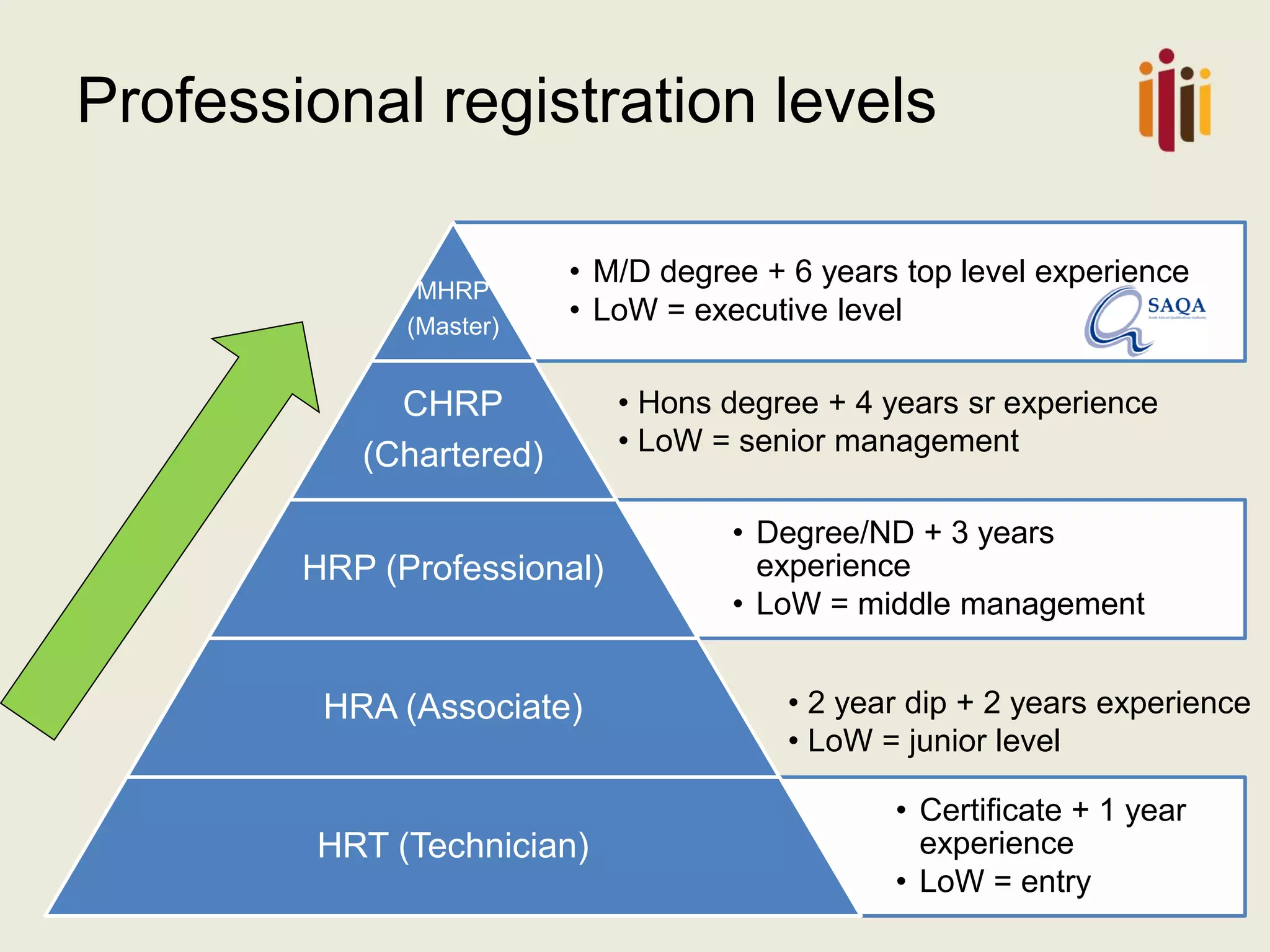
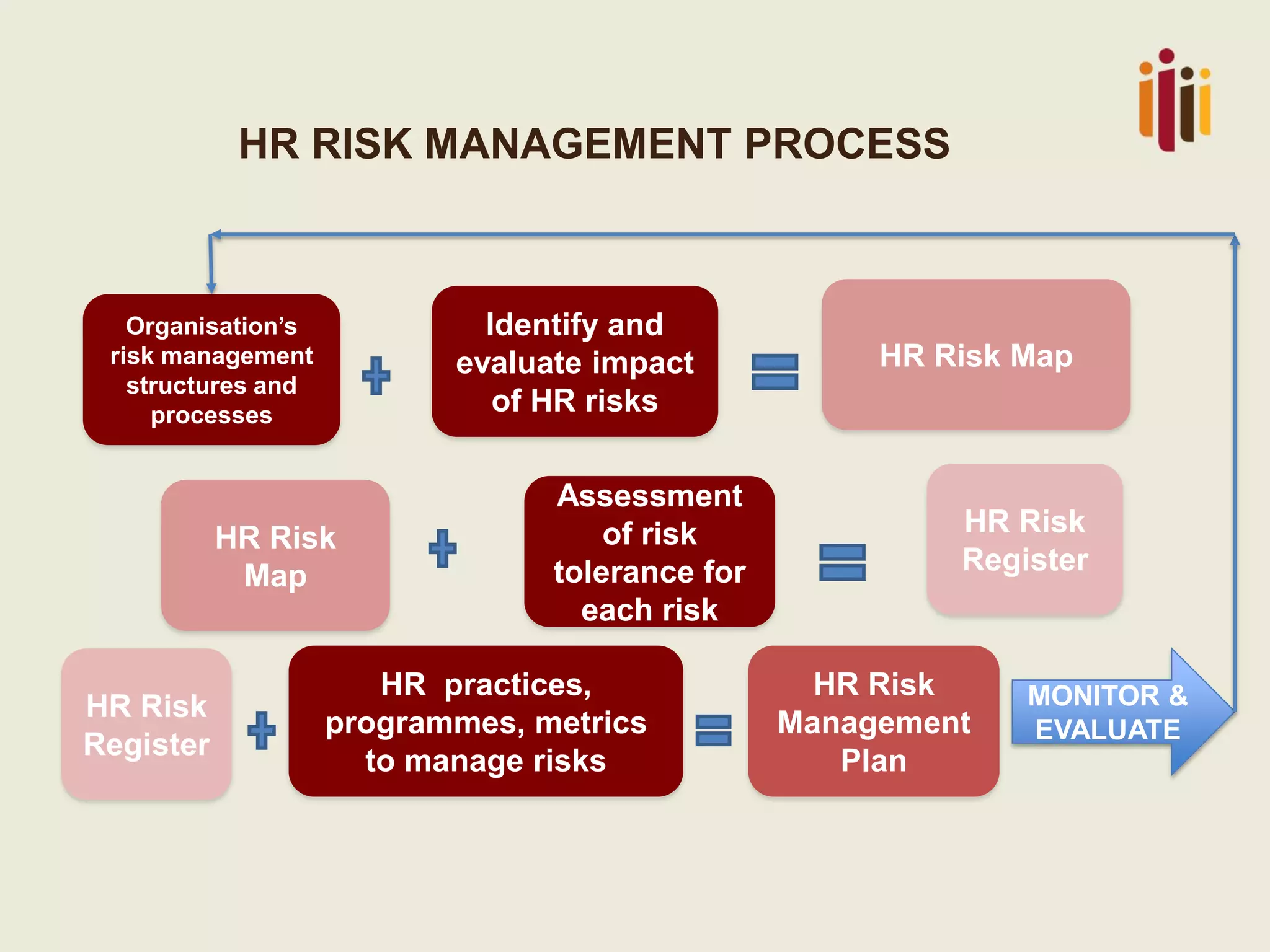
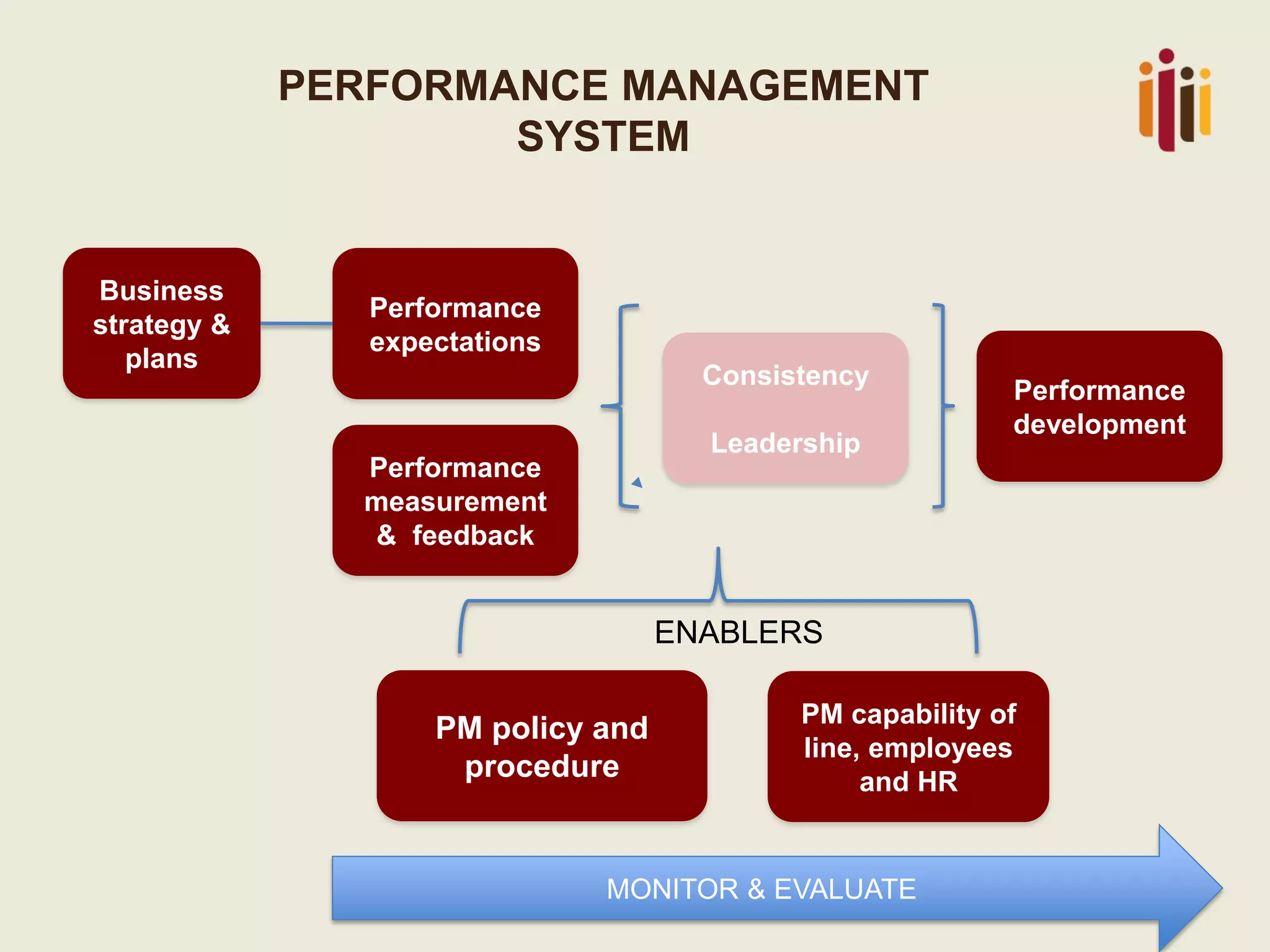
