This document provides an overview of programming languages by discussing:
1) The different types of programs and how programming languages communicate instructions to computers.
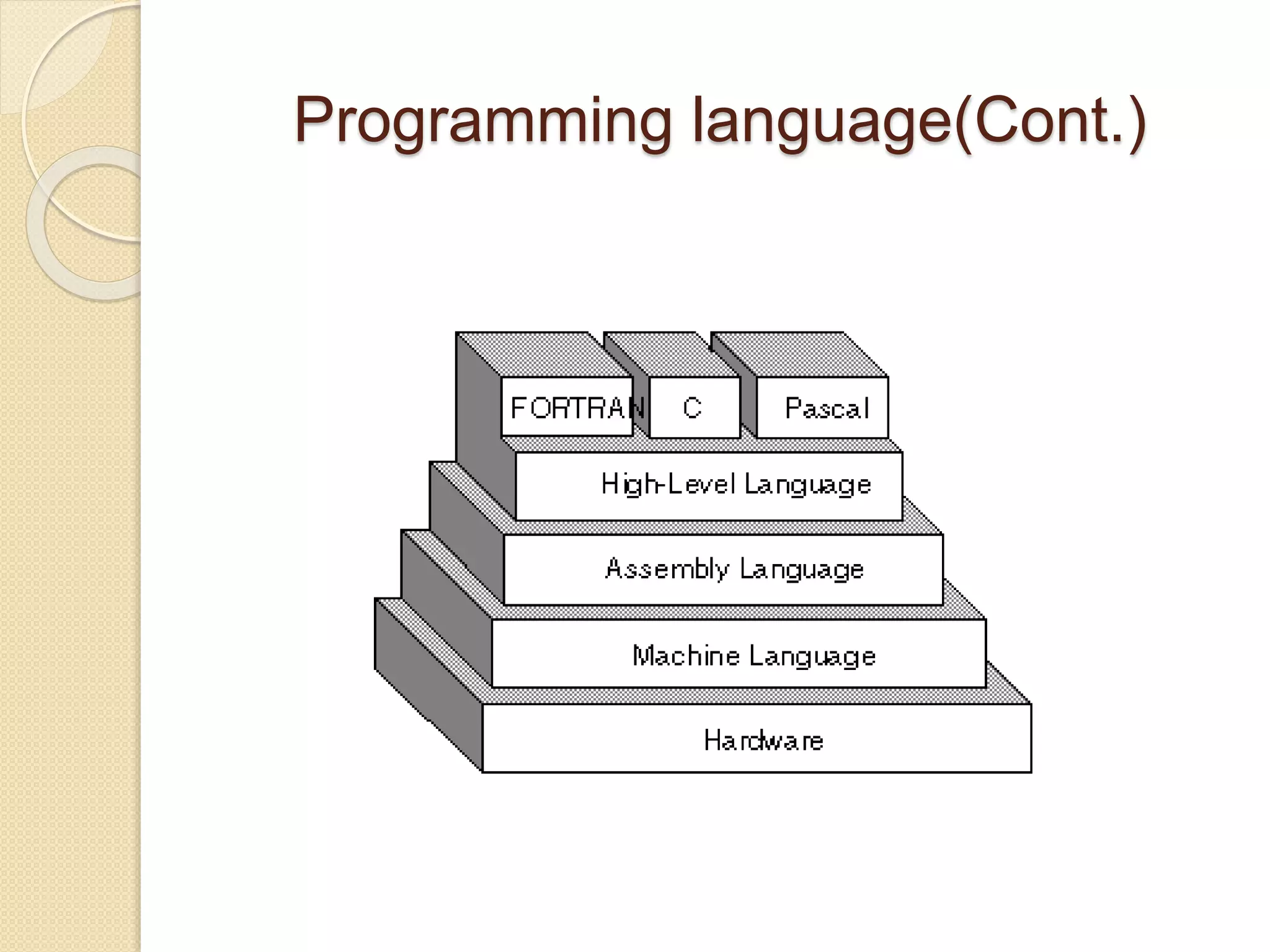
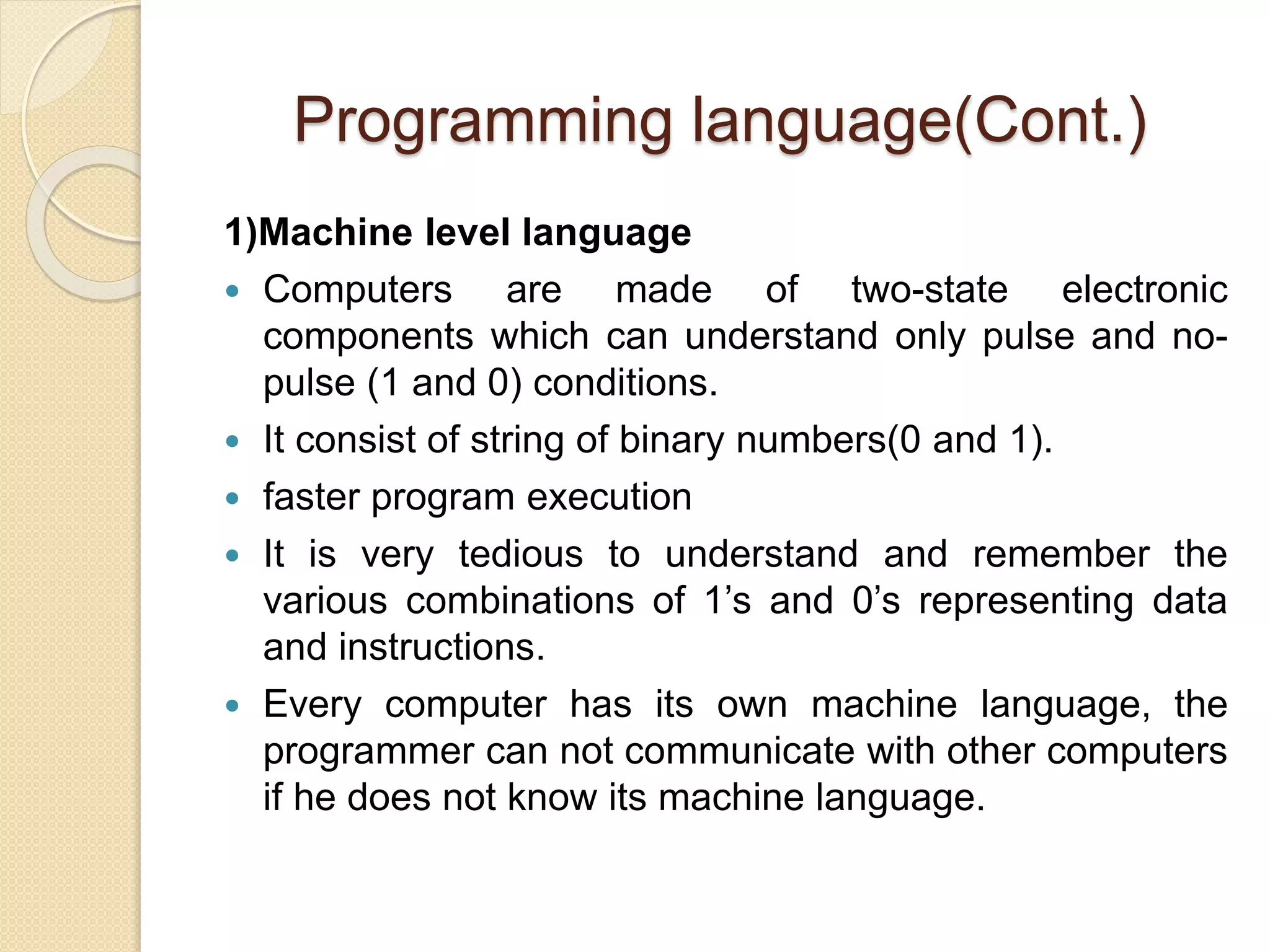
2) The levels of programming languages from machine language to assembly language to high-level languages.
