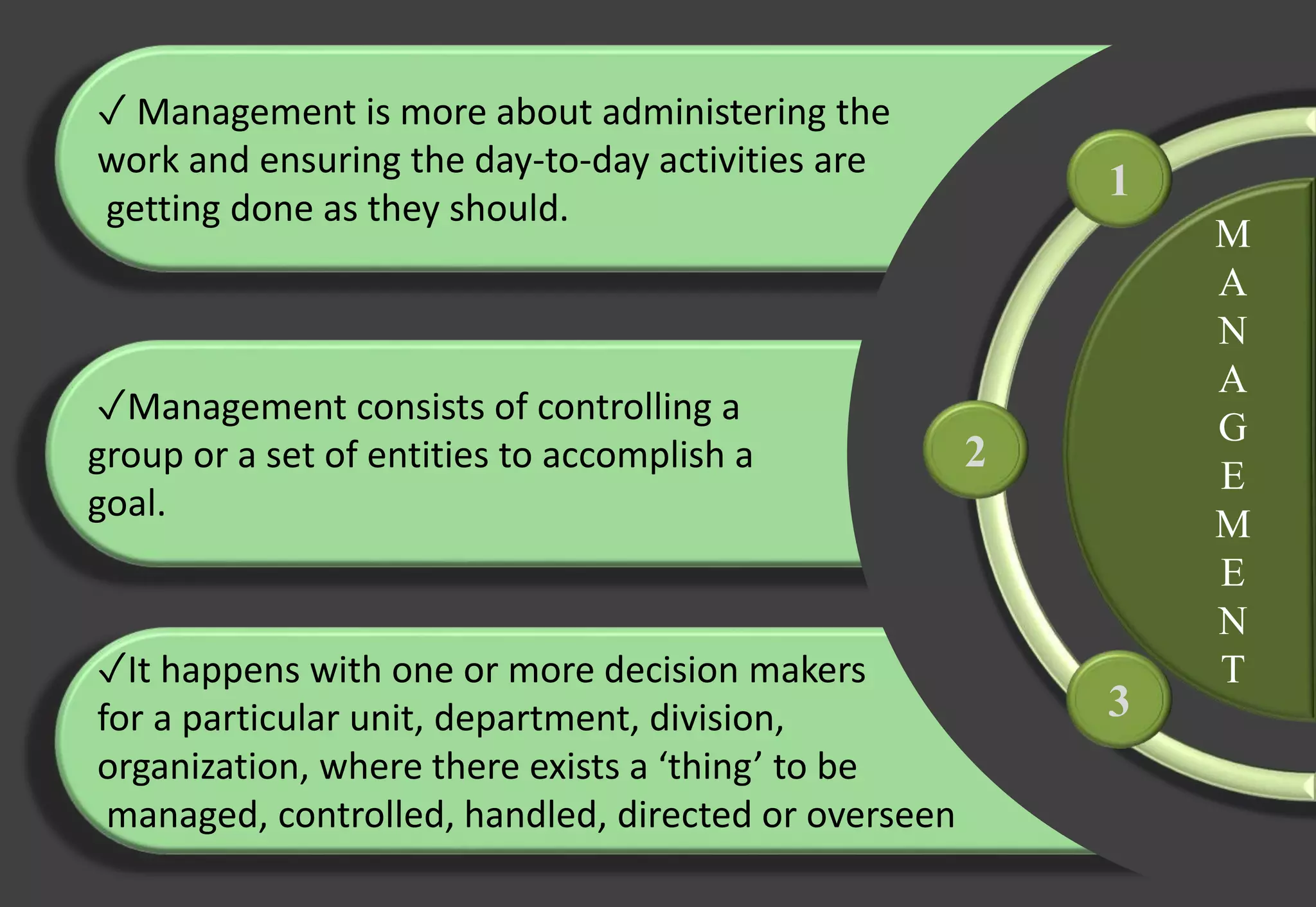
The document discusses the differences between leadership and management. It provides definitions and examples of each:
- Leadership is about motivating people through vision and inspiration to achieve goals, while management focuses on day-to-day operations like planning, staffing, and problem-solving.
- Several experts contribute perspectives on the distinction. John Kotter's 8 steps of change leadership emphasizes creating urgency and empowering others. Warren Bennis contrasts leaders with managers who command versus empower and inspire.
- While distinct, both leadership and management are valuable roles that organizations need. Leaders drive innovation but may lack management skills, and managers excel at execution but not large-scale influence. Together they can achieve greater impact.