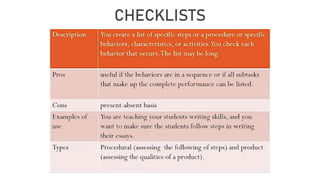
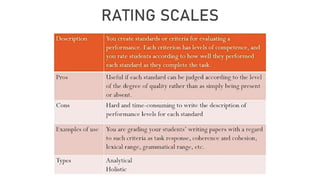
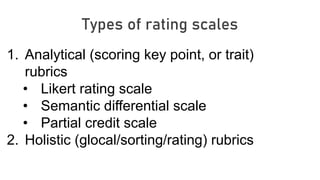
This document provides guidance on scoring performance-based assessments. It discusses different types of instruments that can be used to record student performance, including anecdotal records, behavior tallies, checklists, and rating scales. It focuses on rating scales, distinguishing between analytical and holistic rubrics. Analytical rubrics score different criteria or traits separately while holistic rubrics provide an overall score. The document provides examples and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. It also outlines features of good scoring instruments and common errors to avoid in scoring performance-based assessments.










![More vs less useful scales
• Irrelevant indicators/criteria and descriptors
• Over-lengthened: Too many criteria or descriptors/levels
• Immeasurable descriptors
• Task specific
• Excessively general/ambiguous adjectives [good, bad, average]
• Dysfunctional/untypical
descriptors/criteria/standards/categories for the students
• Student-unfriendly: jargons and technical words
• Double barrel criteria: 2 in 1
• Double negative descriptors
• Descriptors of what students cannot do](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module7-200722165254/85/Language-Assessment-Module-7-17-320.jpg)