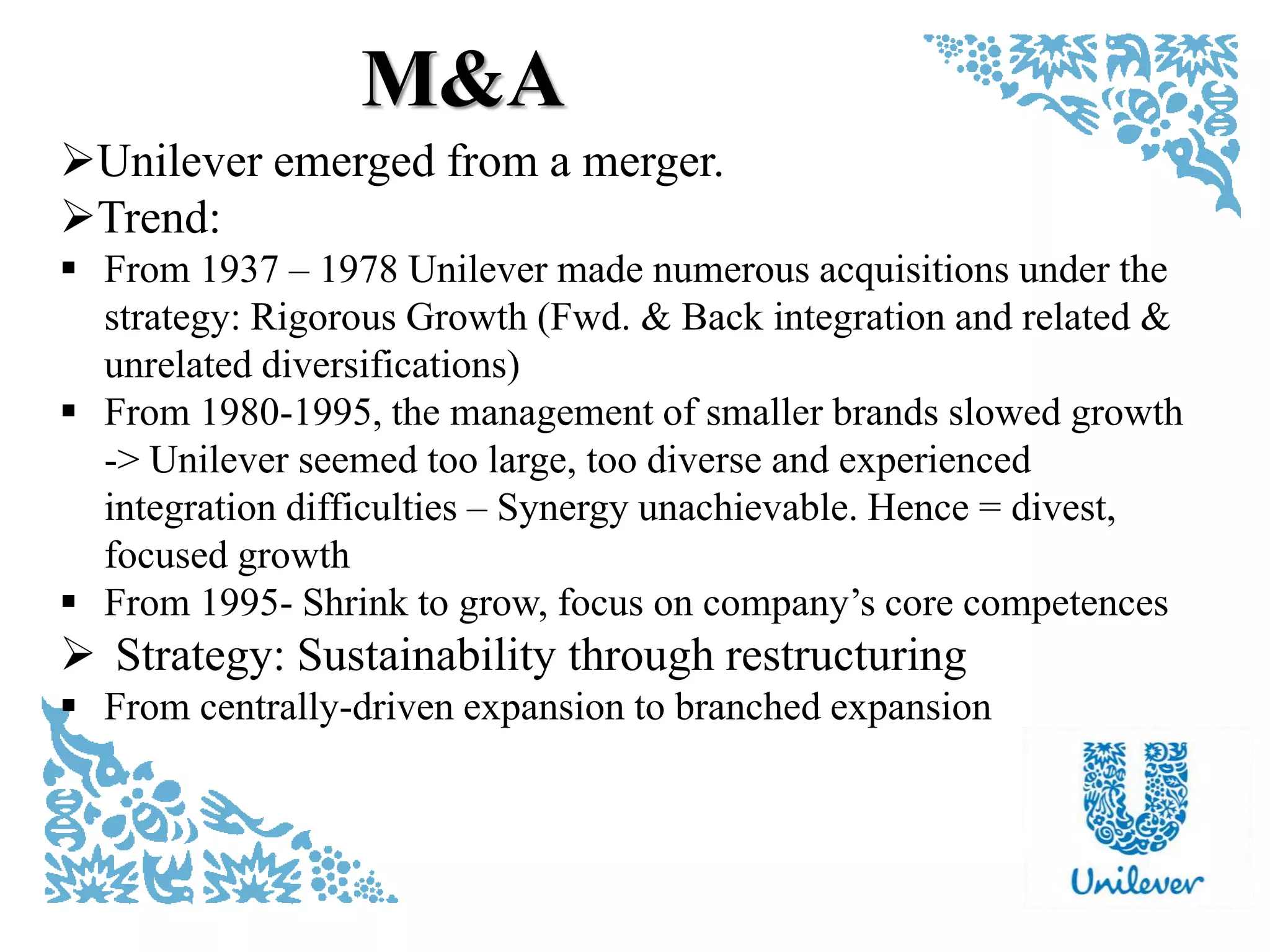
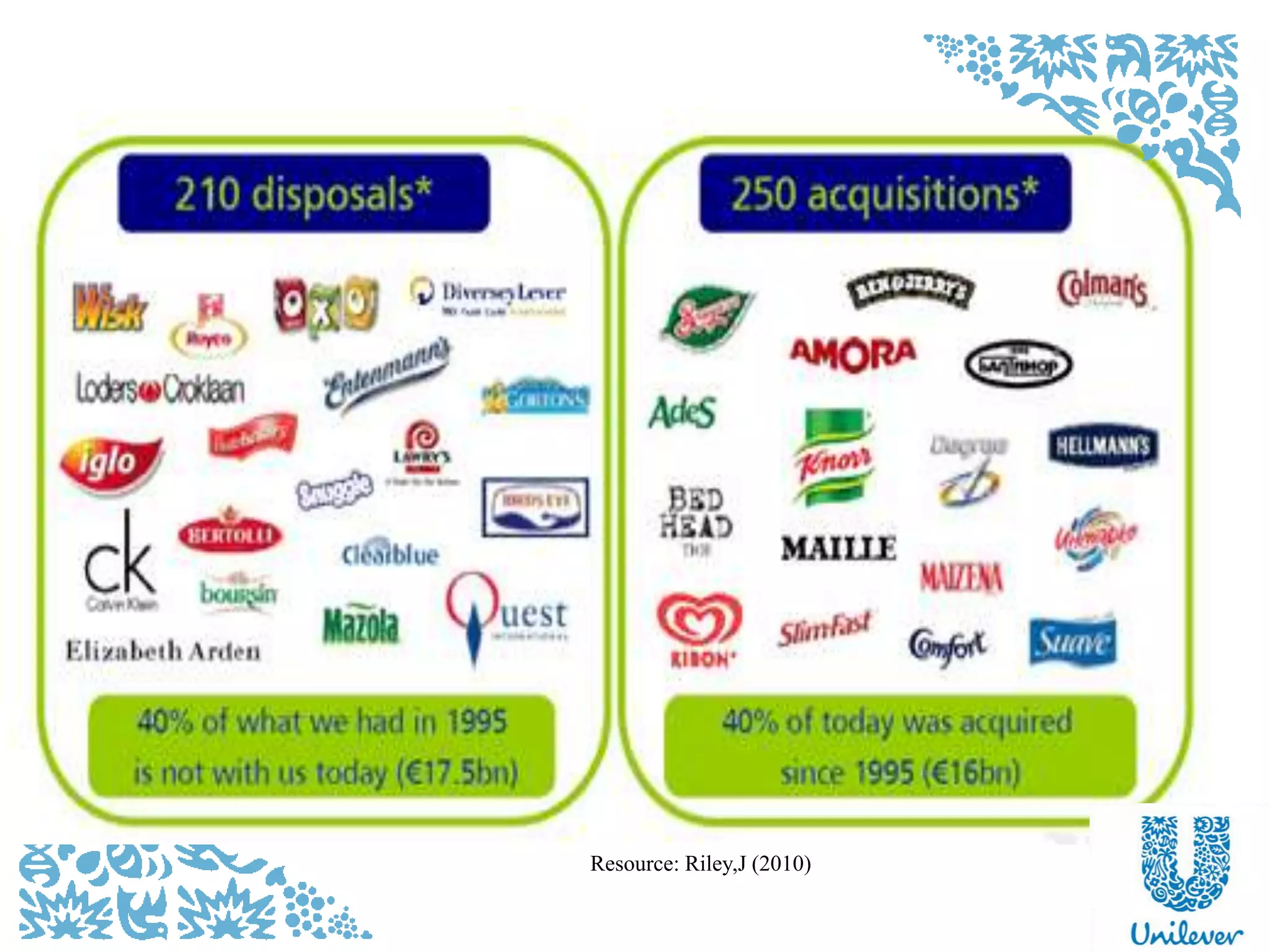
This document provides an analysis of Unilever, a multinational consumer goods company. It includes an external analysis using PEST and five forces models identifying opportunities and threats. An internal analysis uses a resource audit and stakeholder analysis to identify core competencies. The document also discusses Unilever's diversification strategy, mergers and acquisitions history, and corporate social responsibility programs like the Unilever Sustainable Living Plan. It concludes with recommendations to strengthen Unilever's brand and improve quality and local preferences while maintaining competitiveness.


















