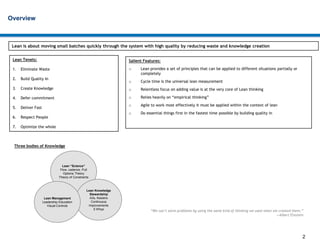
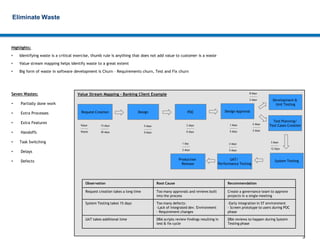
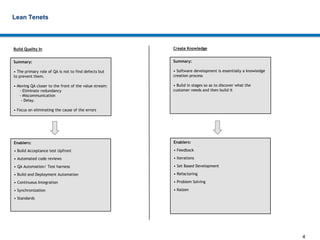
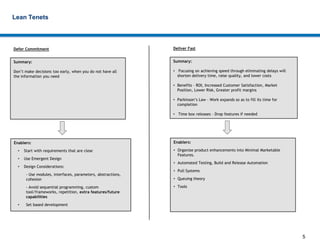
Lean development focuses on eliminating waste to provide the highest customer value. It relies on principles like reducing cycle time, building quality in from the start, and continuously creating and sharing knowledge. Effective lean approaches defer commitment, deliver features fast through techniques like minimal marketable releases, and respect all people as partners in improvement. The overall goal is to optimize the entire development system, not just individual parts, to best meet customer needs.