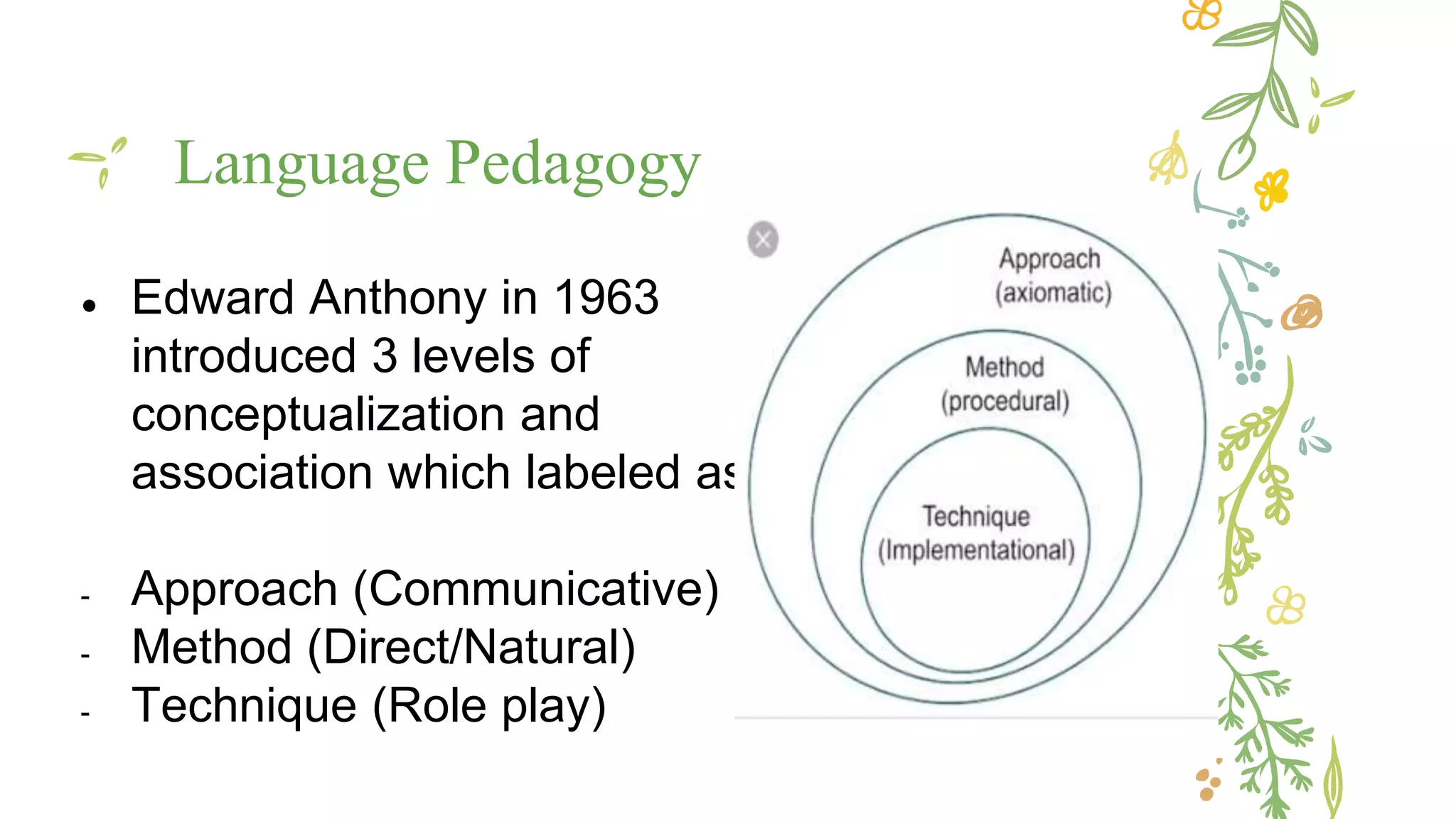
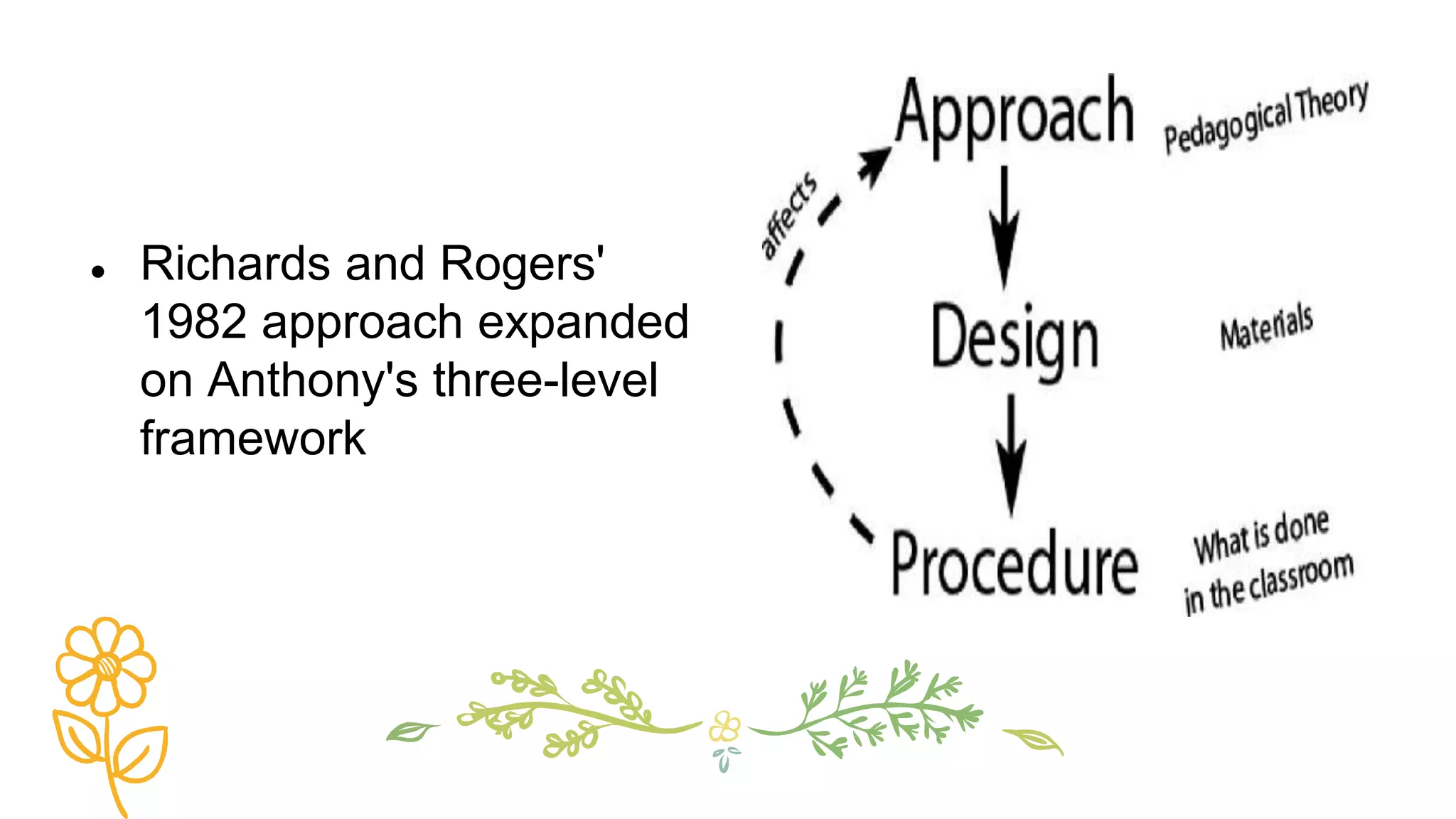
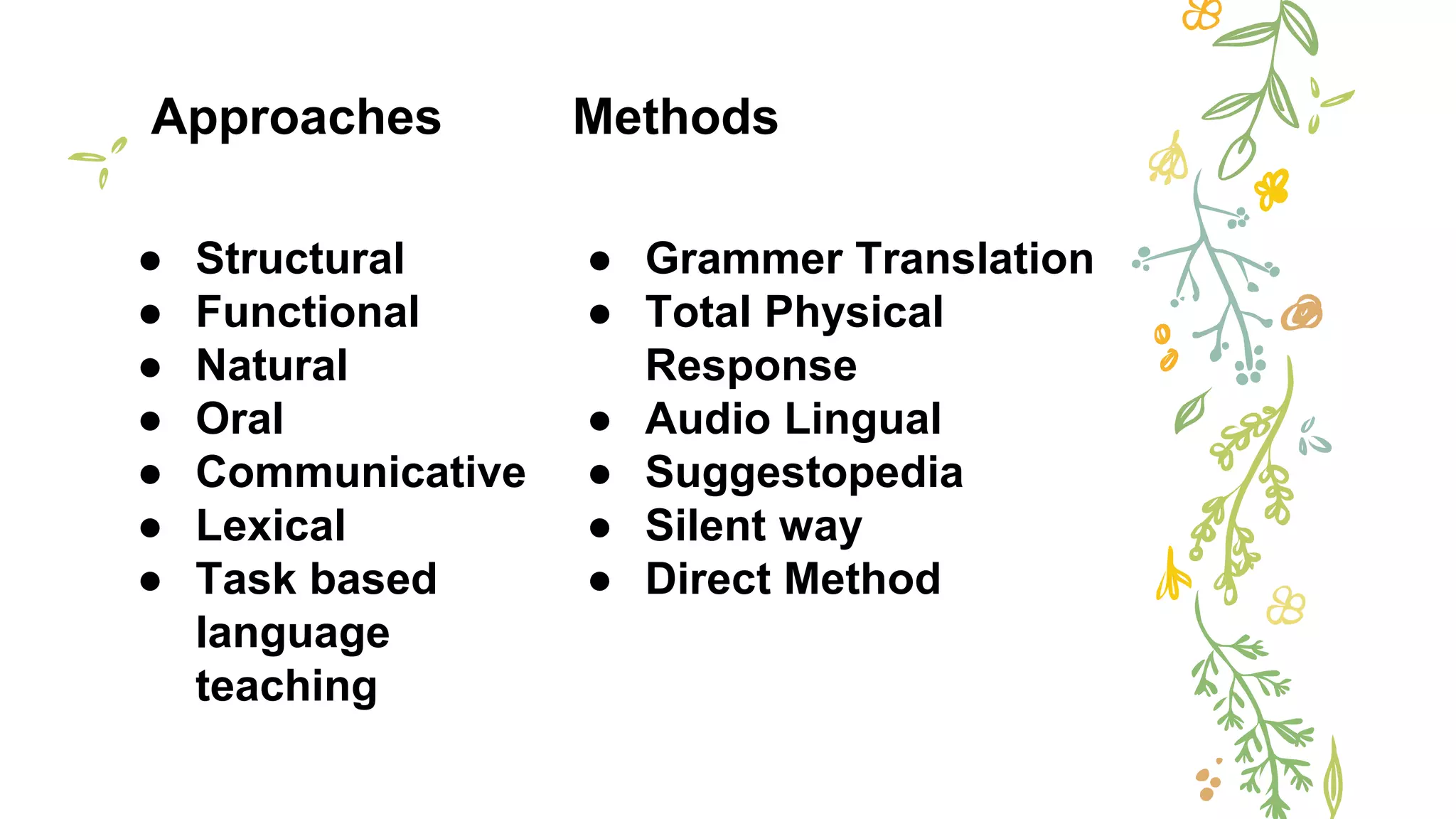
