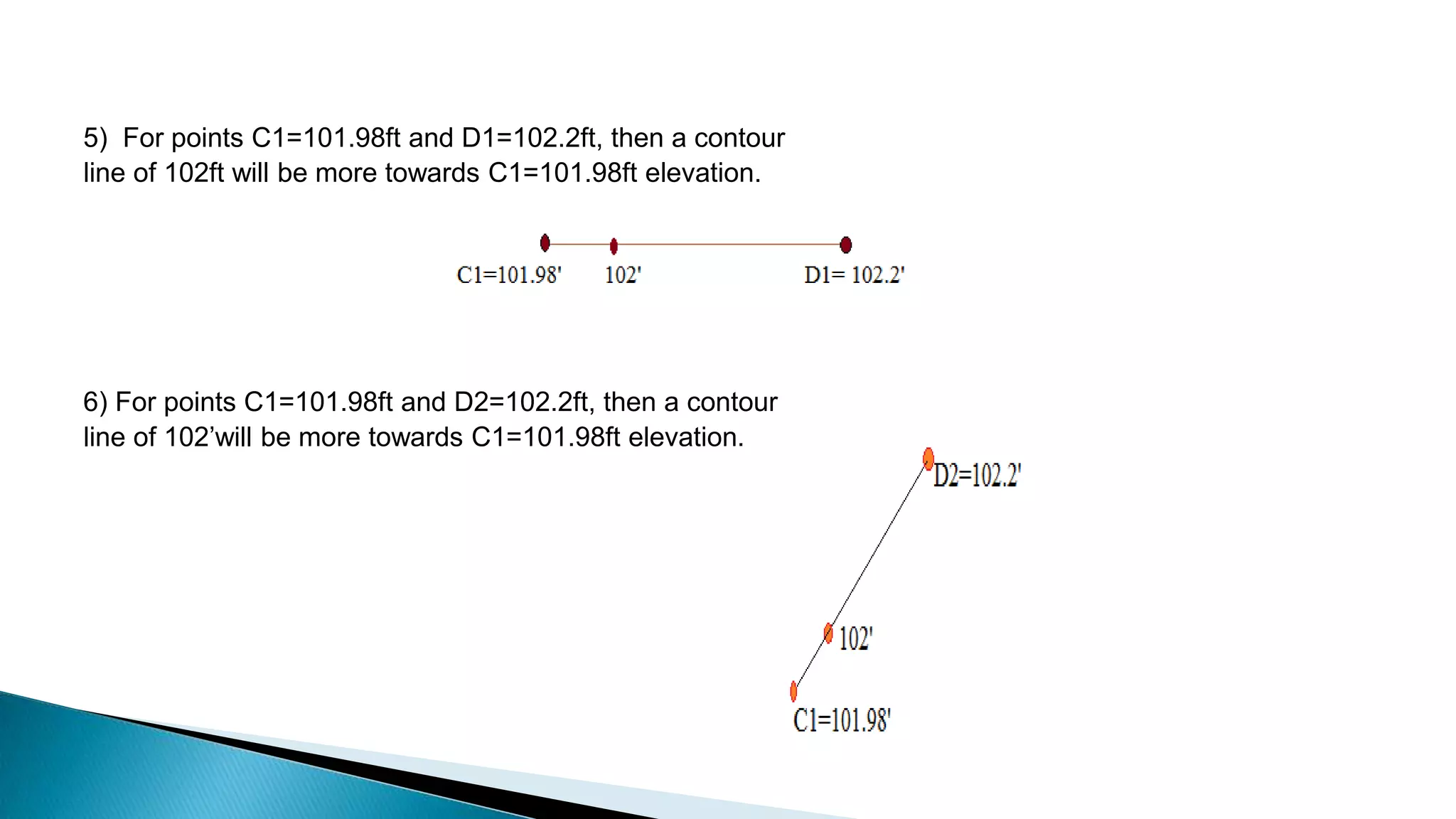