![References
Angwin, D., Cummings, S. and Smith, C. (2007) The Strategy Pathfinder: Core Concepts and Micro-cases, Oxford :
Blackwell Publishing. Library classification to be advised.
Cashian, P. (2007) Economics, Strategy and the Firm, Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan.
Johnson, G., Scholes, K., and Whittington R., (2008) Exploring Corporate Strategy, 8th Edn., Financial Times/Prentice
Hall, Harlow . Library classification 658.401 JOH.
Lynch, R. (2006) Corporate Strategy, 4th Edition,Harlow: Financial Times Prentice Hall. Library Classification
658.4012 LYN.
Stacey, R (2007) Strategic Management and Organisational Dynamics: The Challenge of Complexity, 5th edition,
Harlow : Financial Times/Prentice Hall, Library Classification 658.4012 STA
DeWit, B & Meyer, R (2004) Strategy, Process, Context and Content: An International Perspective, 3rd edition,
Thomson International Business, Library Classification
Reader, W. J. (1980) Fifty years of Unilever, 1930-1980 London:Heinemann
Unilever annual report (2012) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.com/images/ir_Unilever_AR12_tcm13-348376.pdf >
[27 Feb 2014]
Figures &business facts (2014) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.com/aboutus/introductiontounilever/unileverataglance/index.aspx> [27 Feb 2014]
Unilever mission (2014) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.com/aboutus/introductiontounilever/ourmission/> [27 Feb 2014]
Supply management (2013) Unilever named best supply chain in Europe [online] available from
<http://www.supplymanagement.com/news/2013/unilever-named-best-supply-chain-in-europe> [27 Feb 2014]
Value Chain picture [online] available from
<http://www.smartersolutions.com/blog/forrestbreyfogle/wp-content/uploads/2010/07/Michael-Porters-Value-Chain-