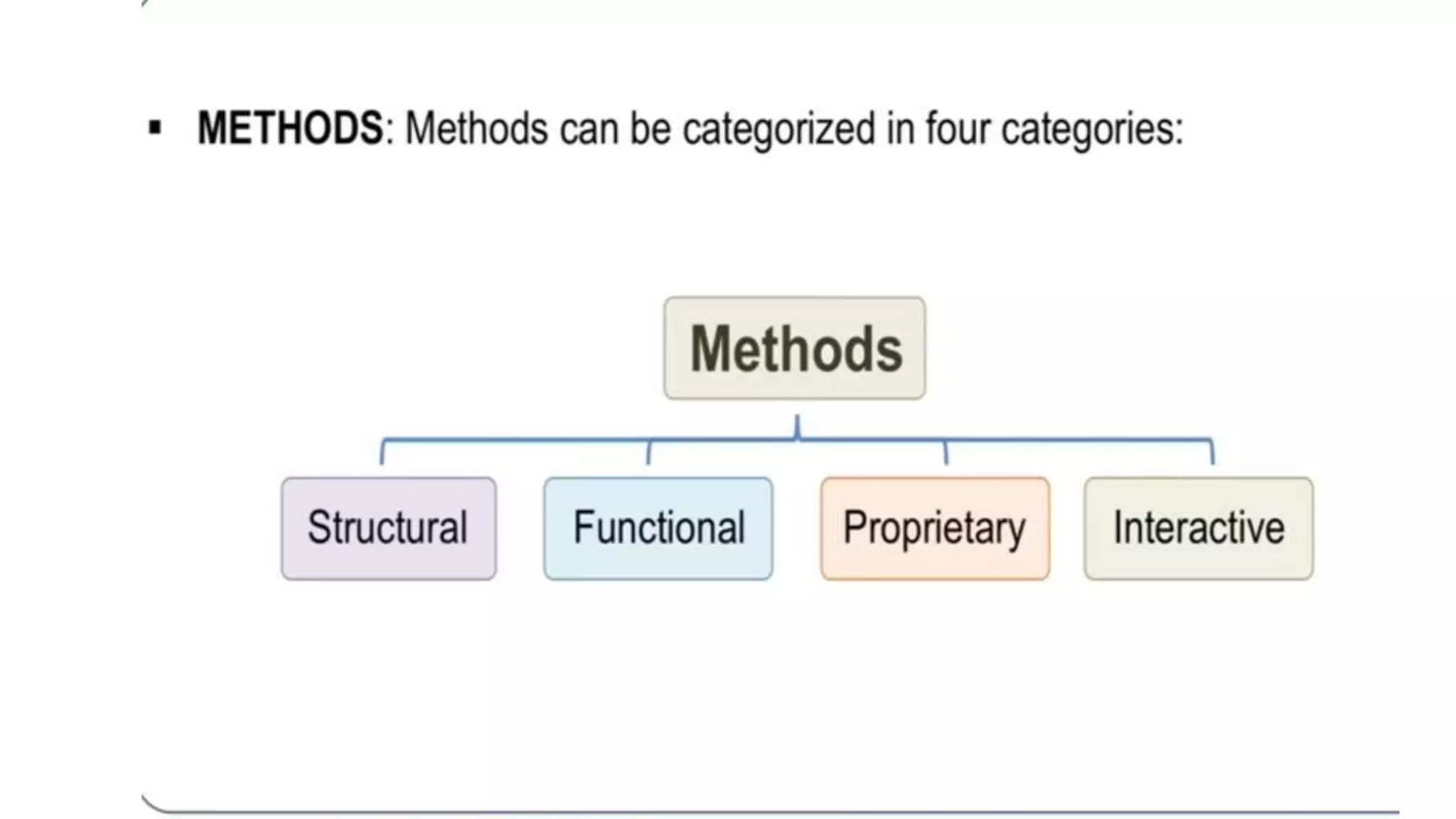
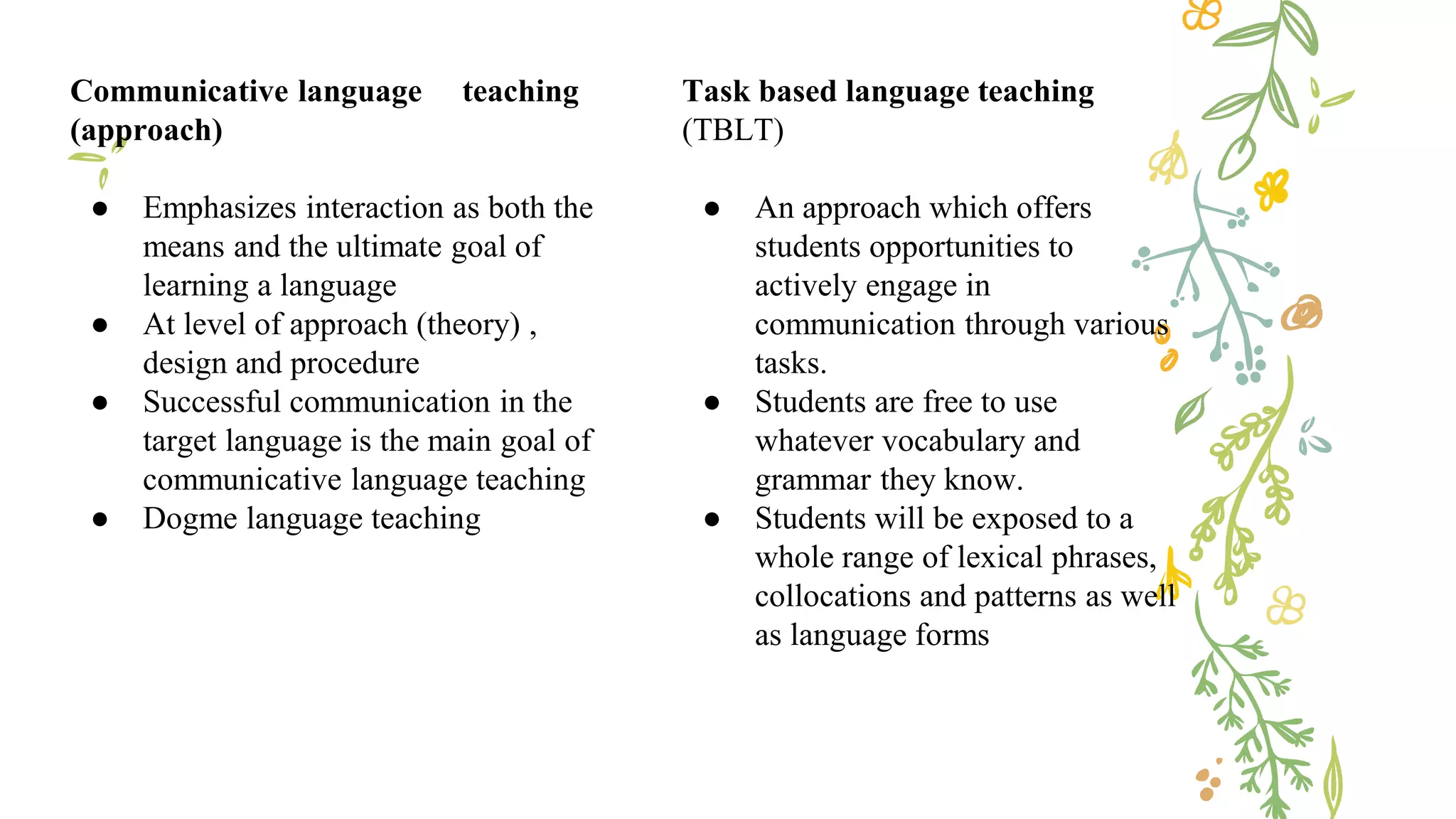
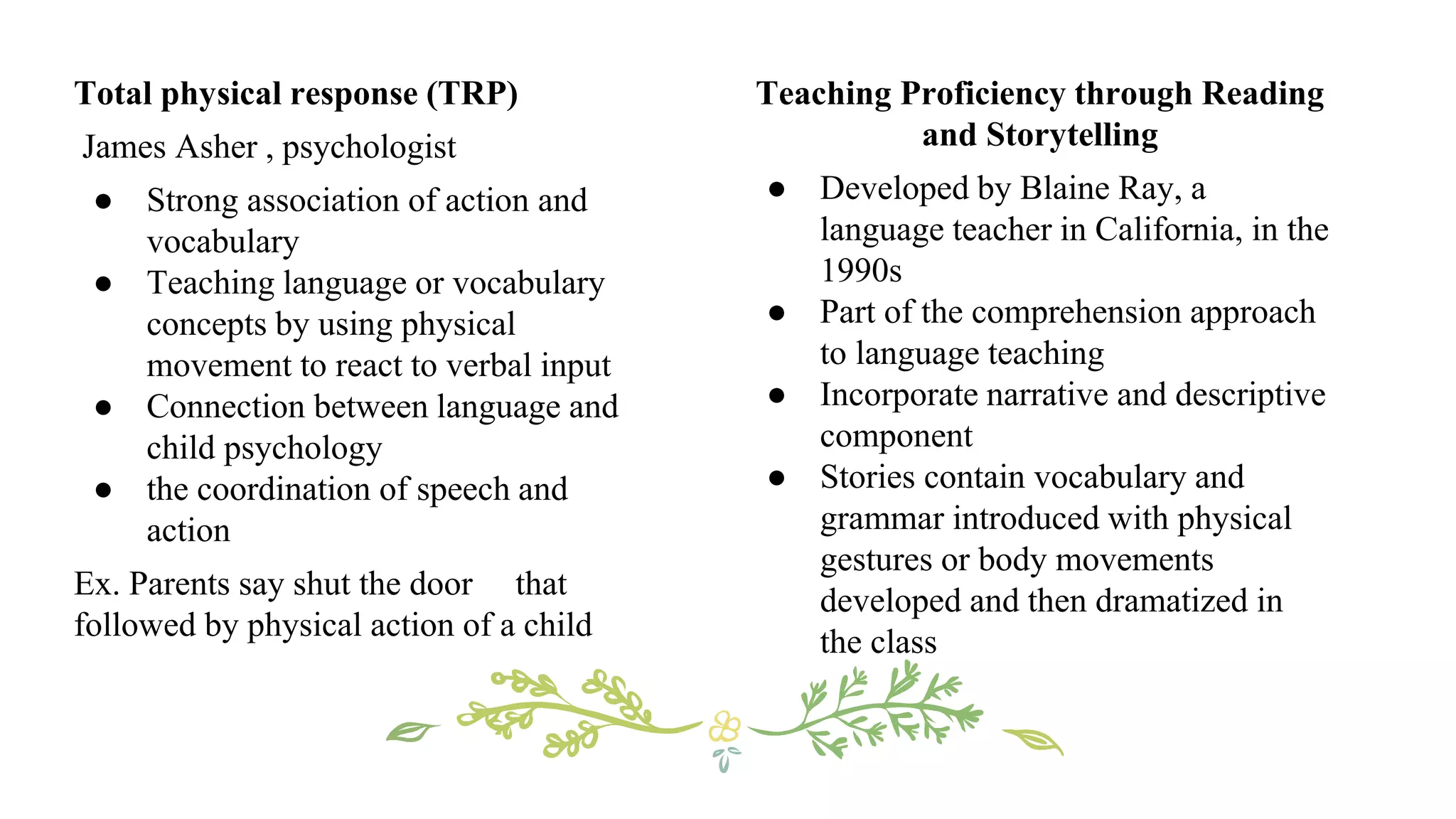