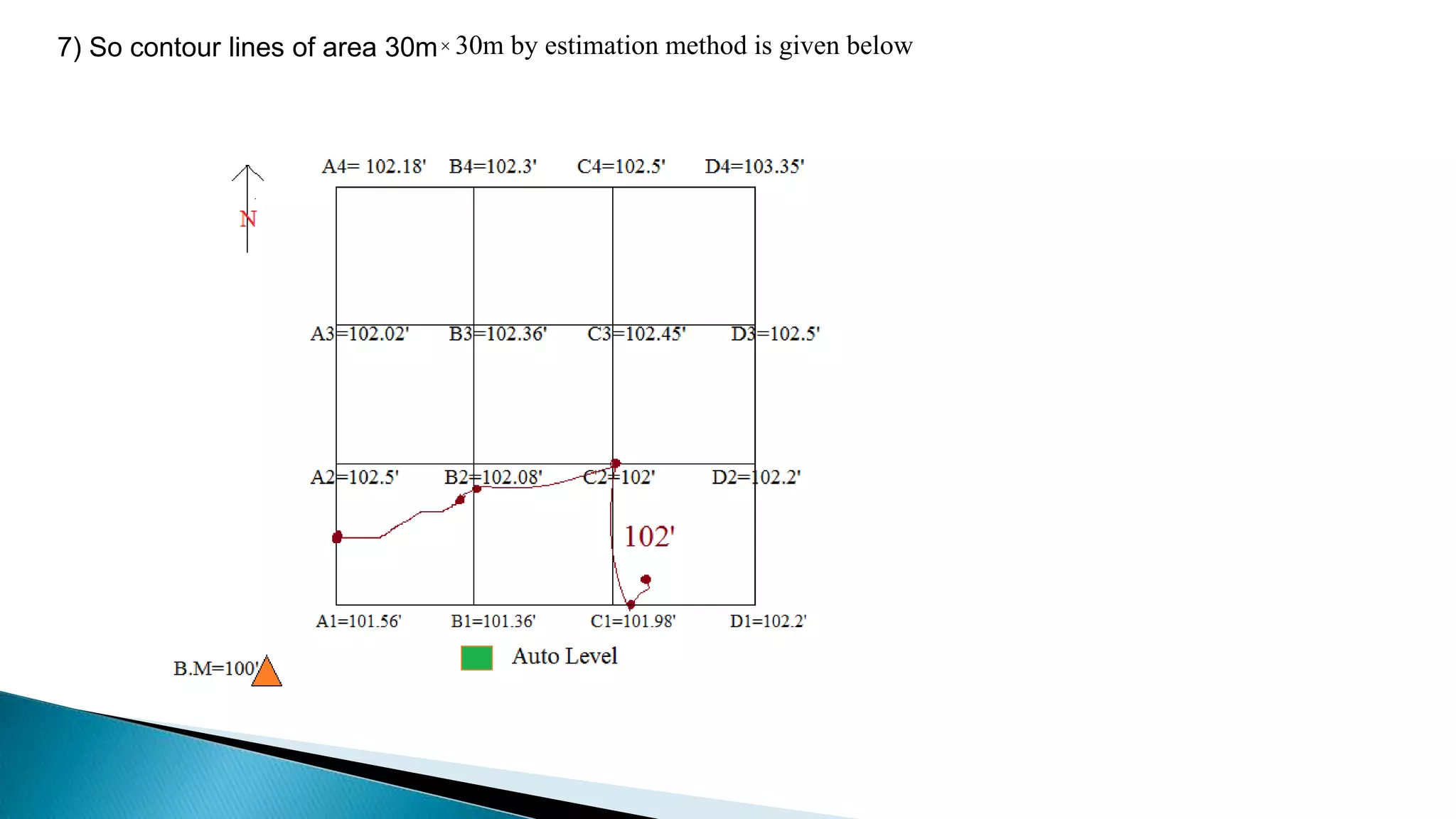
