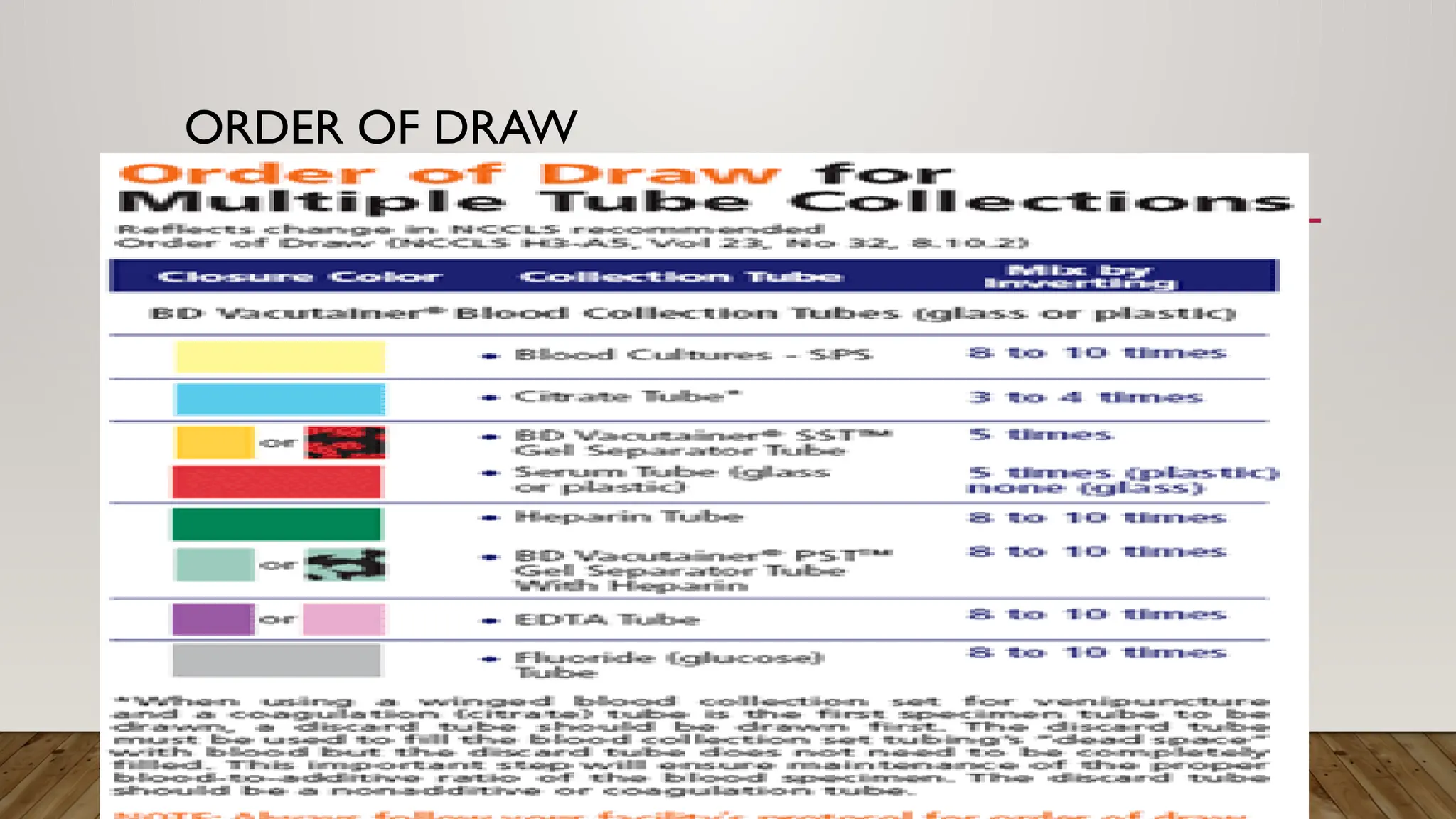
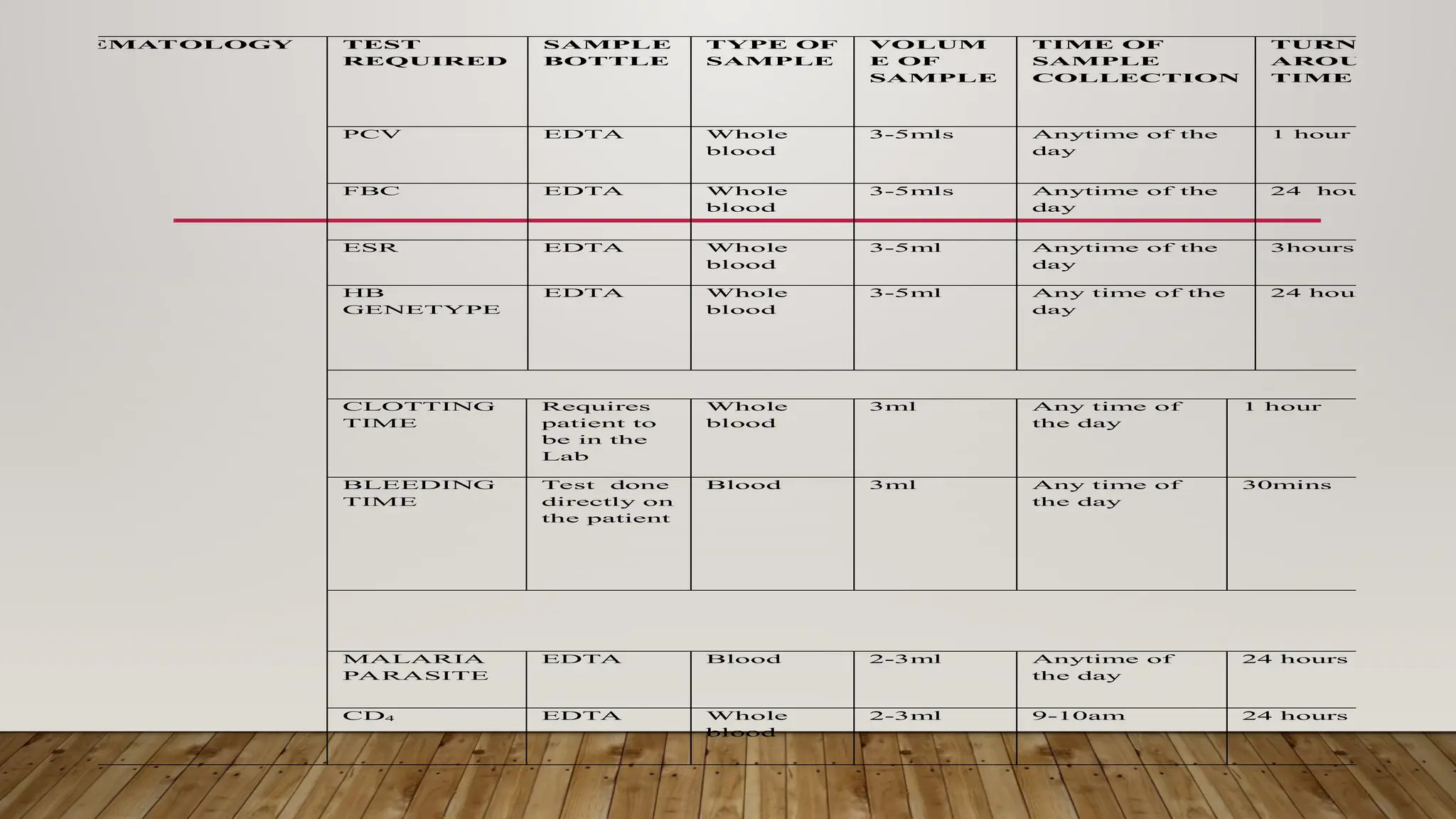
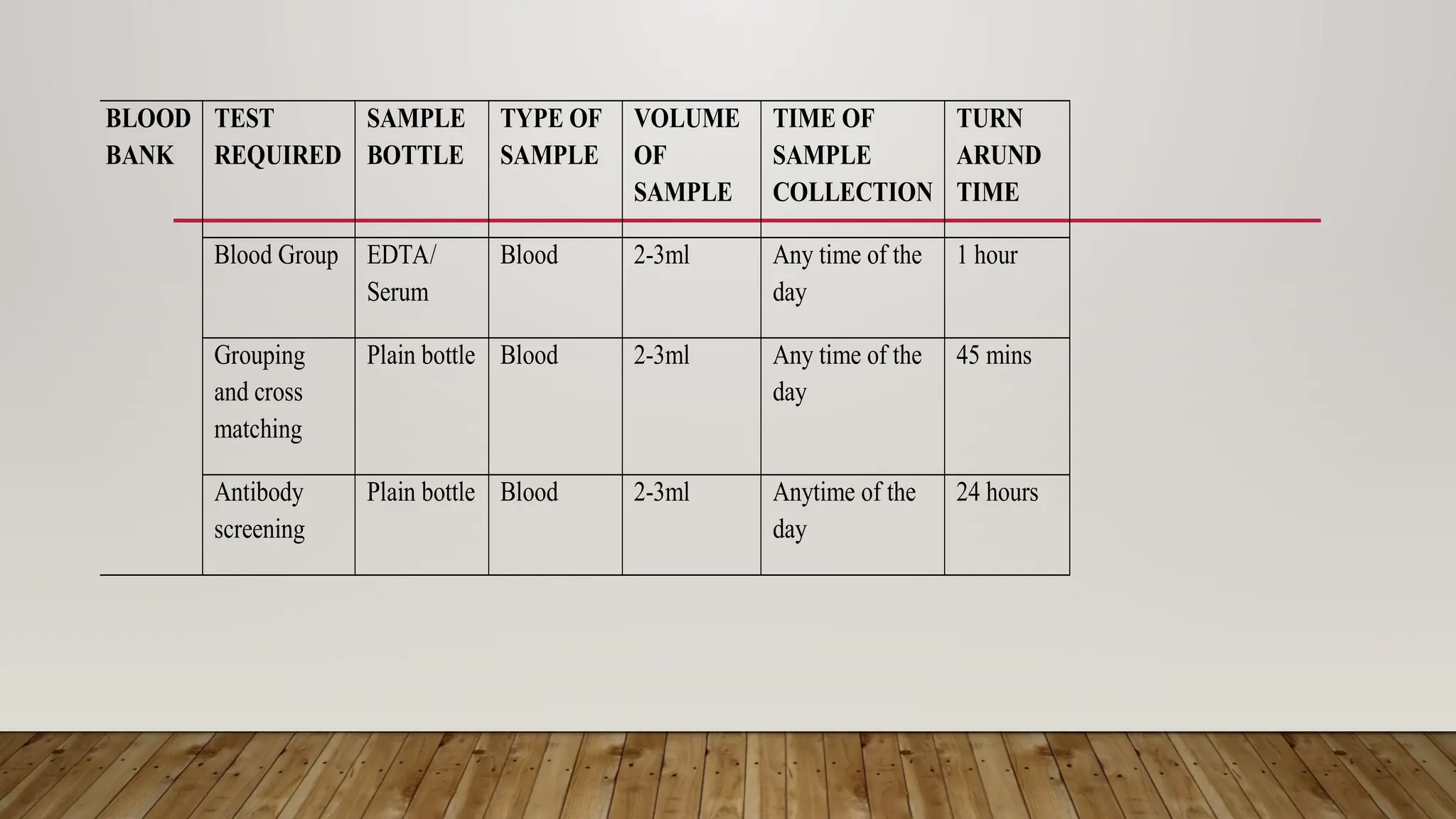
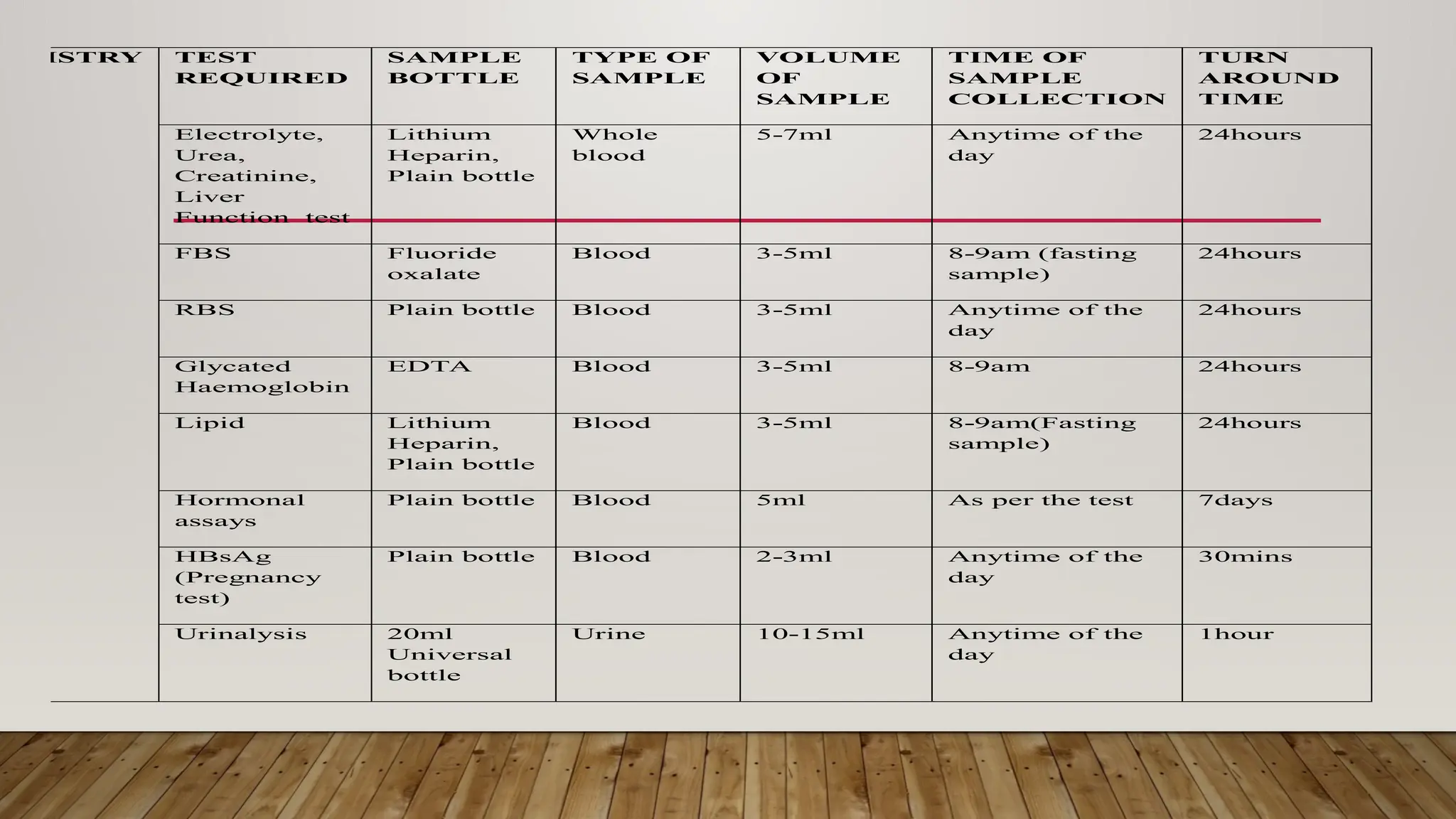
The Laboratory Handbook provides essential guidelines for sample management, including collection procedures, transport, and expected turnaround times for various tests. It aims to enhance laboratory services and customer satisfaction, operating 24/7 for emergencies and specific outpatient hours. Detailed procedures and precautions for specimen collection, labelling, and handling are outlined to ensure accurate testing and reporting.