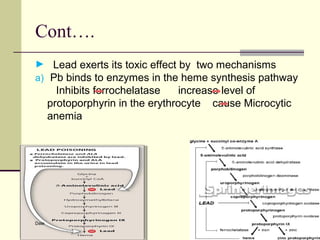
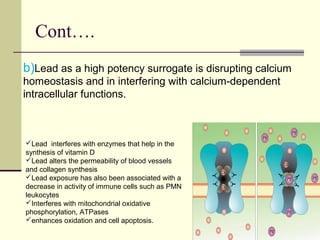
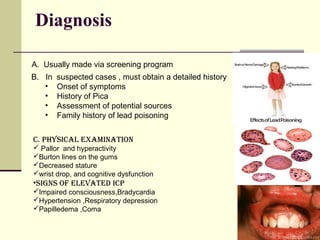
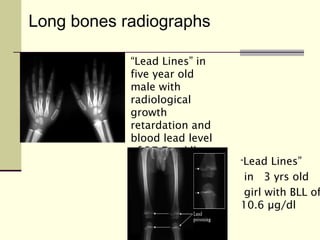
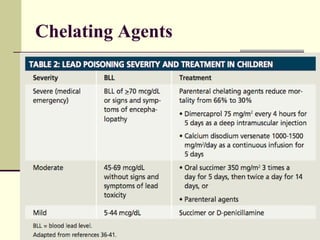
Lead is a toxic heavy metal that can cause lead poisoning when levels become elevated in the body. Lead poisoning was common historically from sources like lead paint and gasoline, and it still impacts an estimated 500,000 children in the US. Symptoms range from vague issues to encephalopathy and death. Diagnosis is made via blood lead level testing. Treatment focuses on chelation therapy, prevention of further exposure, and supportive care, though long-term effects can be permanent. While efforts have reduced exposure, lead poisoning remains an important public health issue.