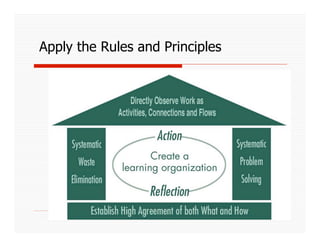
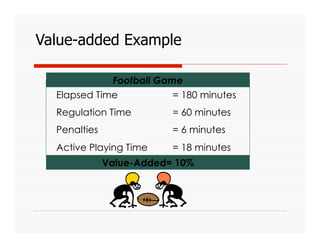
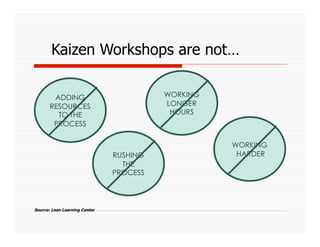
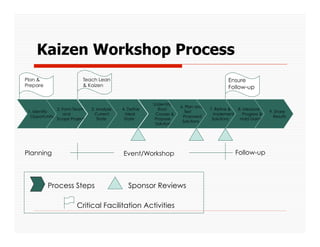
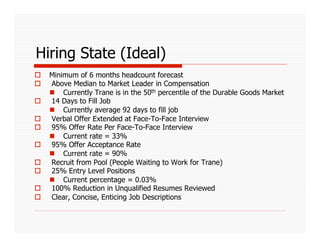
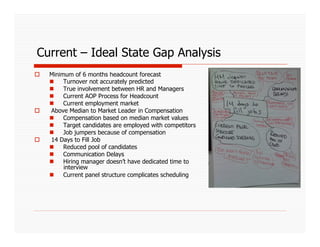
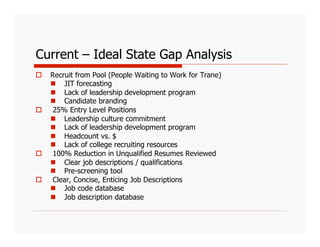
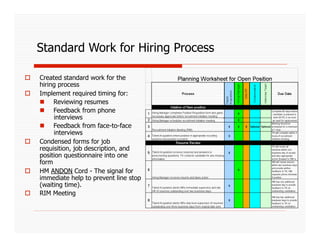
The document discusses applying Lean principles to recruiting and hiring processes. It provides background on Lean manufacturing and defines key terms. It then describes a Kaizen event conducted by the company's Talent Acquisition team to improve their "Days to Fill" a position by reducing waste. The event revealed issues such as a lack of headcount forecasting, non-competitive compensation, and delays in communication. It developed standard work and identified future needs like enhancing the career website and implementing a leadership development program.