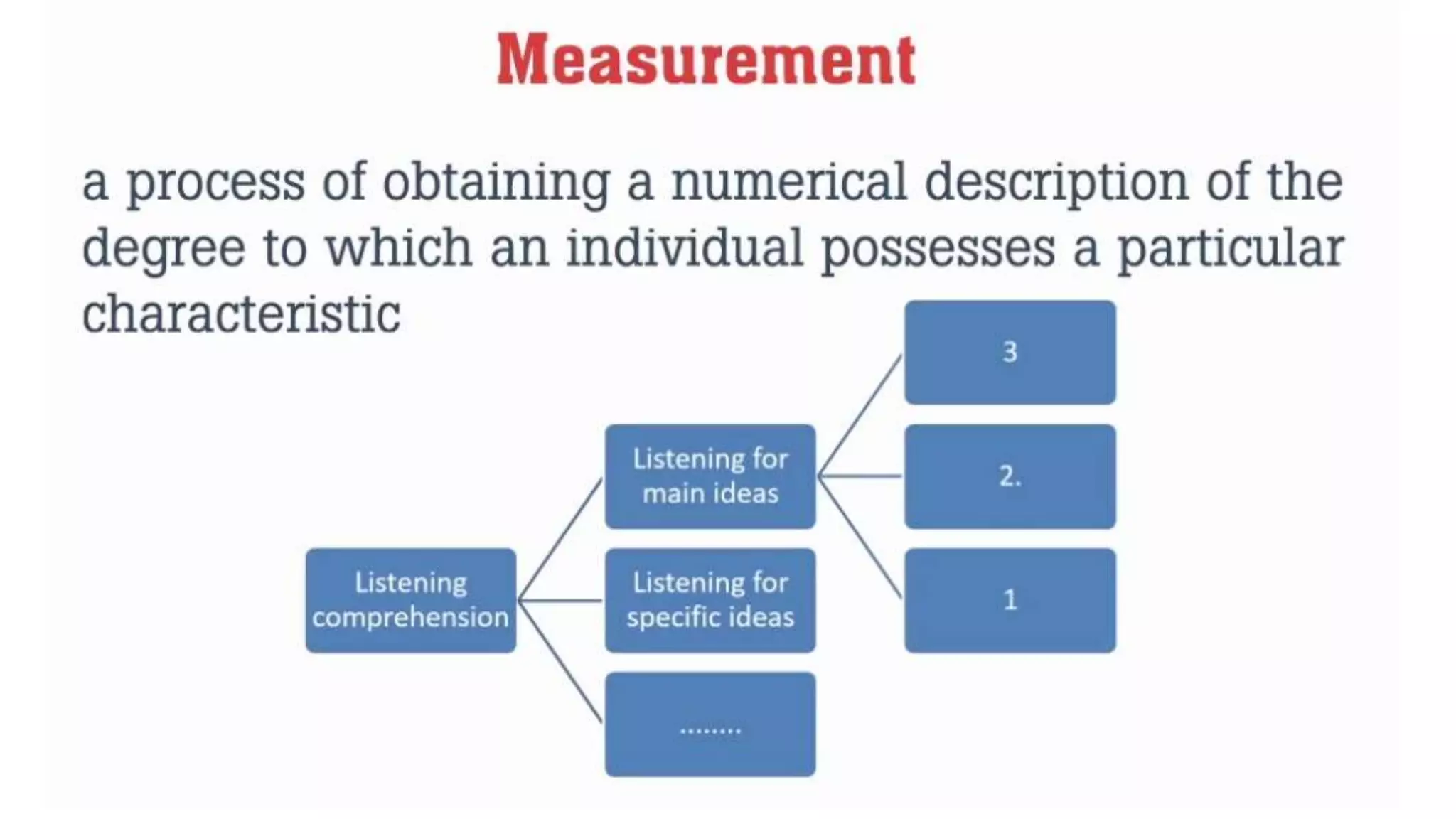
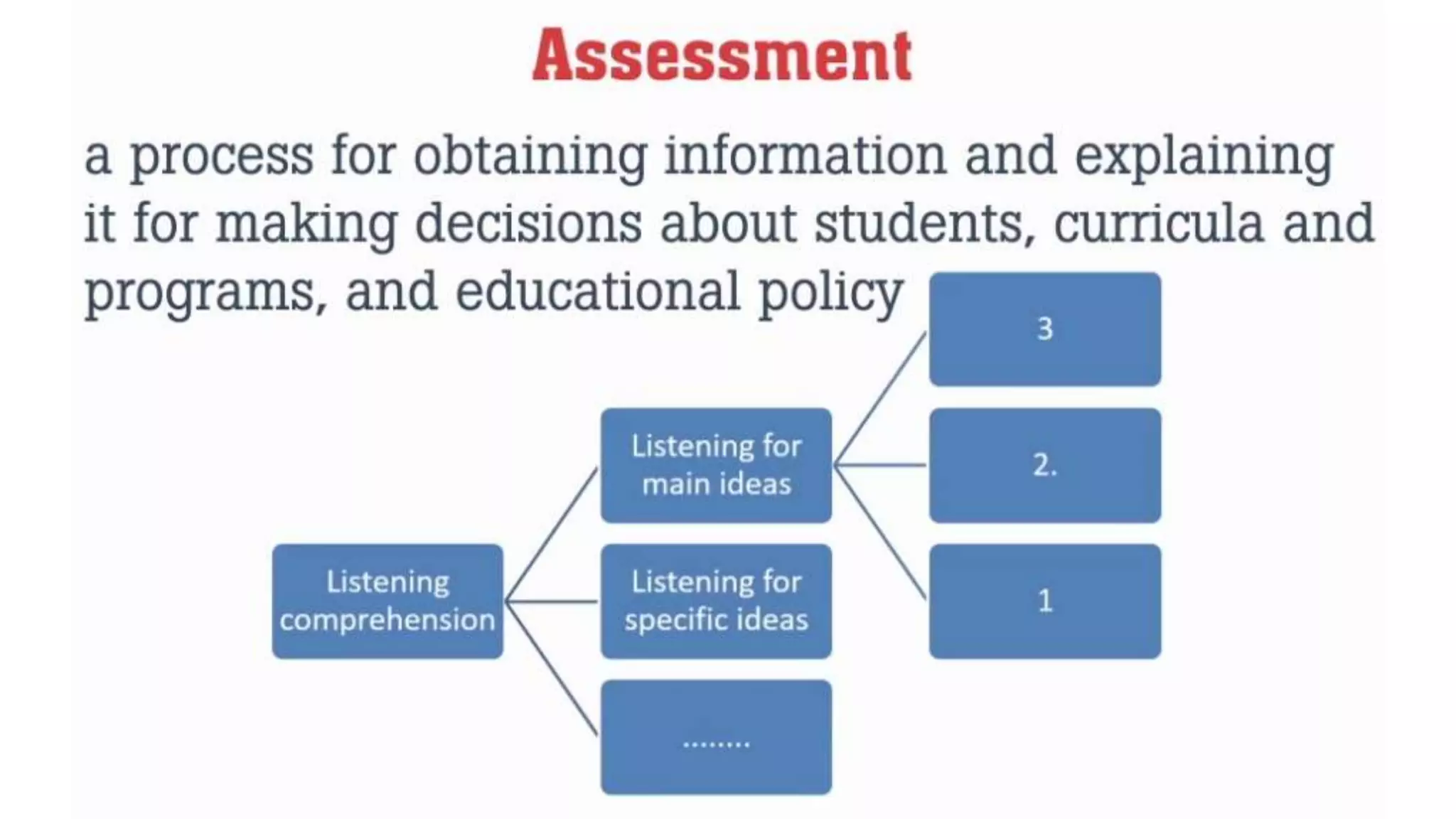
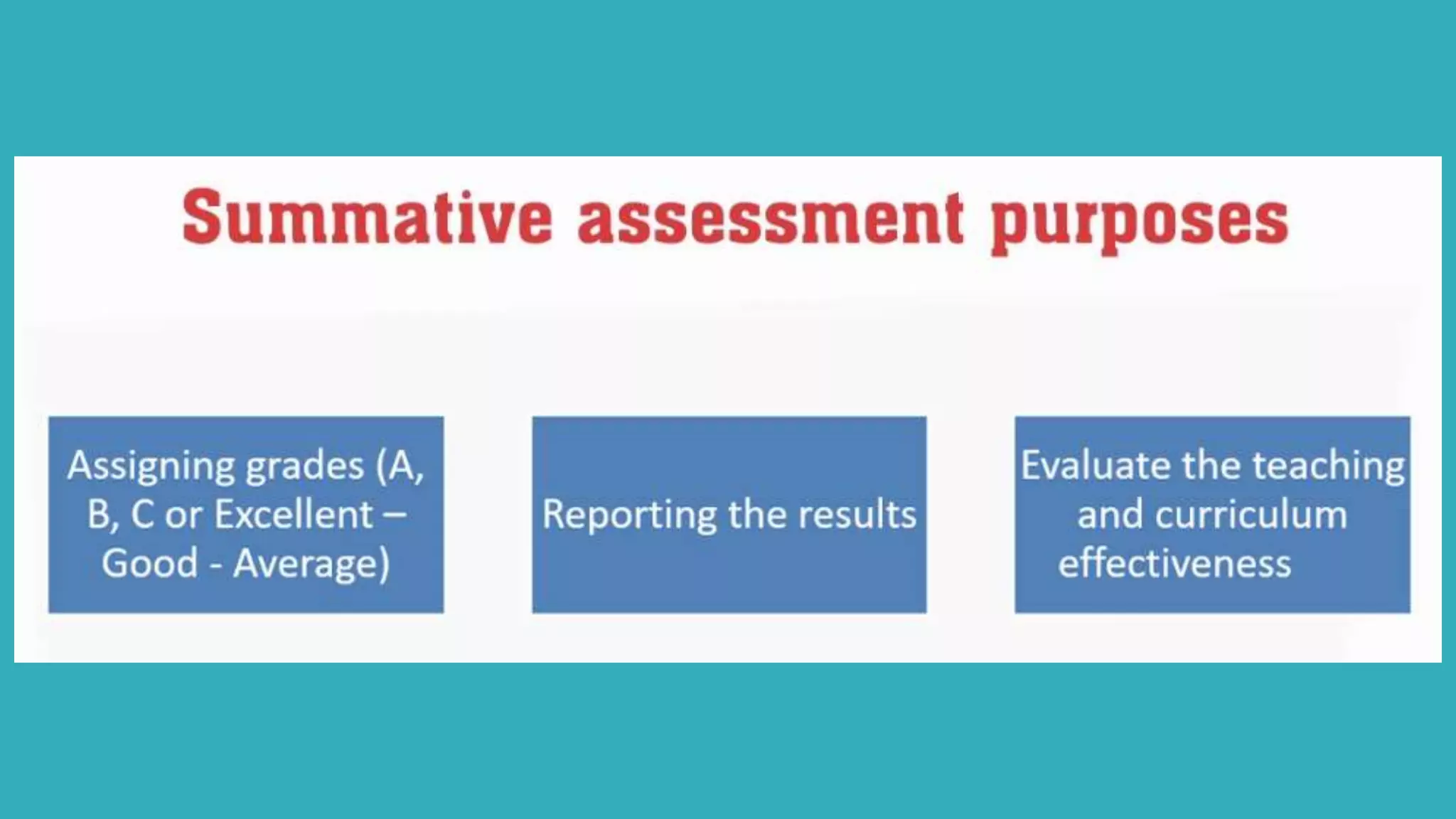
