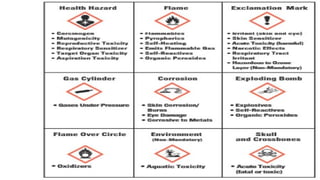
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) provide essential information for the safe handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous substances, organized into multiple sections detailing various safety measures and hazard identifications. Important elements include understanding signal words like 'danger' and 'warning', as well as interpreting pictograms to recognize risks. Proper comprehension of SDSs is critical to minimize accidents, environmental impact, and legal issues associated with chemical handling.