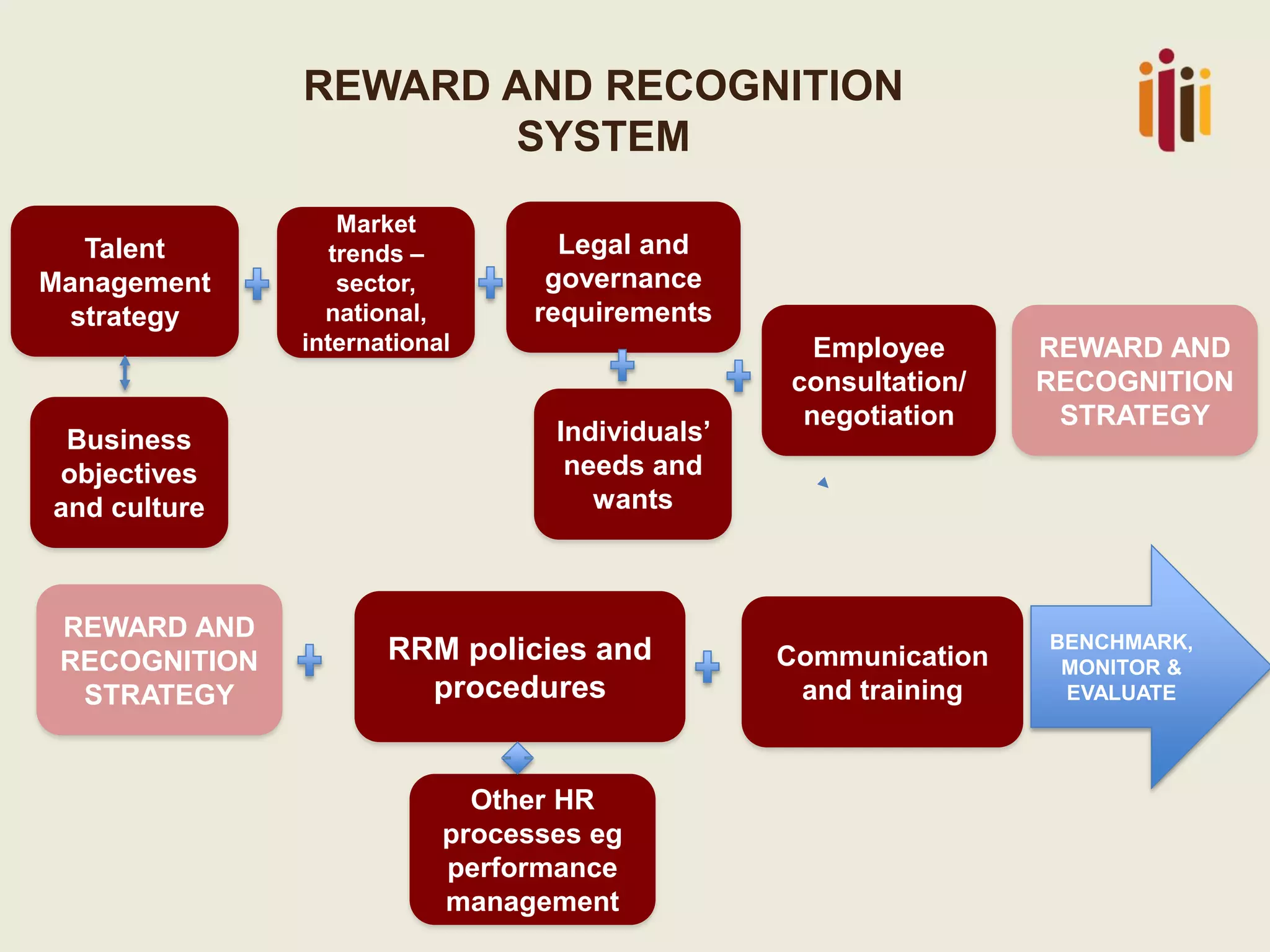
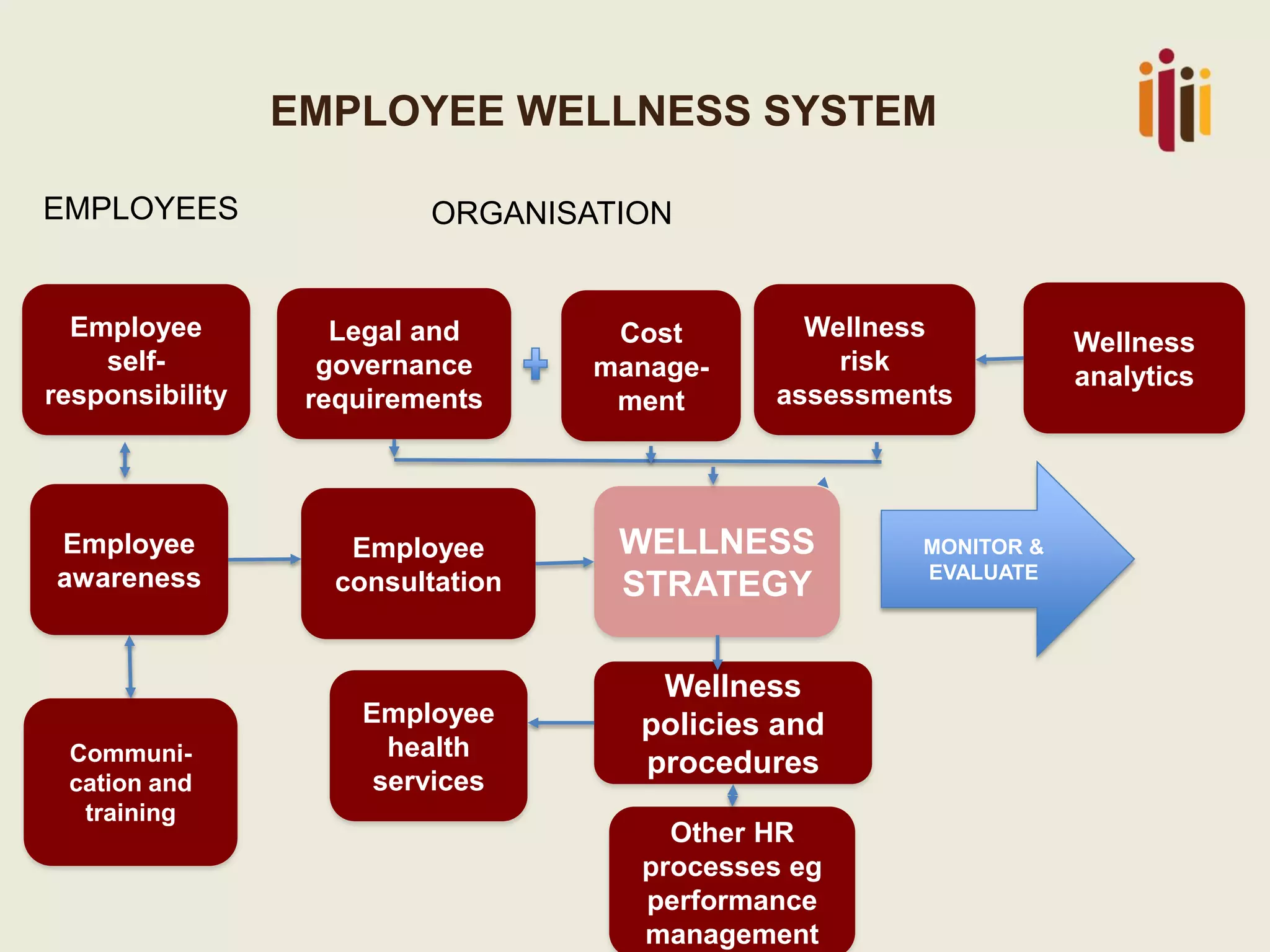
