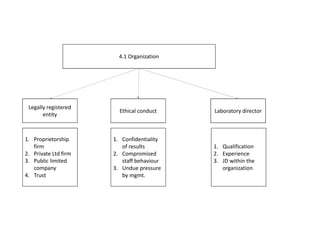
ISO 15189 is an international standard that specifies the general requirements for the competence of medical laboratories. It is based on ISO 17025 for testing and calibration laboratories and ISO 9001 for quality management systems. ISO 15189 has both management and technical requirements that medical laboratories must meet in order to be accredited. The standard is designed to ensure that laboratories consistently deliver accurate, reliable and timely medical testing services.