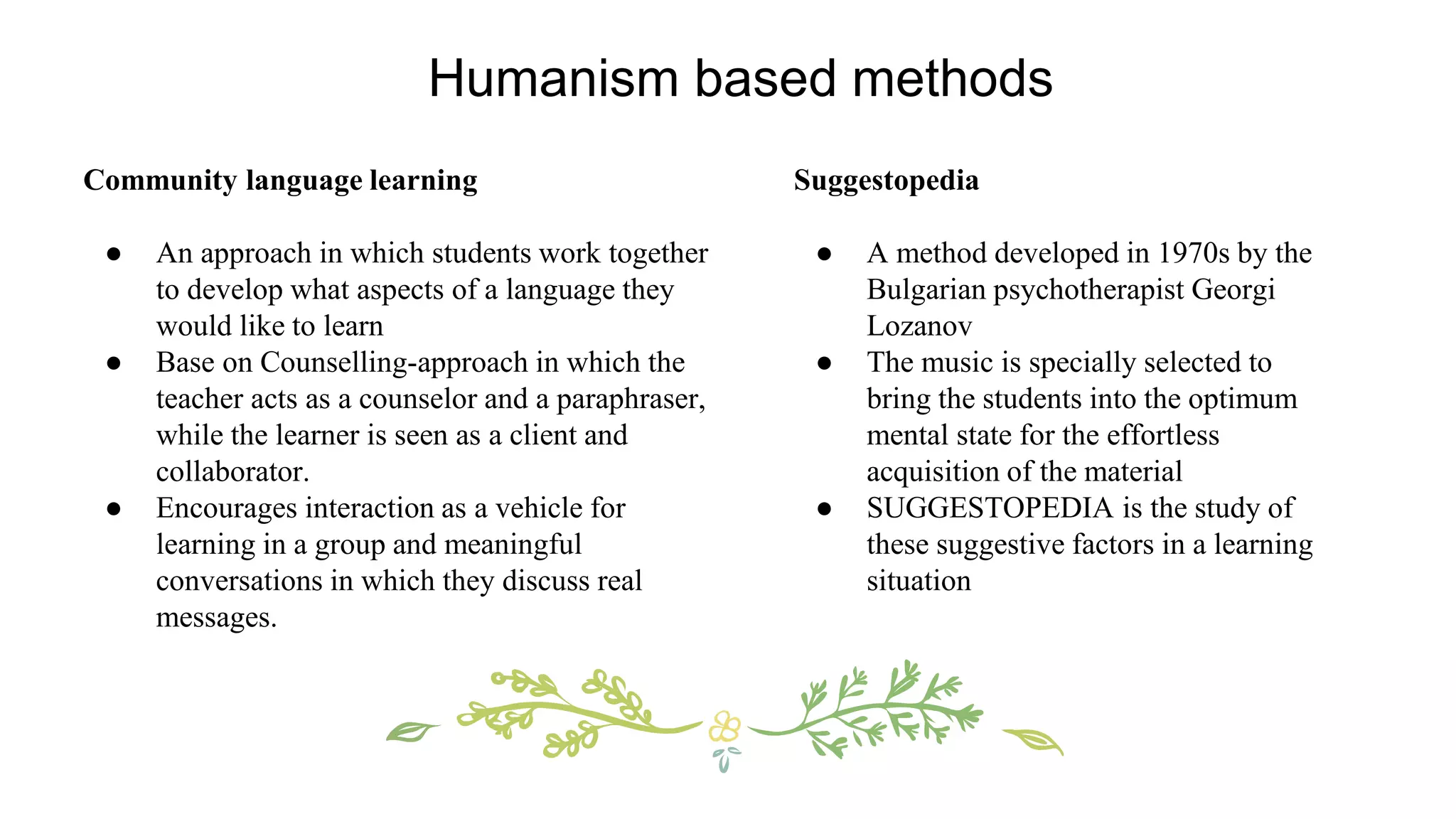
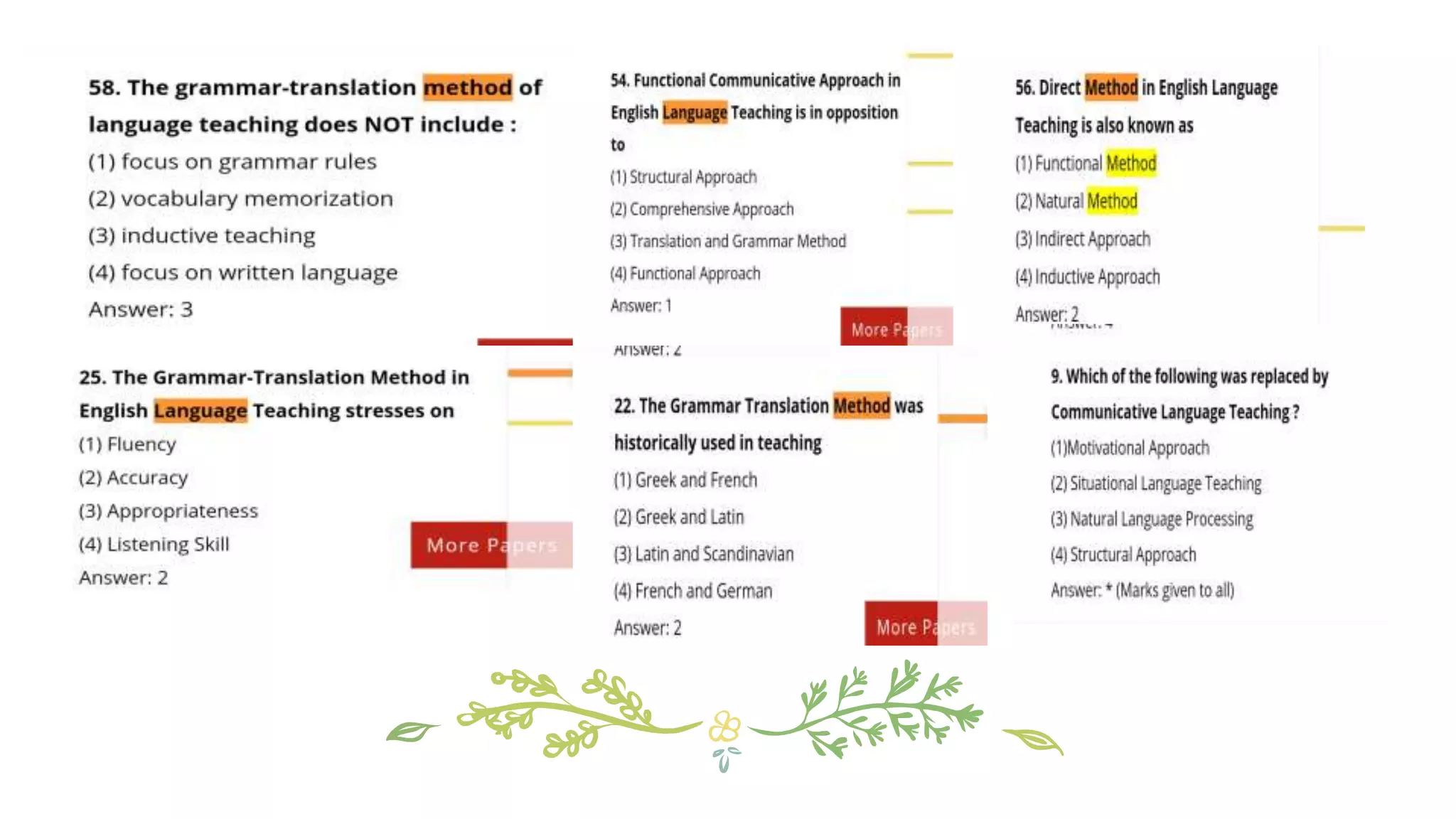
This document discusses various concepts, theories, and approaches related to English language teaching pedagogy. It begins by outlining how English functions as a global lingua franca and is learned as a native, second, or foreign language. Key language concepts like register, dialect, and idiolect are also defined. Theories of language acquisition from behaviorism to constructivism are then summarized. The document proceeds to explain influential frameworks for conceptualizing language pedagogy, from Anthony's three-level model to the structural, functional, and interactive views of language. Finally, specific teaching methods are outlined, such as audiolingualism, the direct method, and communicative language teaching.