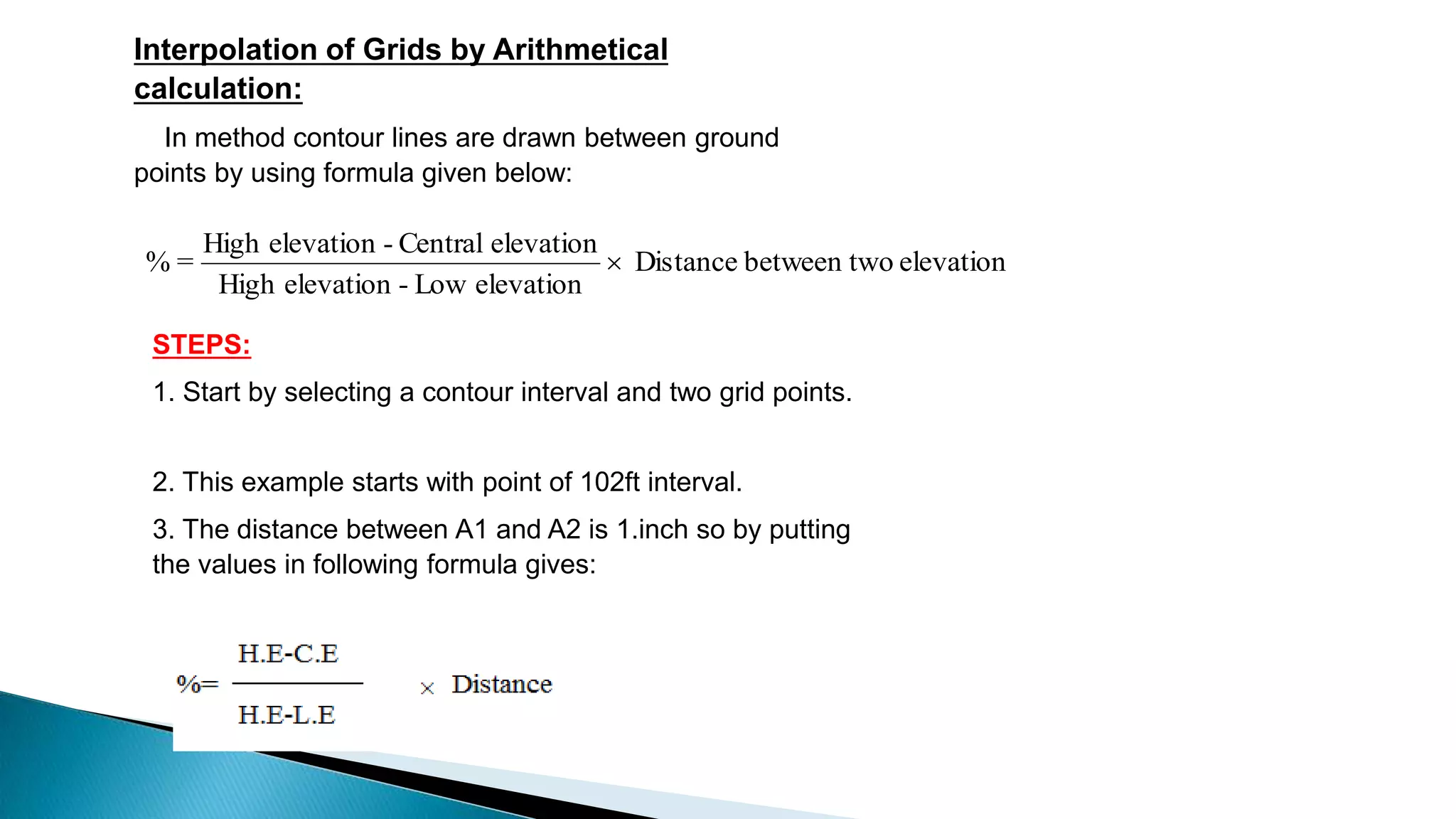
