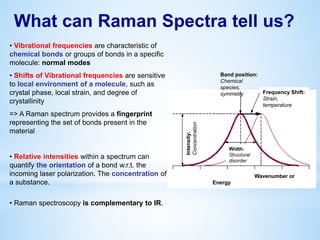
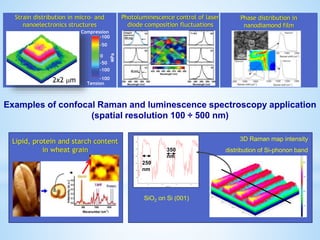
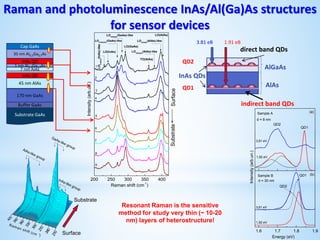
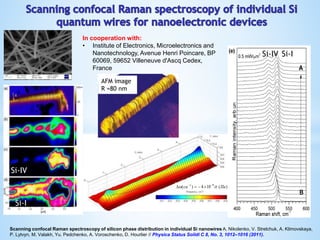
This document provides information about the "Raman and Luminescence Submicron Spectroscopy" Laboratory located at the V. Lashkaryov Institute of Semiconductor Physics, National Academy of Science, Ukraine. The laboratory contains several lasers, spectrometers, microscopes, and temperature control equipment used to perform Raman and luminescence spectroscopy and mapping on semiconductor nanostructures with submicron spatial resolution. The laboratory studies properties such as chemical composition, strain, temperature, carrier mobility and concentration in nanostructures for applications in microelectronics and optoelectronics. Team members and their areas of research interest are also listed.














![1 mm AFM
[001]
[011]
1 2
[011]
~80-85 nm
Self-assembled InGaAs/GaAs
quantum chain structure
For nanoelectronic
E0Eg
Ec
Ev
е2
е1
е0
h0
h1
h2
d
х
E1E2
Growth and characterization
of bilayer InAs/GaAs quantum dot
structuresB. L. Liang, Zh. M. Wang,
Yu. I. Mazur, V. V. Strelchuk, and G.
J. Salamo // Phys. stat. sol. (a) 203
(10) (2006) 2403
In cooperation with:
University of Arkansas, USA
Supported by the State
Program of Ukraine
“Nanotechnologies and
Nanomaterials”
Energy , eV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laboratory-150501150742-conversion-gate01/85/Laboratory-Raman-spectroscopy-ISP-NASU-19-320.jpg)

