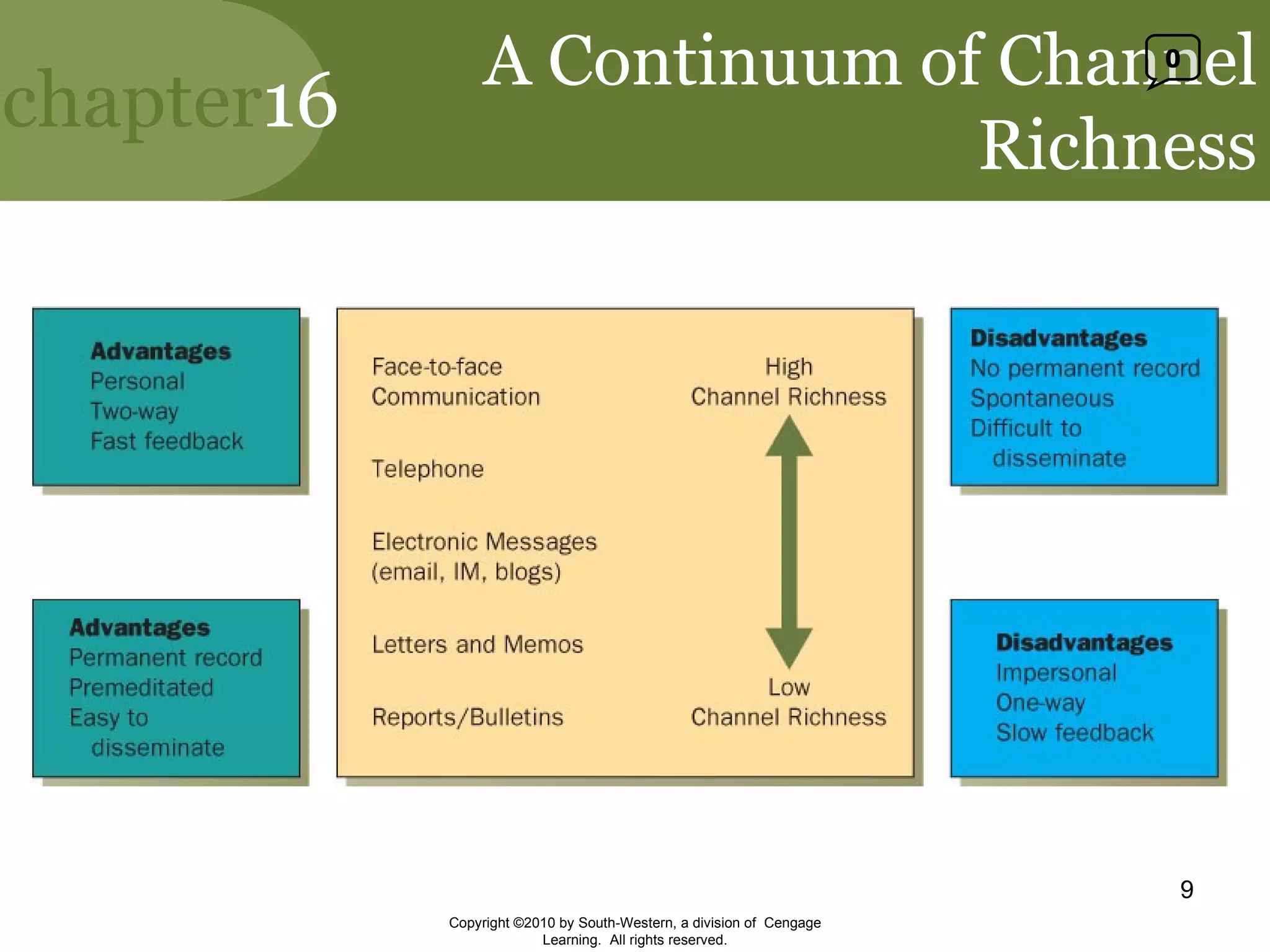
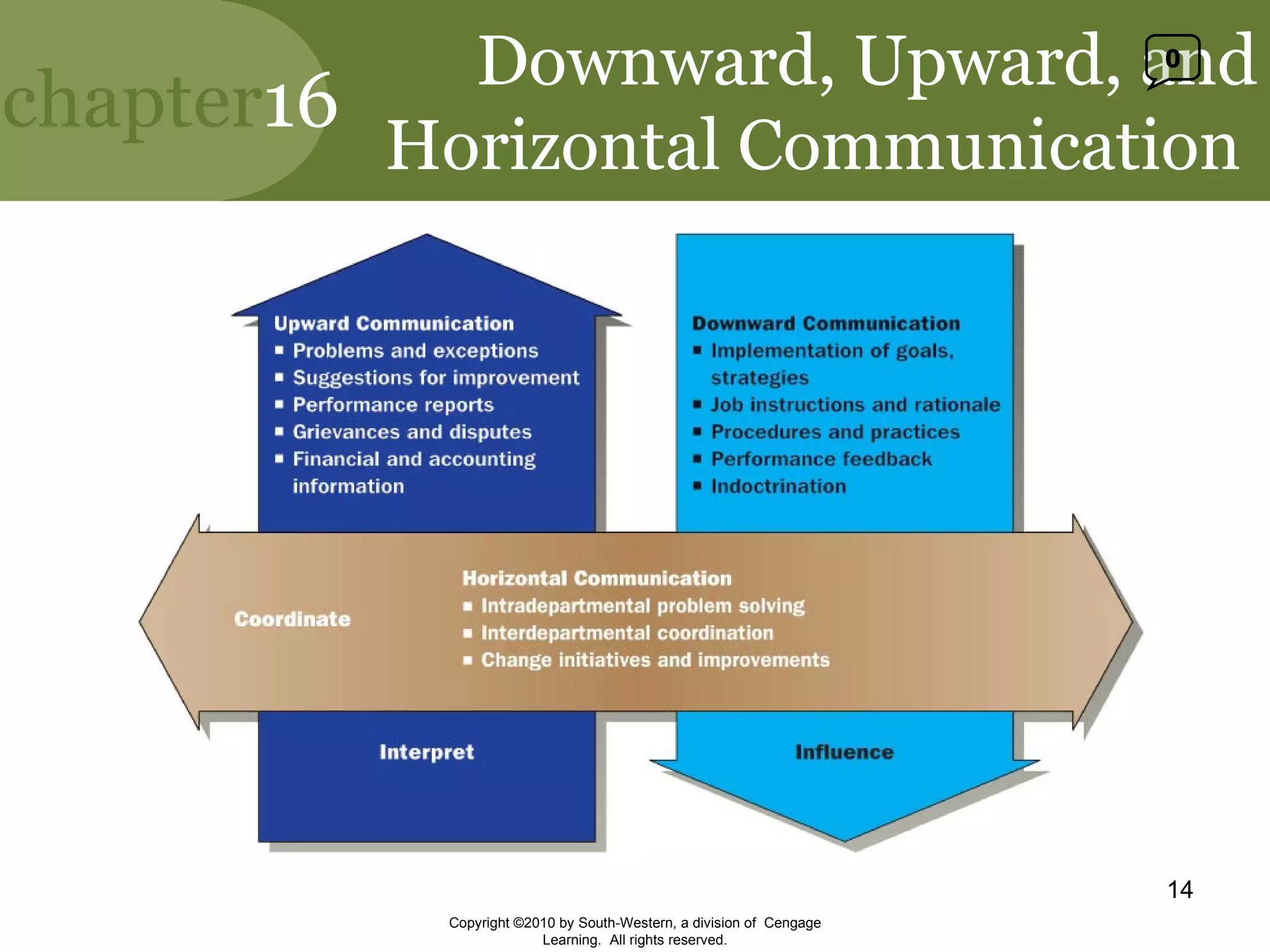
This document discusses effective communication in management. It explains that communication is essential for managers to facilitate strategic conversations through open communication, active listening, and dialogue. It describes different communication channels and how channel richness and selection can influence communication quality. It also discusses how gender differences, nonverbal cues, and listening skills can impact communication effectiveness. Finally, it outlines downward, upward, and horizontal communication channels in organizations and their importance.