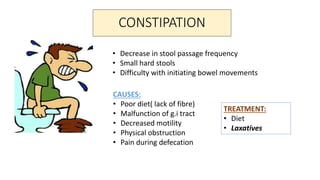
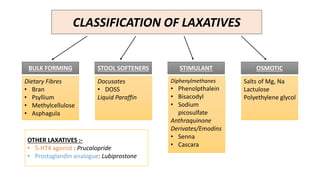
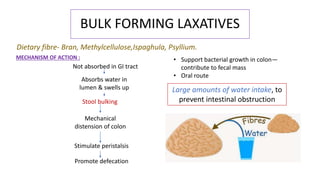
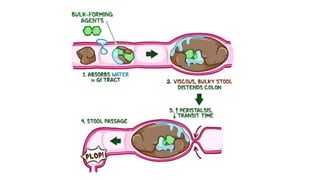
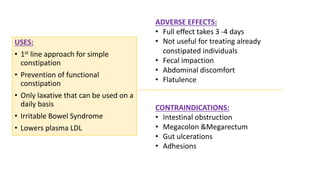
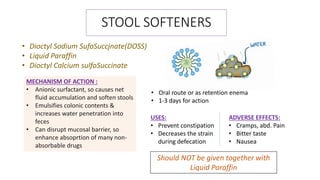
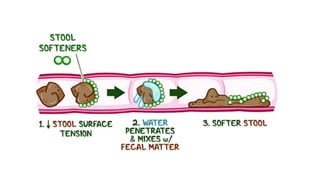
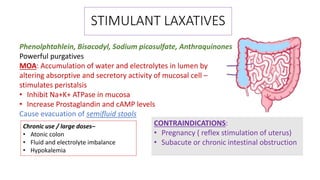
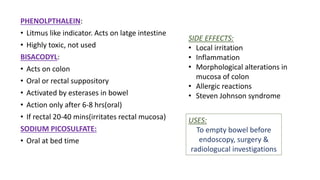
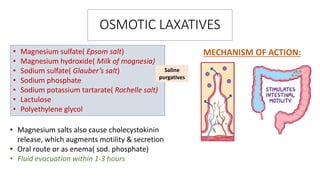
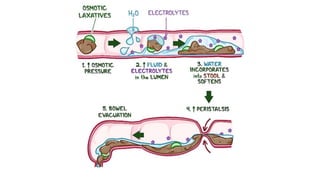
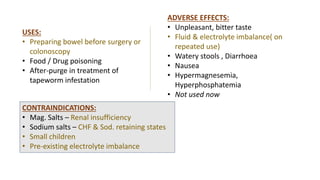
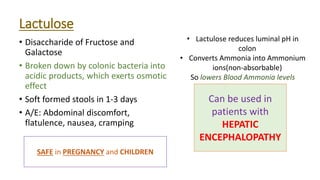
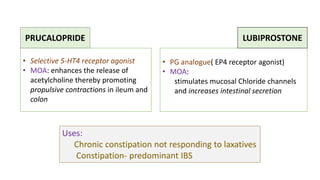
This document discusses different types of laxatives used to treat constipation. It describes bulk forming laxatives like bran and psyllium that work by adding bulk to stool. Stool softeners like docusate sodium work by emulsifying stool. Stimulant laxatives like bisacodyl and senna work by increasing intestinal secretions and peristalsis. Osmotic laxatives like magnesium hydroxide and lactulose work by drawing water into the intestines. The document provides details on the mechanism of action, uses, and side effects of various laxatives to help guide appropriate treatment of constipation.