The document details a webinar on language development for teachers, presented by Marisa Constantinides. It covers topics such as classroom instruction, discourse analysis, and effective feedback techniques, emphasizing the importance of language accuracy and appropriateness in teaching. Additionally, it includes tasks and examples for analyzing teacher-student interactions and highlights the relevance of using various teaching materials.





![Classroom Discourse Task 1
Look at the transcript of a transaction on the next page [from Papaefthymiou-
Lytra S (1990), Explorations in Foreign Language Classroom Discourse] and decide
how you would divide it into exchanges, moves, and acts.
T: Can you guess/think of one reason why doesn’t he like city-life?
L: Because the city is with many θορύβους
T: There is too much noise or too many noise?
Ls: Much noise.
T: Much noise.
L: City have a lot of buildings.
T: Cities have a lot of buildings.
Big buildings.
L: There are much cars/many cars.
They are ugly.
T: There are many cars.
L: And they must work.
T: They must work.
People in villages work even more.
L: All the city people are in a hurry.
T: Yes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ldt1-111116124552-phpapp01/85/LANGUAGE-DEVELOPMENT-FOR-TEACHERS-LDT-7-320.jpg)
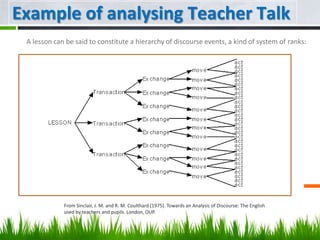
![Classroom Discourse Task 2
Look at the definitions below [from Sinclair and Coulthard (1975), Towards an
Analysis of Discourse] and label the transcript in the previous task
accordingly.
A transaction typically consists of an initial boundary exchange followed by a series of
teaching exchanges.
A boundary exchange consists of a move which marks a boundary between larger stages
in the discourse (frame) and a move which indicates which direction the lesson is likely to
proceed in (focus).
A teaching exchange characteristically consists of an initiating move followed by a
responding move or moves. the typical teaching exchange consists of Initiation (by the
teacher), Response (by the learner) and Feedback (by the teacher).
More specifically, teaching exchanges may belong to one of the following categories:
teacher elicit [IRF], teacher direct [IR(F), where R is a nonverbal action], teacher inform
[I(R)], checking [IR(F), where I represents a genuine teacher question, ie, one to which
the teacher does not know the answer], pupil elicit [IR, where I is performed by the
pupil] and pupil inform [IF, where I is performed by the pupil]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ldt1-111116124552-phpapp01/85/LANGUAGE-DEVELOPMENT-FOR-TEACHERS-LDT-8-320.jpg)
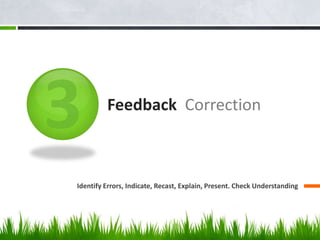
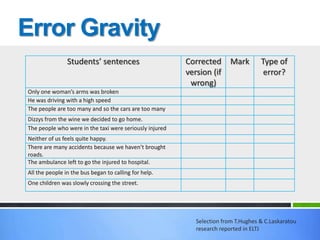







![WRITING -----Original Message-----
From: Khalid Shammad
[mailto:kshammad@hotmail.com]
Sent: Thursday, May 17, 2001 11:08 PM
To: celt@celt.edu.gr
Subject: drama disertations
I'm interested in applying dramatic
techniques in teaching English in my
country, so I want you to provide me
with some abstracts of studies related to
this subject in order to conduct a study
about using drama in
our schools.
Thank You
I did not reply to this letter as I felt it was too
demanding/aggressive. Can you rewrite it so it
becomes more likely the writer will get a response?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ldt1-111116124552-phpapp01/85/LANGUAGE-DEVELOPMENT-FOR-TEACHERS-LDT-18-320.jpg)










