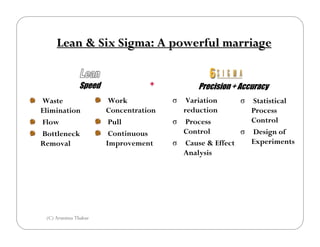
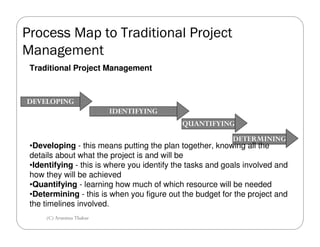
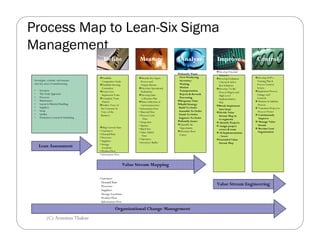
Lean Six Sigma project management aims to streamline projects with higher predictability and lower variations than traditional project management. It focuses on eliminating waste and non-value-added steps through a DMAIC process of defining opportunities, measuring key metrics, analyzing processes, improving processes by eliminating sources of variation, and controlling performance. Lean Six Sigma projects emphasize continuous improvement through small experiments, empowered cross-functional teams, and a pull-based approach driven by customer demand.