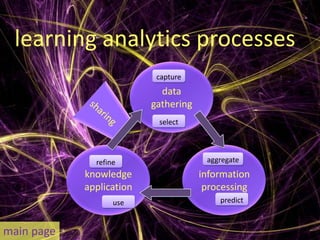
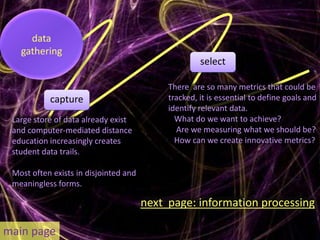
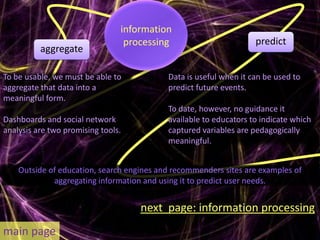
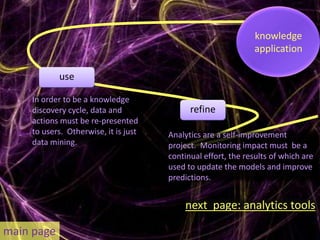
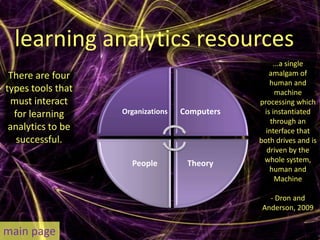
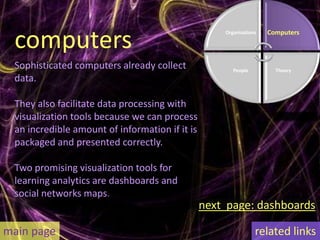
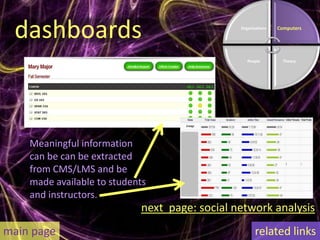
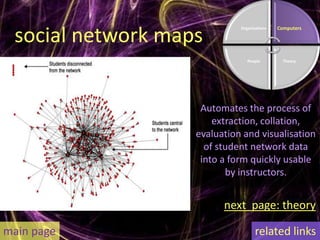
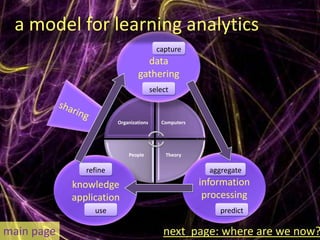
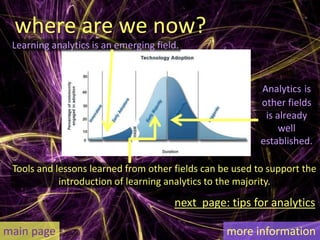
Learning analytics aim to enhance student success through real-time data usage by students, instructors, and advisors. It involves developing tools and processes to improve learning and teaching, drawing insights from related fields like business intelligence and web analytics. Currently, learning analytics is an emerging field, and implementation tips include learning from established disciplines and effectively combining various data types.















![references (continued)
McFadden, C. (2005). Optimizing the Online Business Channel with Web Analytics [blog
post]. Retrieved October 5, 2010 from
http://www.webanalyticsassociation.org/members/blog_view.asp?id=533997&post=8932
8&hhSearchTerms=definition+and+of+and+web+and+analytics
NextGeneration: Learning Challenges (n.d.). Learning Analytics [website]. Retrieved
October 12, 2010 from http://nextgenlearning.com/the-challenges/learning-analytics
Norris, D., Baer, L., Leonard, J., Pugliese, L. and Lefrere, P. (2008). Action Analytics:
Measuring and Improving Performance That Matters in Higher Education, EDUCAUSE
Review 43(1). Retrieved October 1, 2010
from http://www.educause.edu/EDUCAUSE+Review/EDUCAUSEReviewMagazineVolume4
3/ActionAnalyticsMeasuringandImp/162422
Zhang, H. and Almeroth, K. (2010). Moodog: Tracking Student Activity in Online Course
Management Systems. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 21(3), 407-429.
Chesapeake, VA: AACE. Retrieved October 5, 2010 from http://0-
www.editlib.org.aupac.lib.athabascau.ca/p/32307.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learninganalyticsoer-110113083950-phpapp01/85/Learning-Analytics-Oer-26-320.jpg)