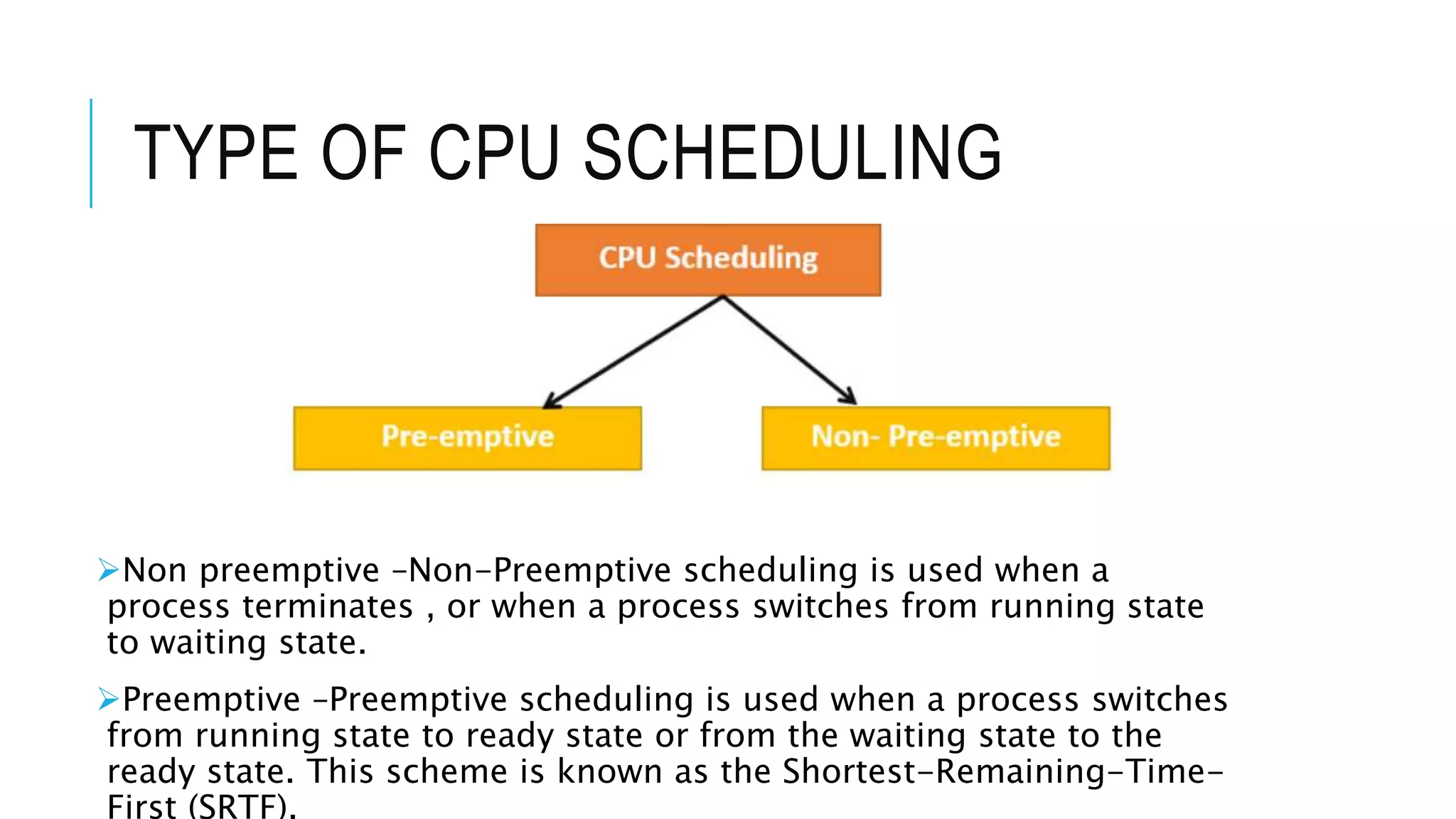
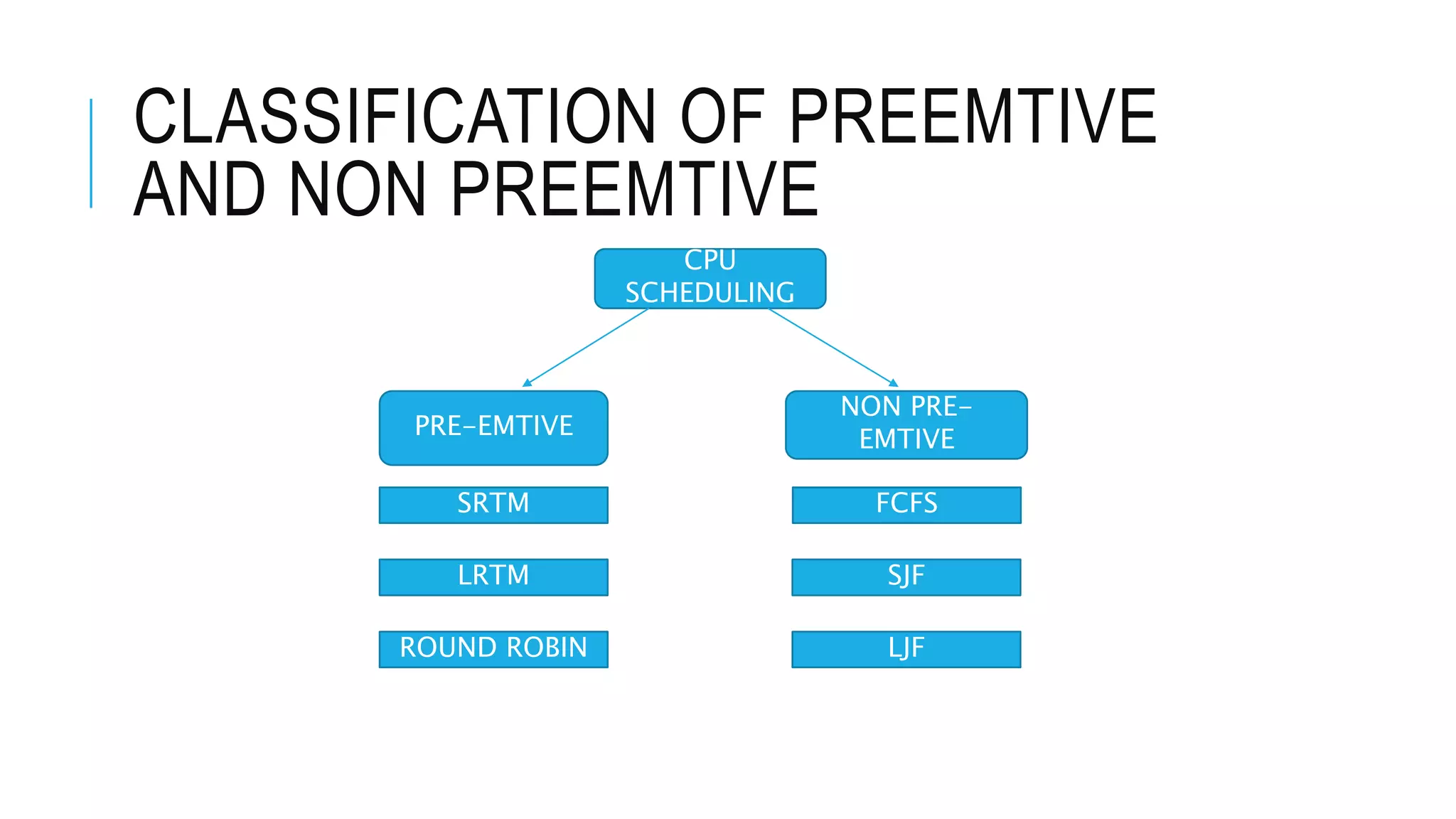
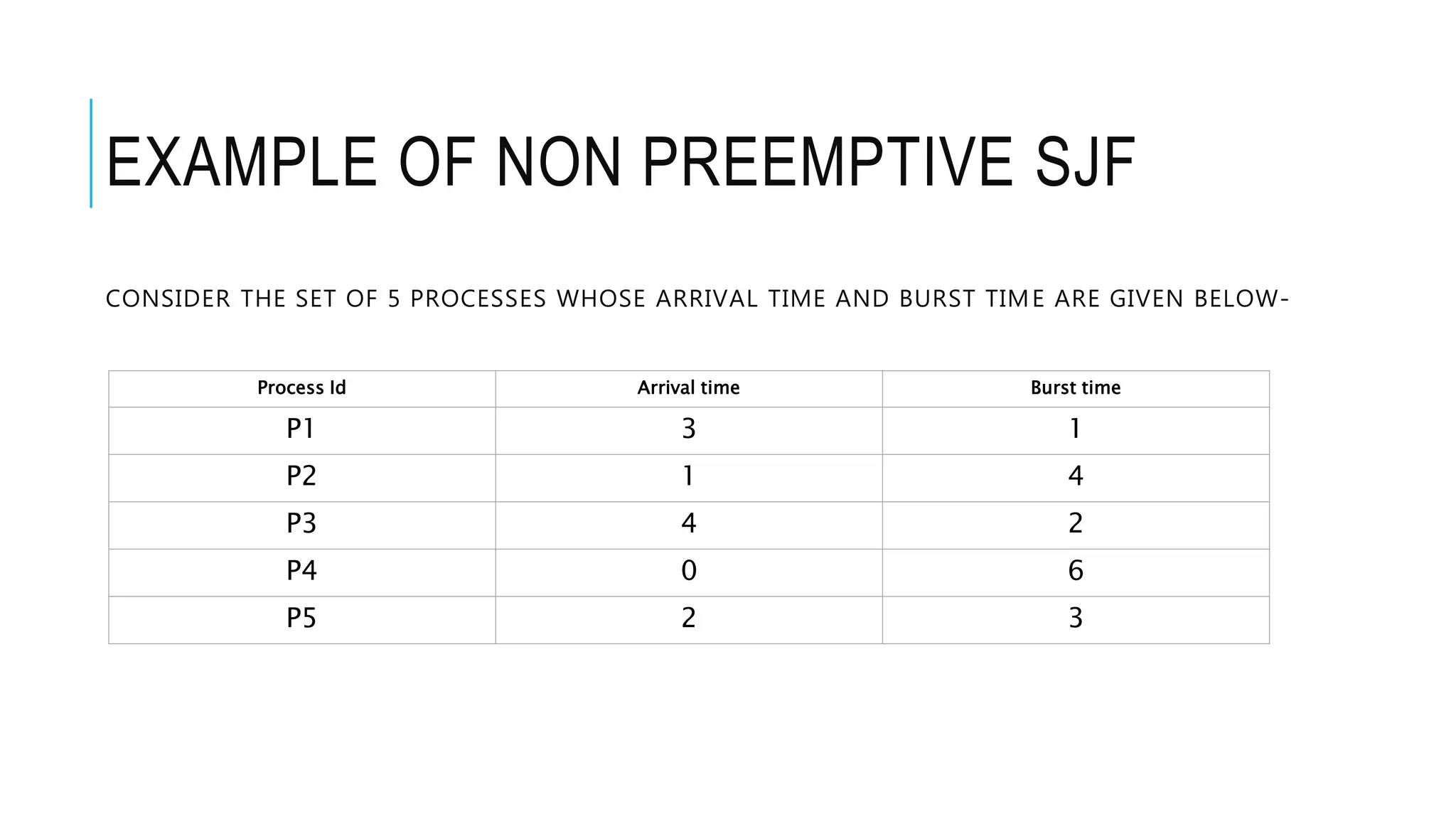
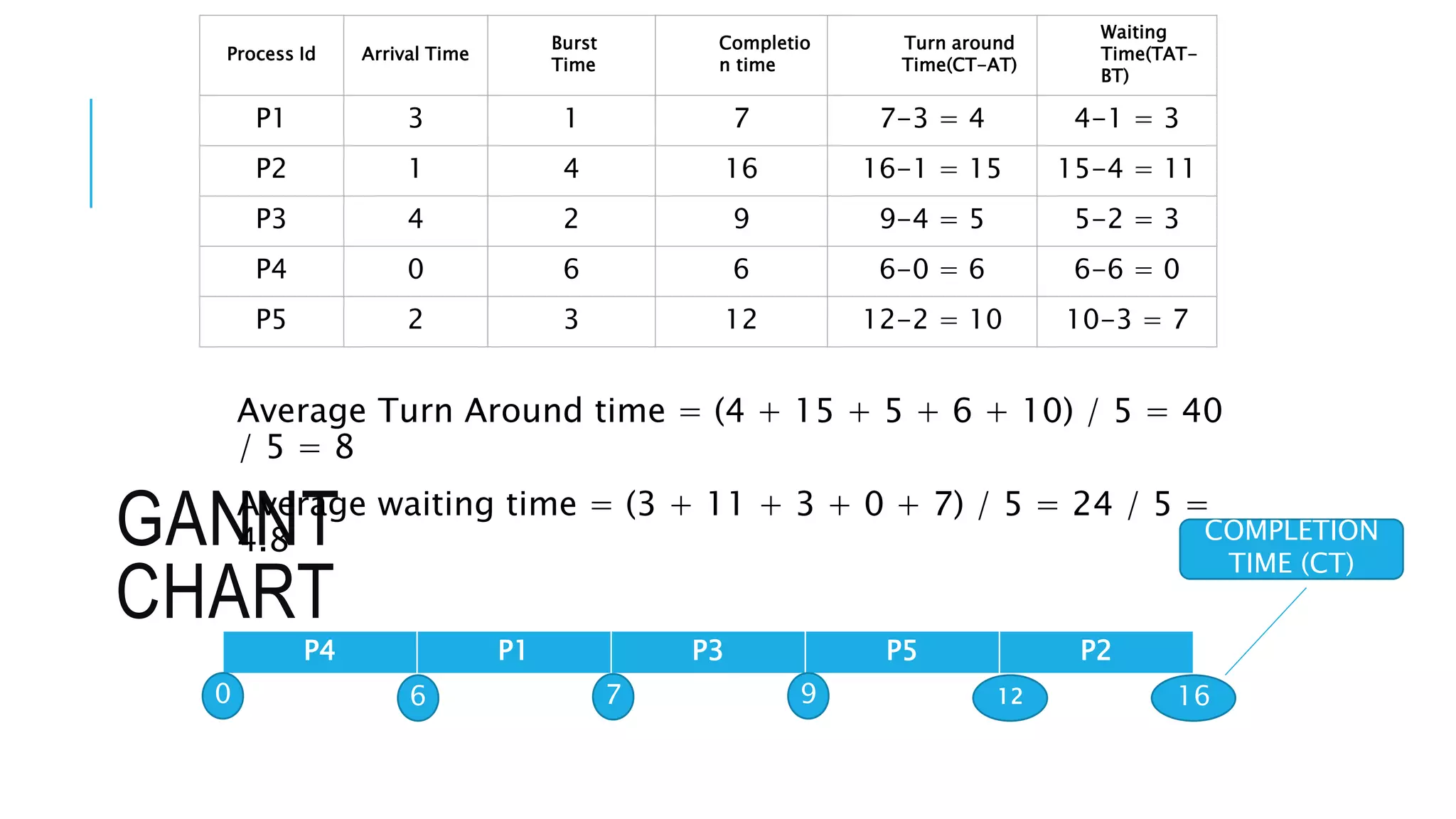
The document discusses the Shortest Job First (SJF) CPU scheduling algorithm. SJF is a preemptive scheduling policy that selects the waiting process with the shortest execution time/burst time to execute next. The algorithm involves sorting processes by arrival time and selecting the process with the shortest burst time. An example shows the Gantt chart and calculations for average turnaround time and waiting time using SJF. Advantages include shorter jobs being favored and minimum average waiting time, while disadvantages are potential starvation of longer jobs and inability for short-term CPU scheduling.