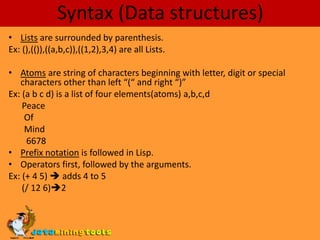
Lisp was invented in 1958 by John McCarthy and was one of the earliest high-level programming languages. It has a distinctive prefix notation and uses s-expressions to represent code as nested lists. Lisp features include built-in support for lists, dynamic typing, and an interactive development environment. It was closely tied to early AI research and used in systems like SHRDLU. Lisp allows programs to treat code as data through homoiconicity and features like lambdas, conses, and list processing functions make it good for symbolic and functional programming.