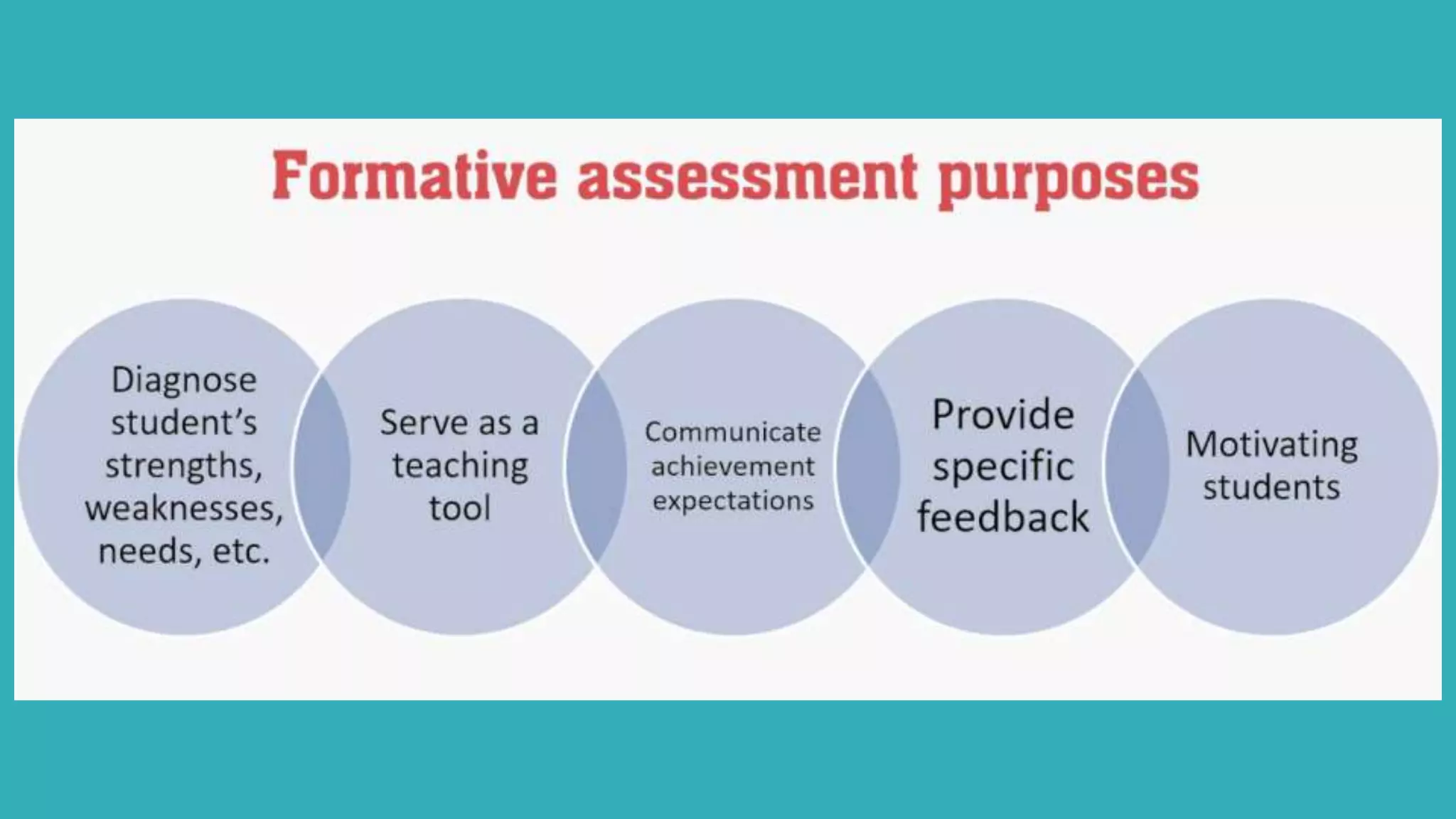
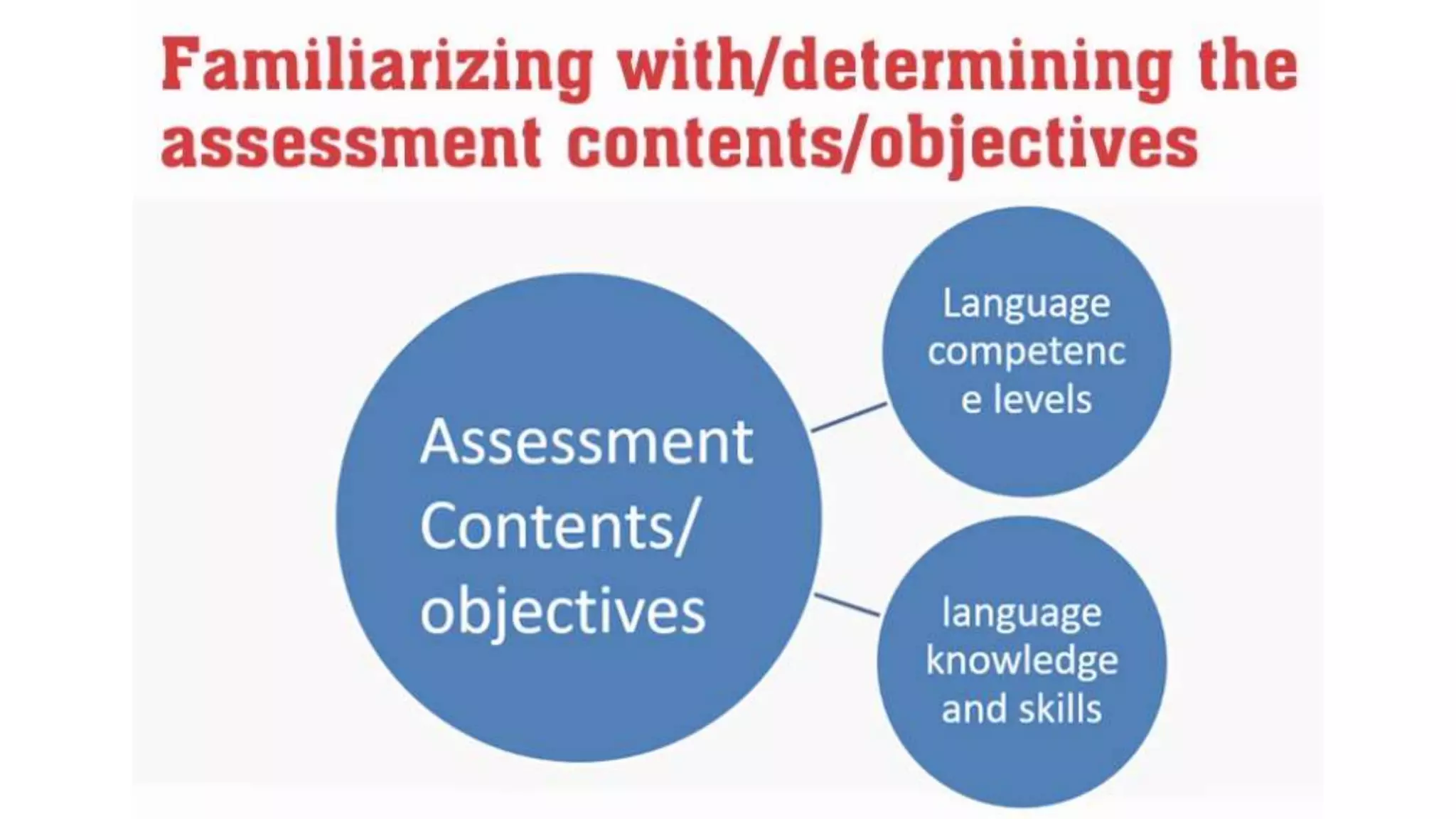
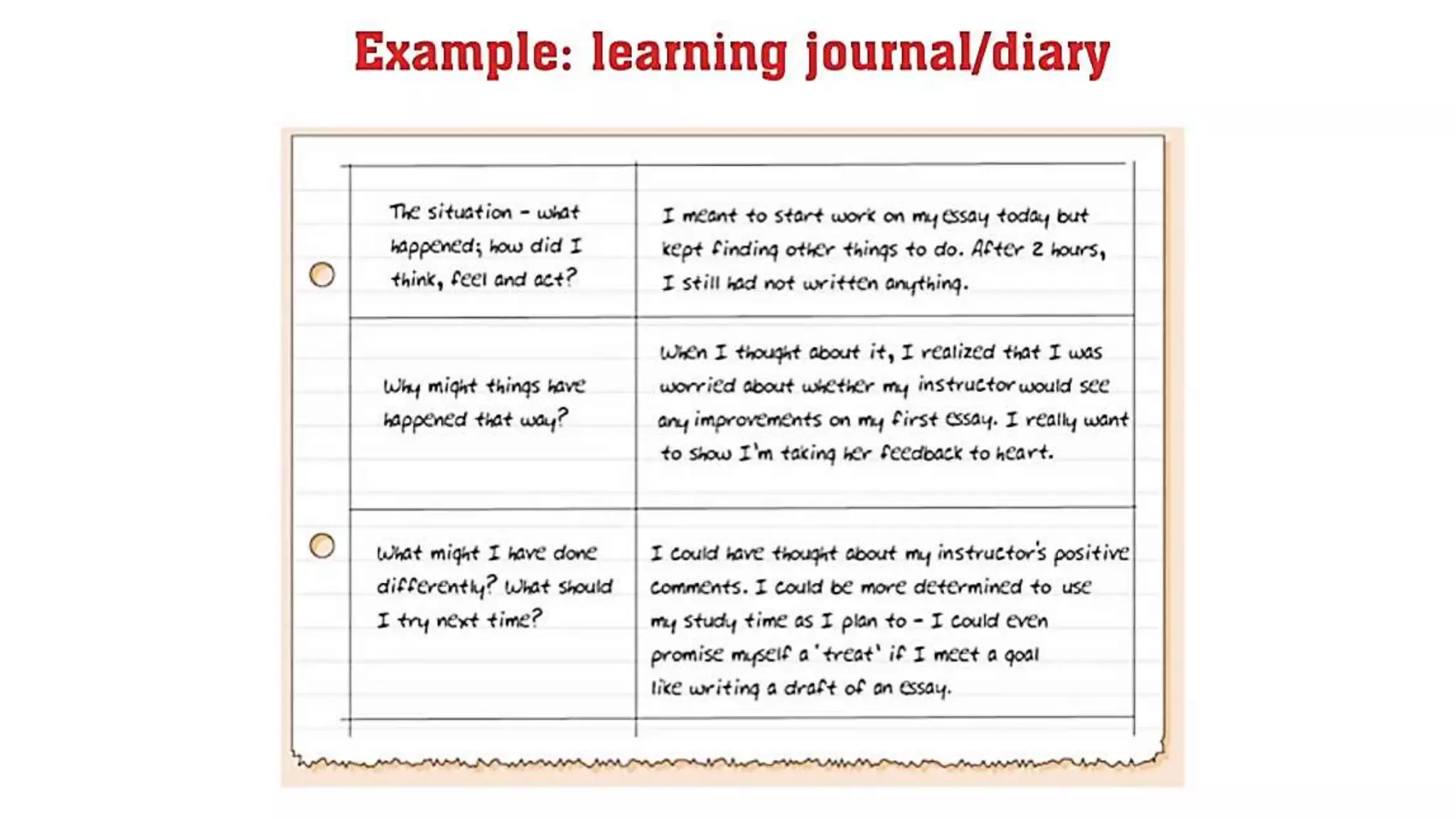
