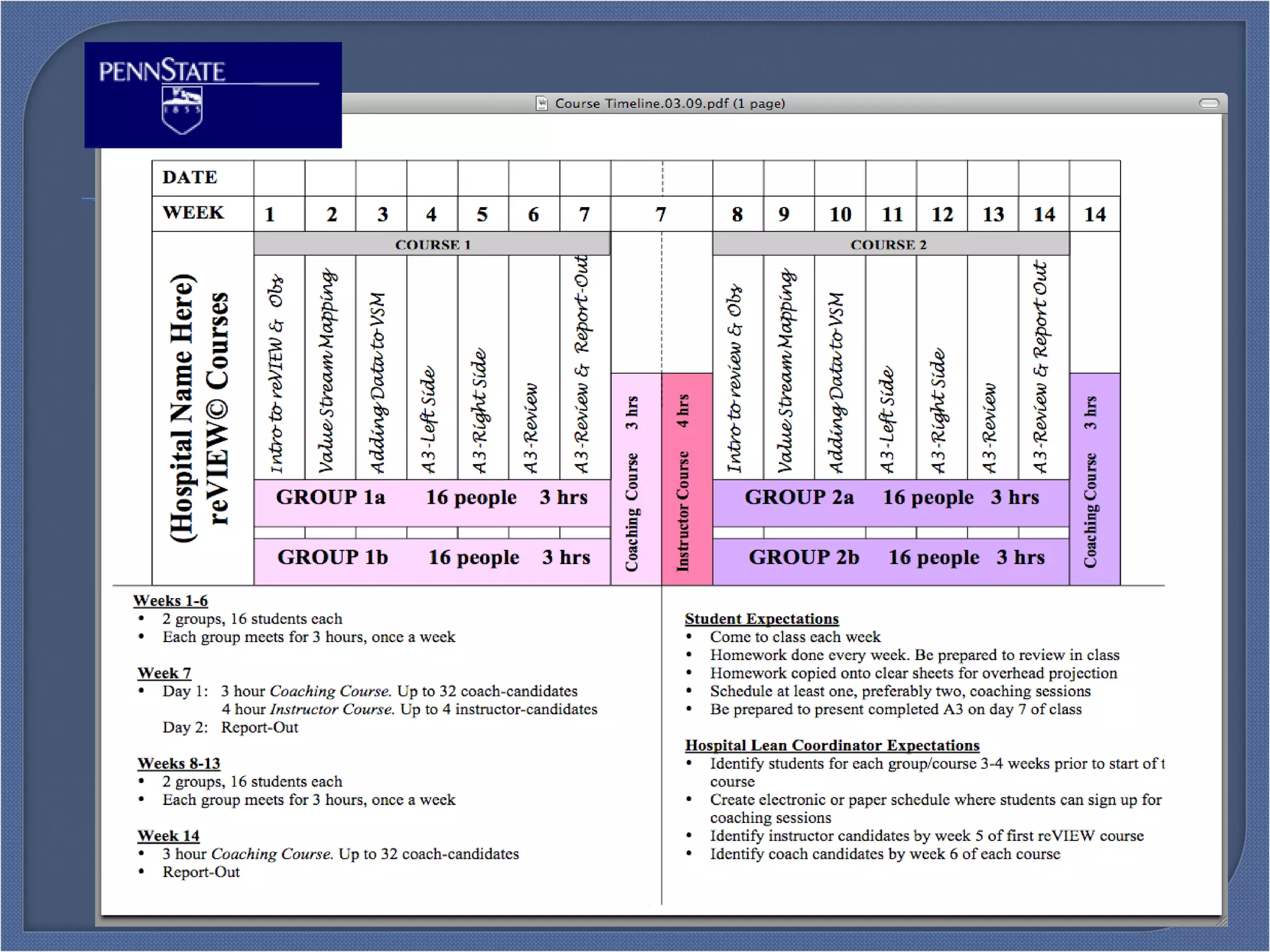
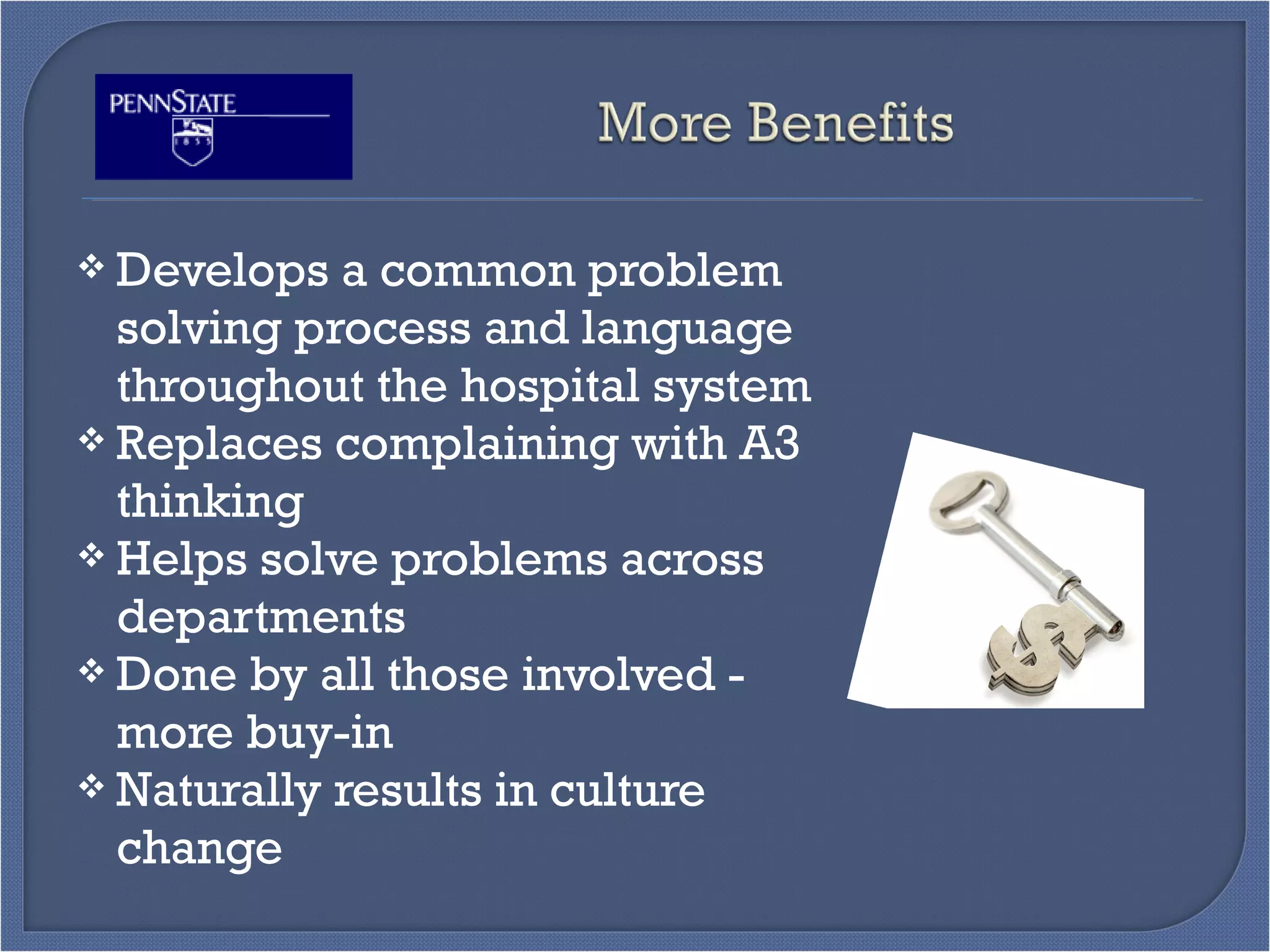
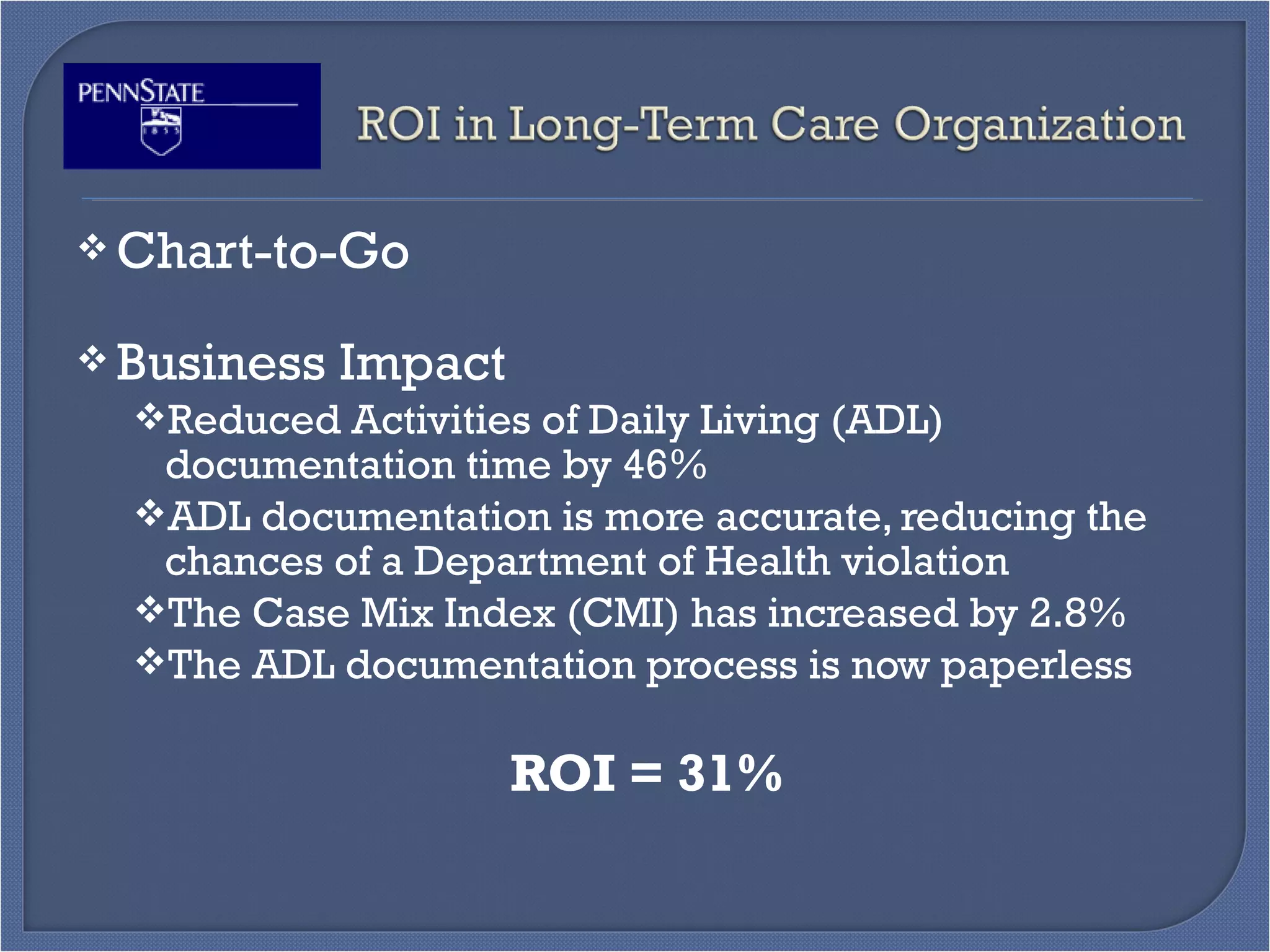
This document outlines the objectives and content of a Toyota Production System (TPS) training curriculum. The objectives are to: familiarize participants with TPS; review critical elements like the four rules of TPS; examine the curriculum's uniqueness; develop awareness of benefits and improvements; discuss the unique selling proposition; and discuss opportunities and challenges. The content includes comparisons of traditional vs lean culture, explanations of key TPS tools like value stream mapping and A3 problem solving, details of the 7-day training schedule and follow-up coaching, examples of past projects and their impacts, and perspectives from previous participants on the training's benefits.