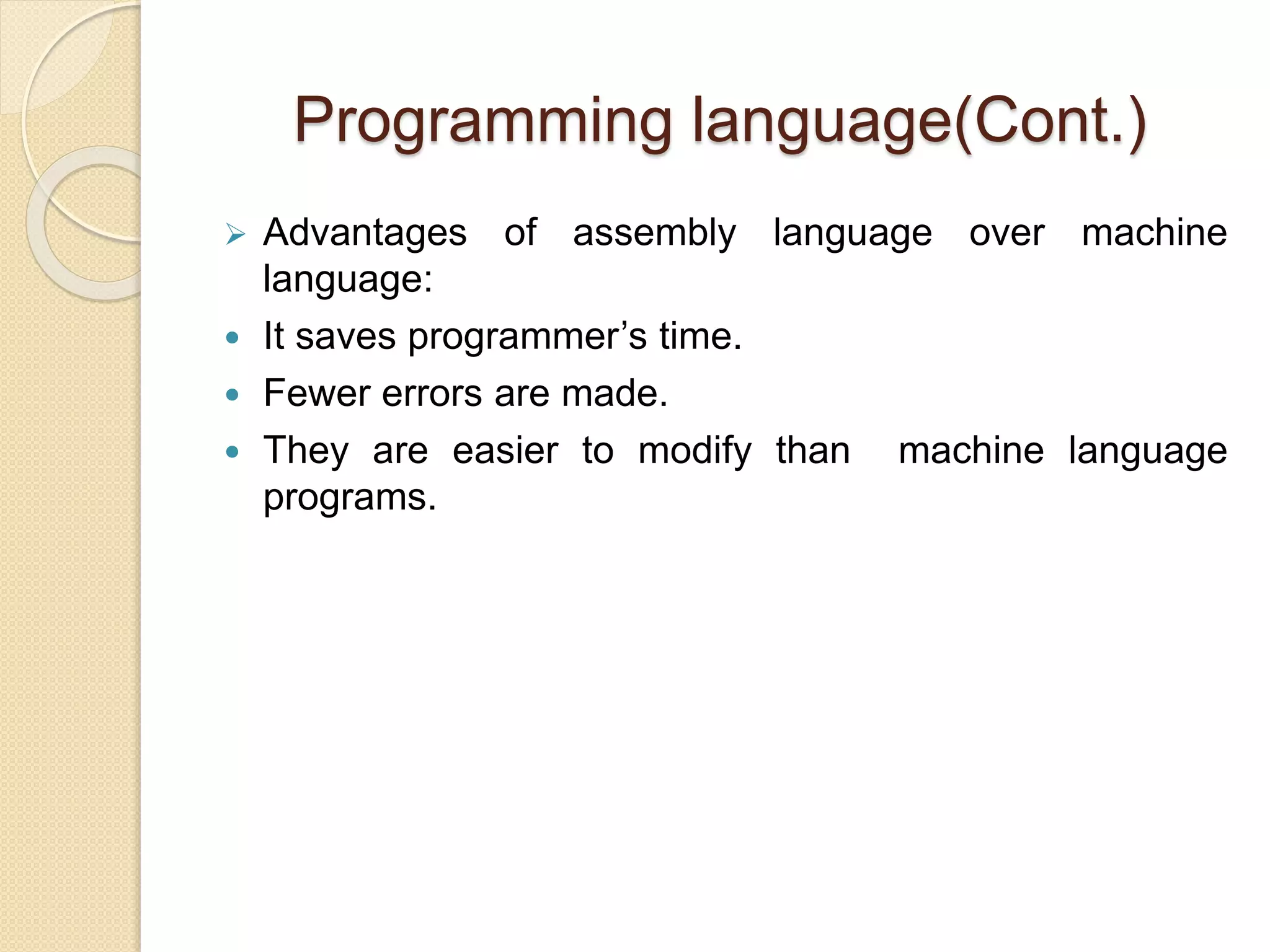
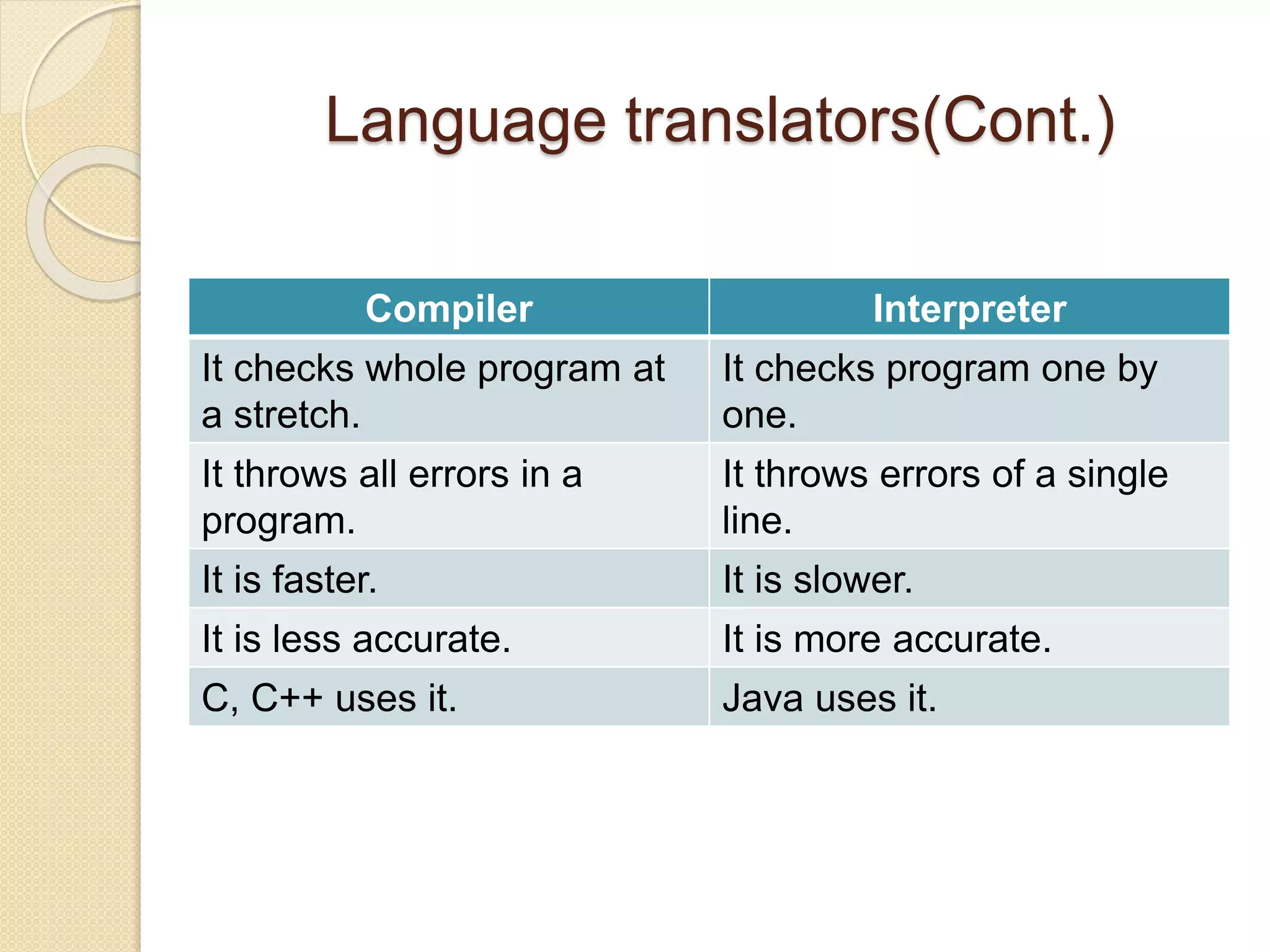
3) The advantages and disadvantages of each language level as well as how language translators like compilers and interpreters work.