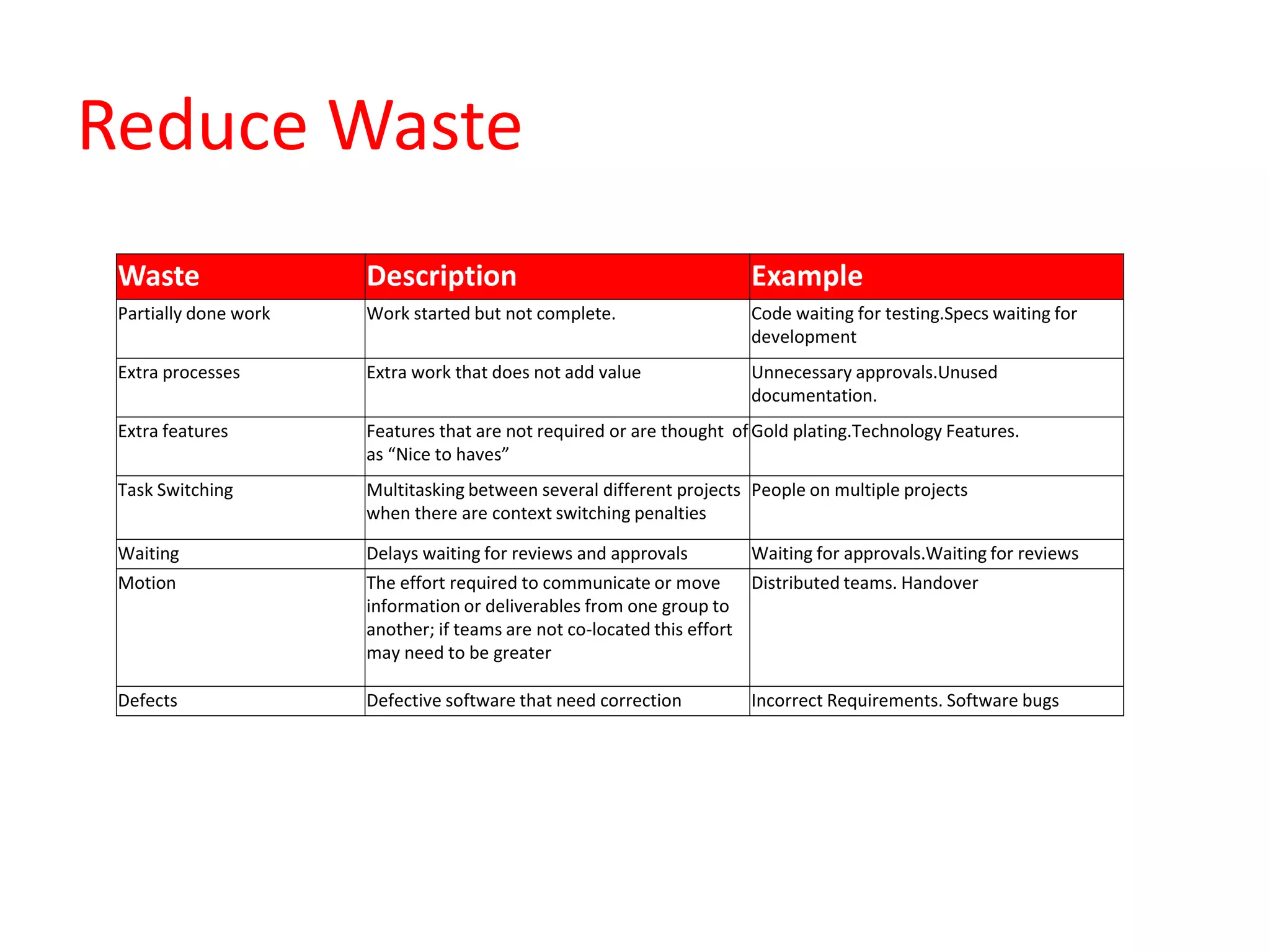
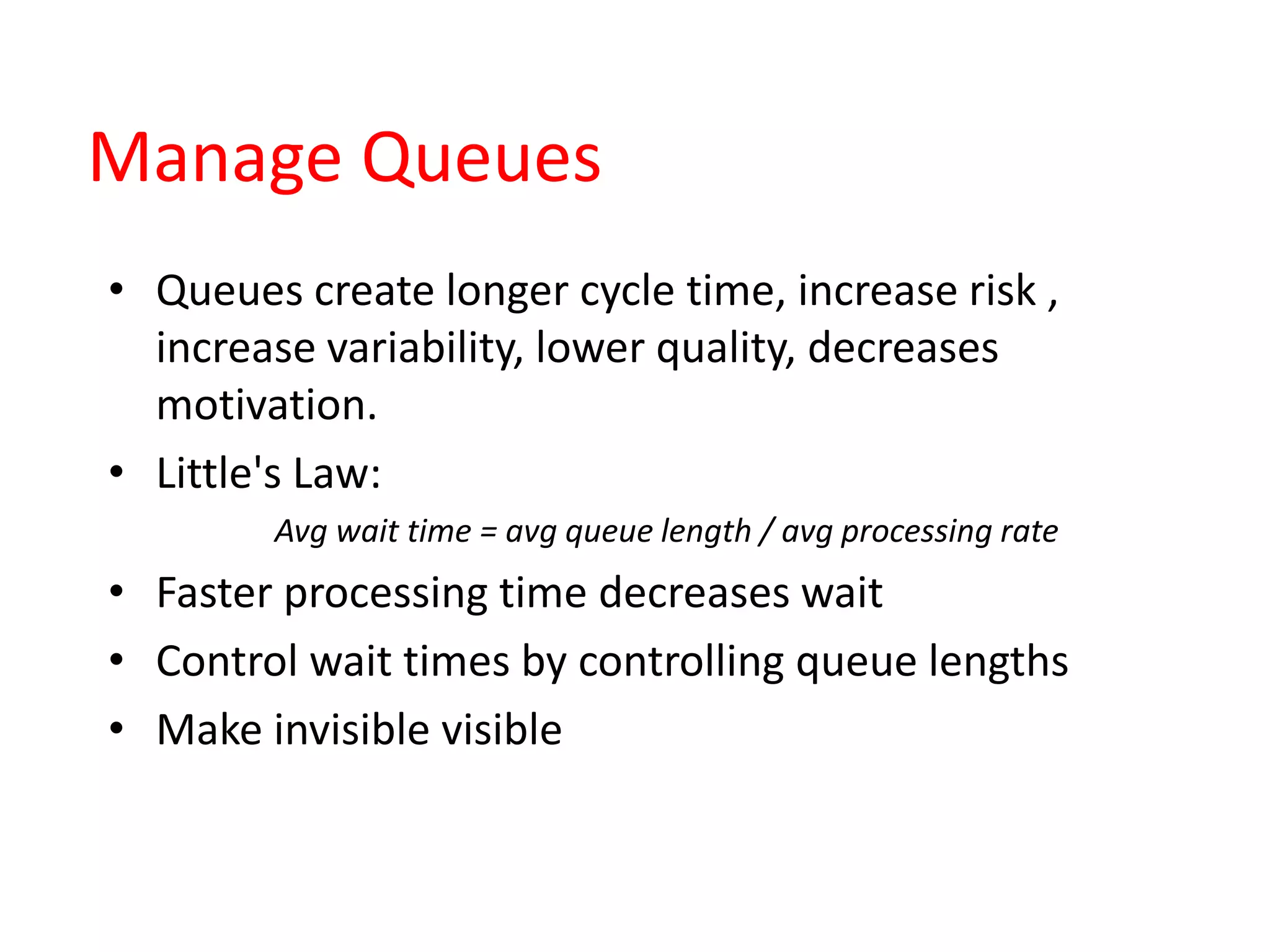
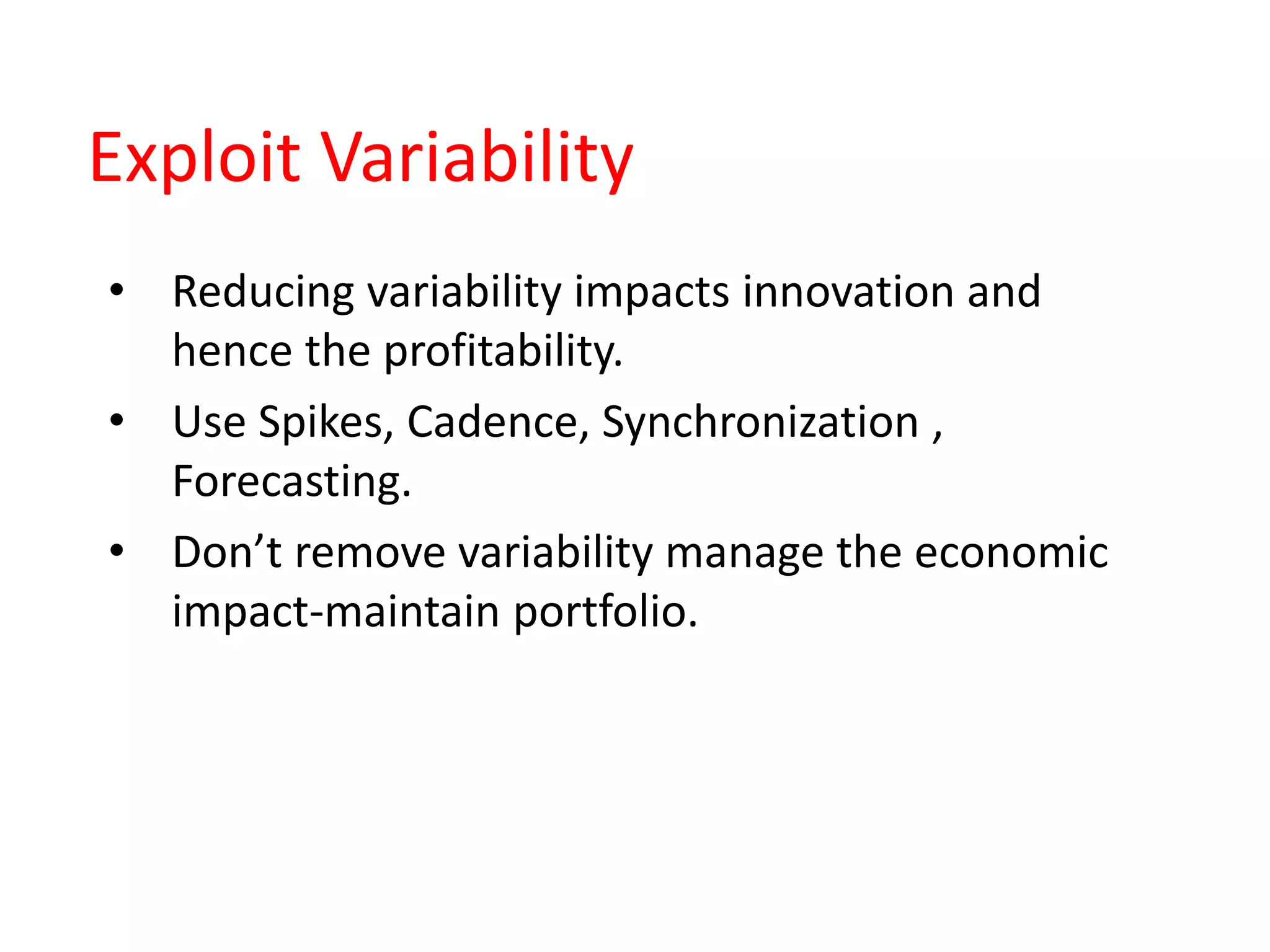
Lean practices for software development focus on maximizing customer value while minimizing waste. This includes reducing partially completed work, extra processes, extra features, task switching, waiting, motion, and defects. Developers should take an economic view by quantifying the cost of delay. They should also manage queues to reduce wait times, exploit variability while maintaining economic impact, reduce batch sizes to improve cycle times, apply work-in-progress constraints, and accelerate feedback through small batches.