Cc984967_BusDrivenEvalofDistComp02en-usMSDN_10.jpg > [27 Feb 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m26unileverpresentation-140506161512-phpapp02/75/M26-unilever-presentation-29-2048.jpg)
![References
Unilever HR management (2013) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.co.uk/Images/6550_Unilever_MBY_6pp_HR_tcm28-365478.pdf > [28 Feb 2014]
Unilever innovation (2014) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.co.uk/innovation/> [28 Feb 2014]
Unilever procurement (2014) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.com/aboutus/supplier/unileverprocurement/> [28 Feb 2014]
Distribution &transport (2014) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.com/sustainable-living/greenhousegases/transport/> [28 Feb 2014]
Unilever & PepsiCo to expand ready-to-drink tea joint venture (2007) [online] available from
<http://www.unilever.com/mediacentre/pressreleases/2007/UnileverPepsicotoexpand.aspx> [27 Feb 2014]
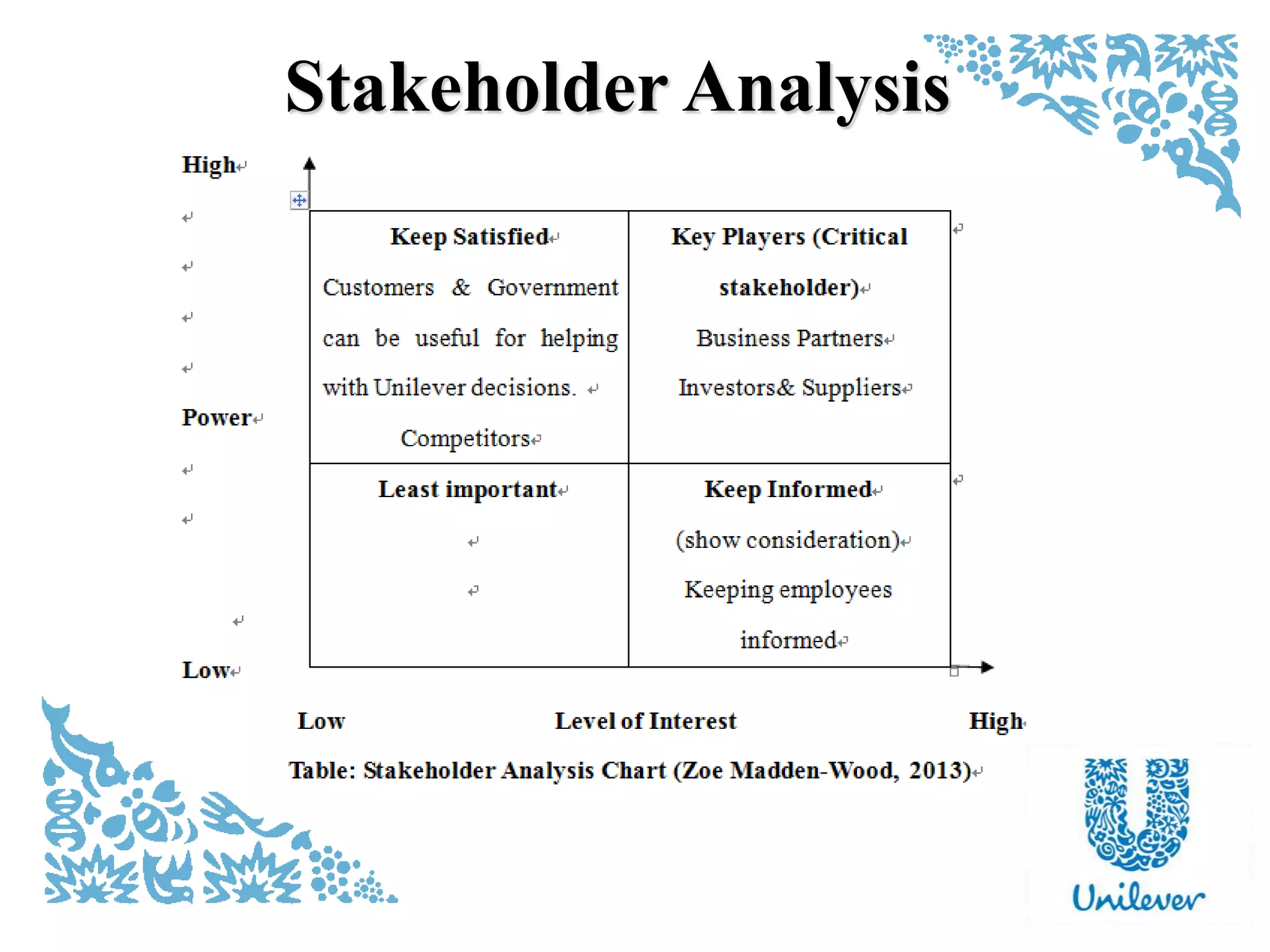
Stakeholder analysis map
http://leadershiplearning.org/blog/zoe-madden-wood/2013-01-29/project-management-starting-your-project-change
The World Bank. (2007) „Tools for institutional political, and social analysis of policy reform‟. Journal of writing studies
[online], 125-126. Available from
<http://books.google.com.hk/books?id=gZWncS4cd4gC&pg=PA126&dq=stakeholder+analysis&hl=zh-
CN&sa=X&ei=vKsQU9ilCcmshQfoz4GgDQ&ved=0CEYQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=stakeholder%20analysis&f=true
> [28 Feb 2014]
Our suppliers (2014) [online] available from<http://www.unilever.com/aboutus/supplier/> [28 Feb 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m26unileverpresentation-140506161512-phpapp02/75/M26-unilever-presentation-30-2048.jpg)