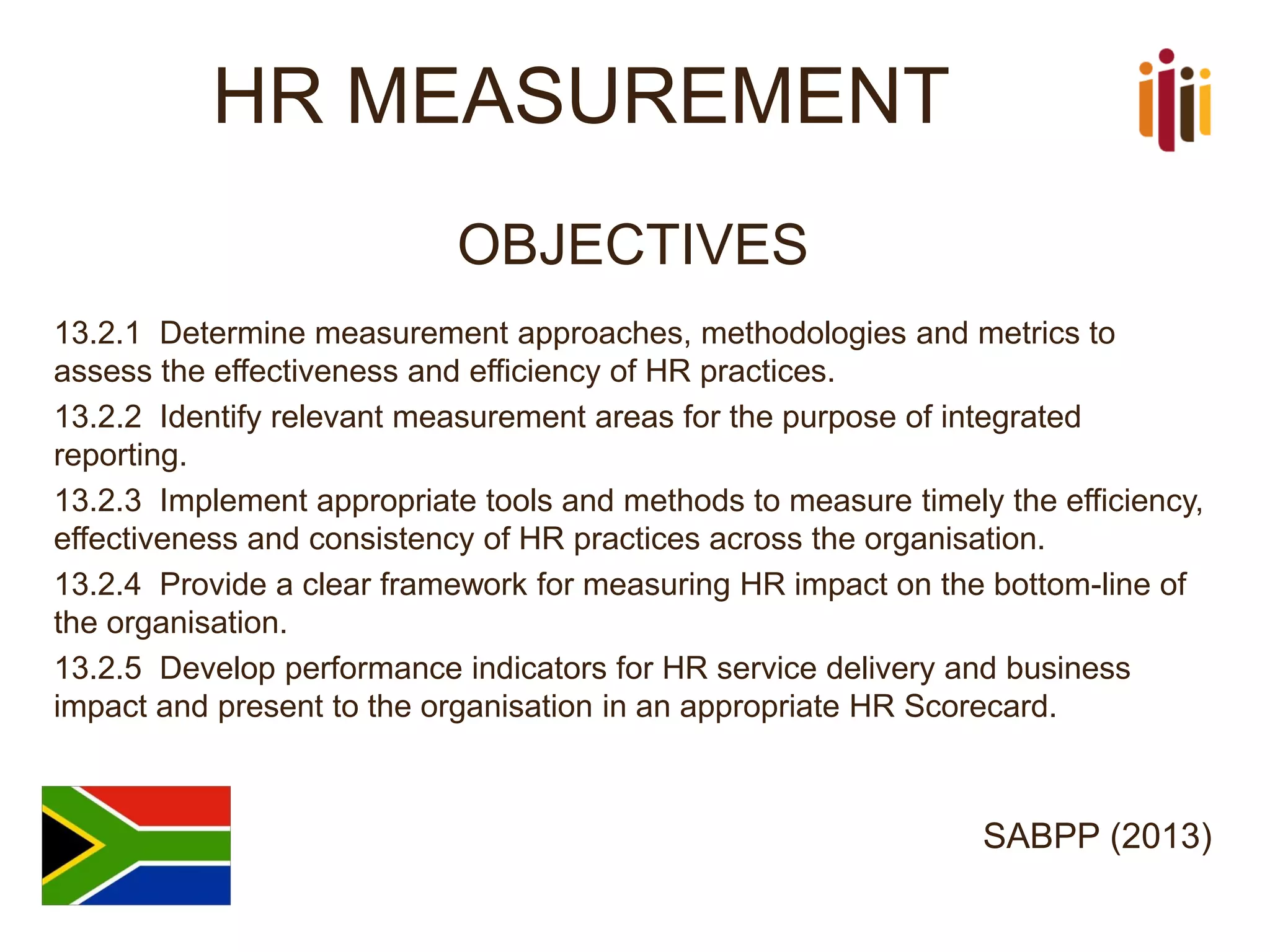
This document summarizes the key topics from a presentation on human resource standards in South Africa. It discusses the development of HR standards since 2013 by SABPP and over 460 HR leaders. The standards cover 13 elements of an HR management system, including strategic HR, talent management, HR risk management, and workforce planning. The document also provides objectives and processes for each standard element.