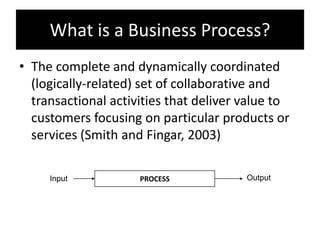
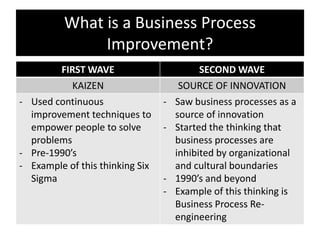
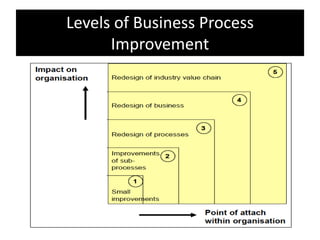
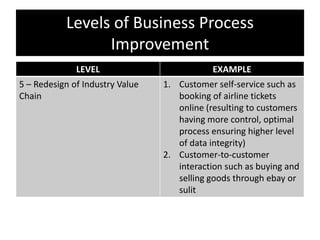
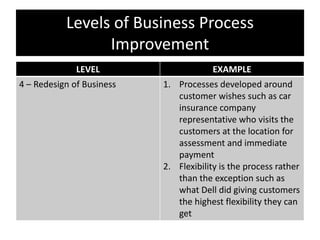
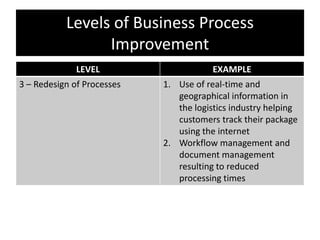
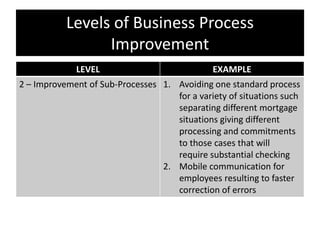
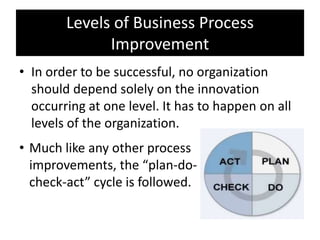
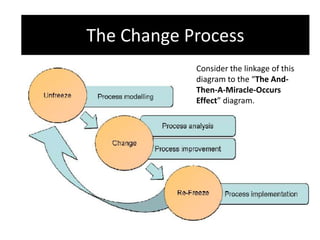
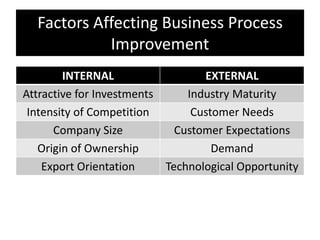
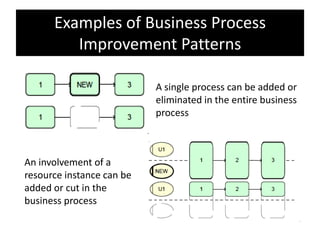
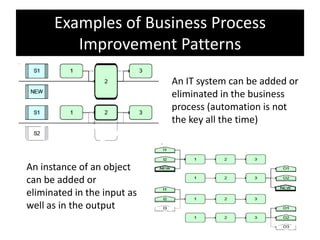
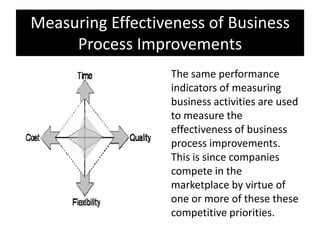
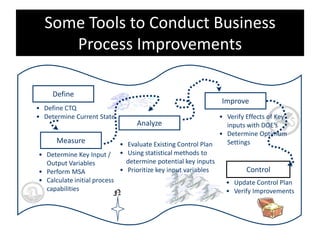
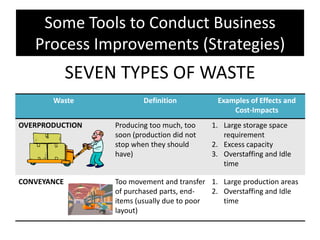
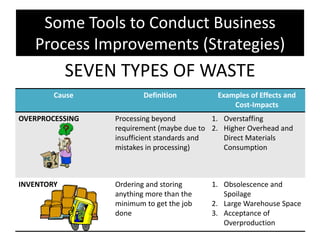
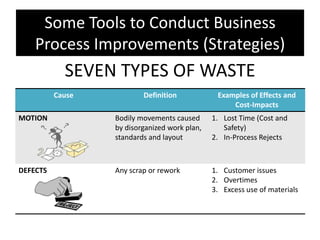
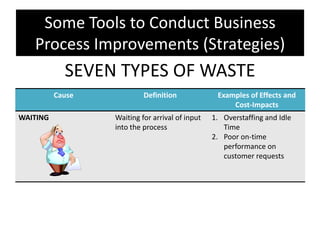
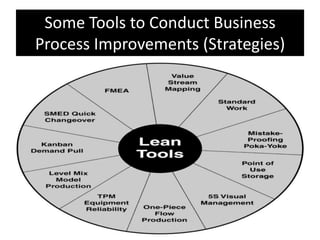
The document provides an overview of business process improvement (BPI), highlighting its definition, objectives, and various strategies for implementation. It emphasizes the importance of aligning business processes with organizational goals and customer satisfaction while exploring different levels and tools, such as Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing, for enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. Successful implementation of BPI involves systematic approaches and engagement from management and stakeholders, with an ongoing focus on quality improvement.