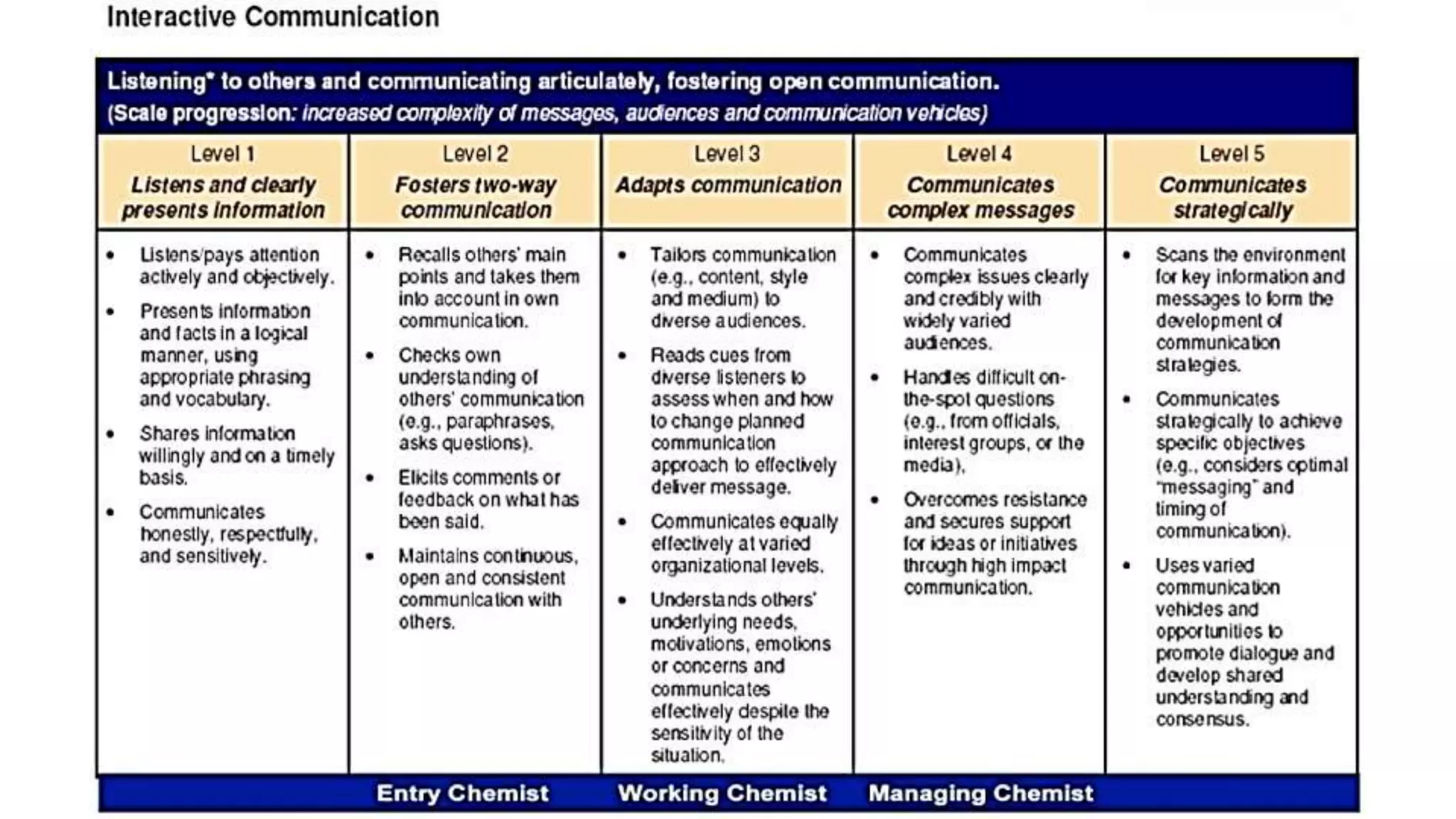
This document provides an overview of Module 1 of a training on language assessment for English teachers. The module introduces key concepts related to the purposes and process of language assessment. It defines important terms and distinguishes different assessment purposes. It also outlines the main steps in the language assessment process and options within each step, with the goal of helping teachers understand and apply the assessment process. The training module aims to equip teachers with knowledge of how to effectively assess student language skills.