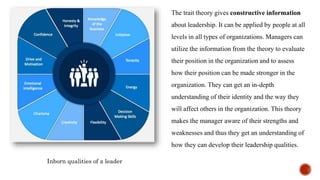
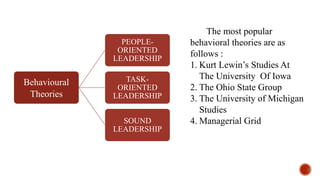
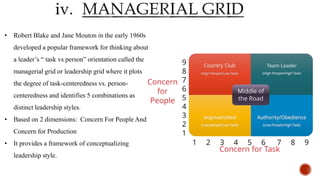
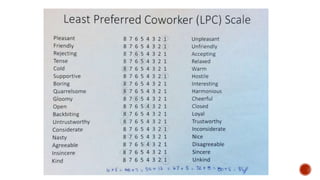
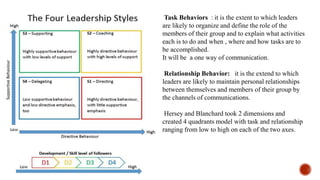
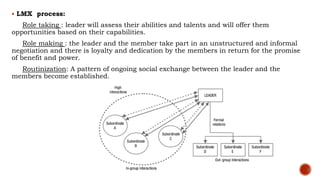
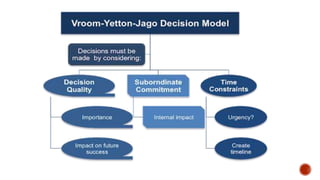
The document discusses various theories of management and leadership. It describes trait theory, which proposes that effective leaders are born with certain traits. Behavioral theories are discussed, including studies at Ohio State University that identified consideration for employees and focus on tasks as key leadership behaviors. The University of Michigan studies classified behaviors as employee-oriented or production-oriented. Blake and Mouton's managerial grid plots concern for tasks versus people to define leadership styles. Contingency theory proposes there is no single best leadership style and the most effective style depends on the situation.