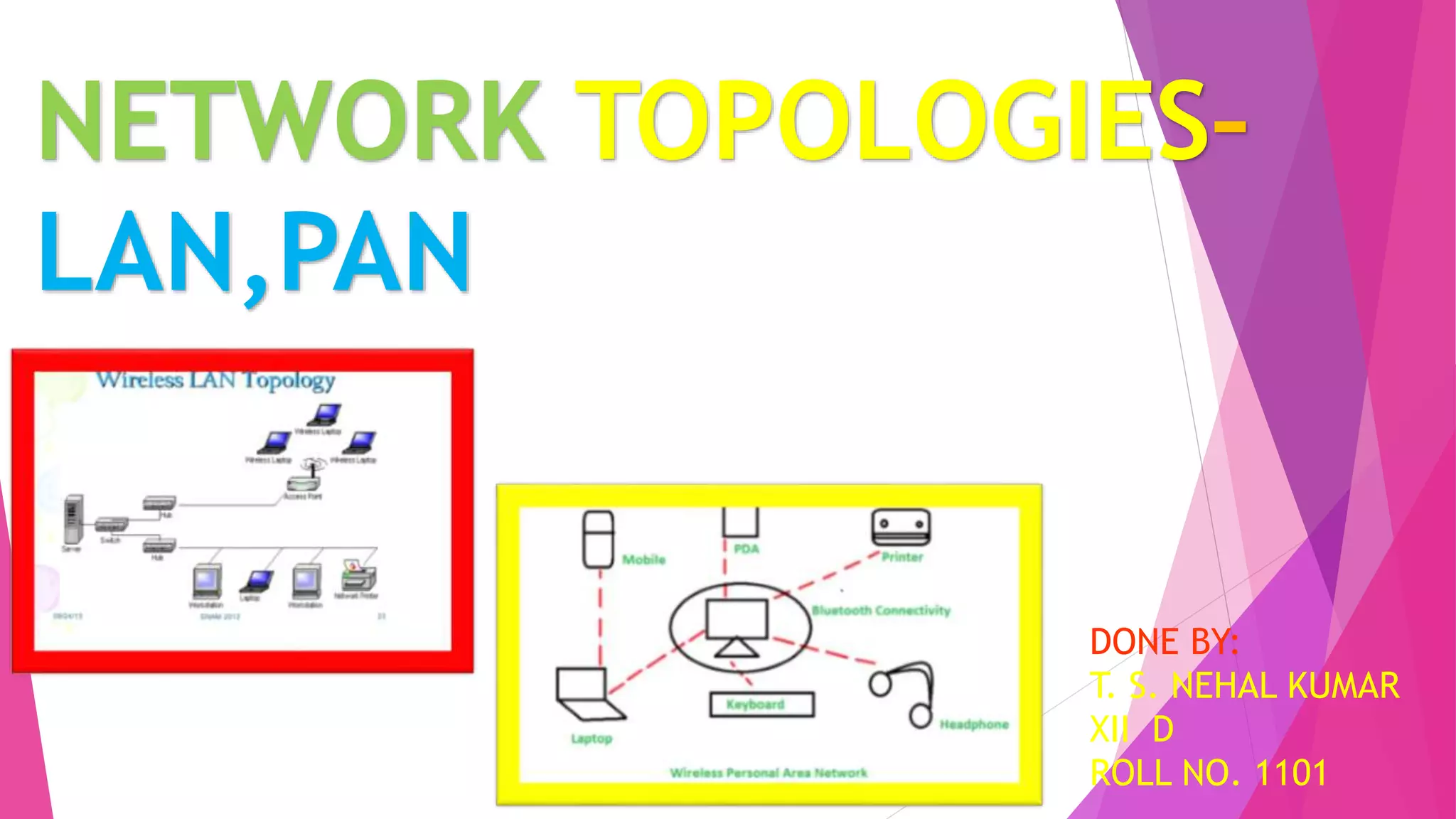
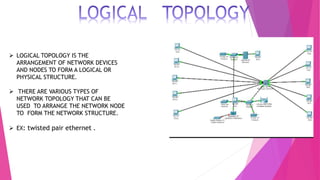
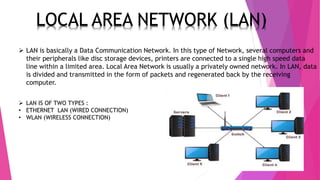
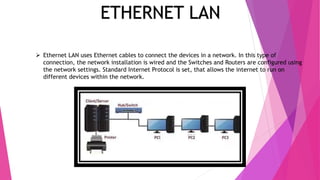
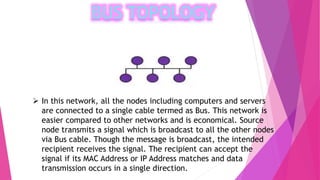
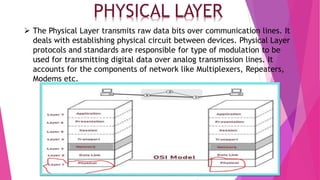
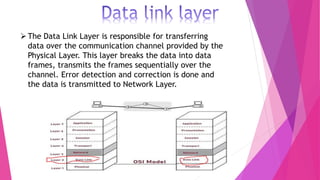
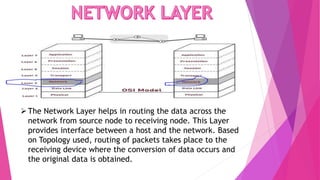
This document discusses network topologies and local area networks (LANs). It describes physical topology as the physical placement of network components, while logical topology refers to the logical arrangement of nodes. LANs connect computers and devices within a limited area through technologies like Ethernet or wireless. Common LAN topologies include star, ring, and bus. The document also discusses how LANs work using the OSI model and provides examples of LAN applications and advantages. It defines a personal area network (PAN) as connecting devices within 10 meters of an individual.