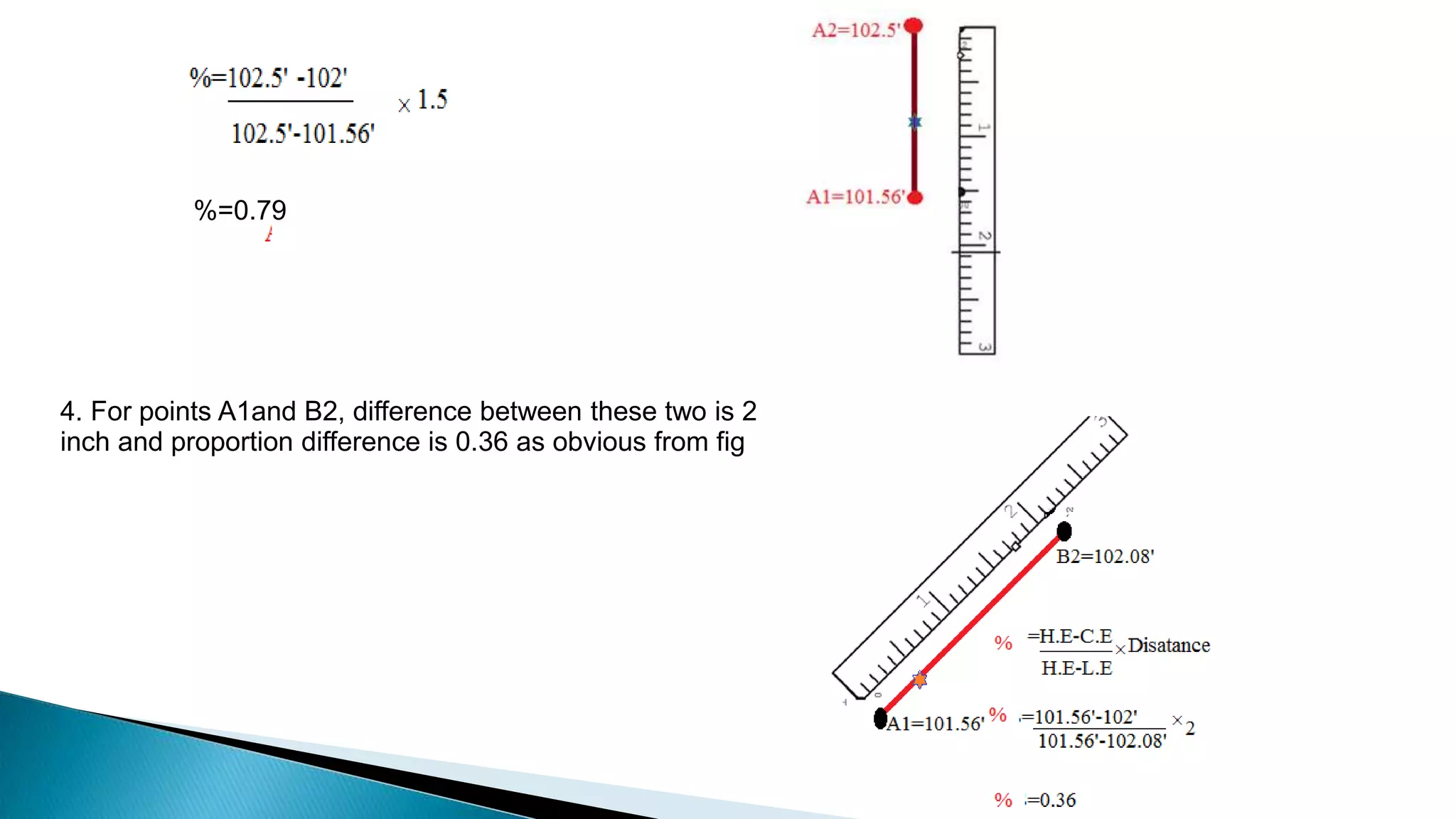
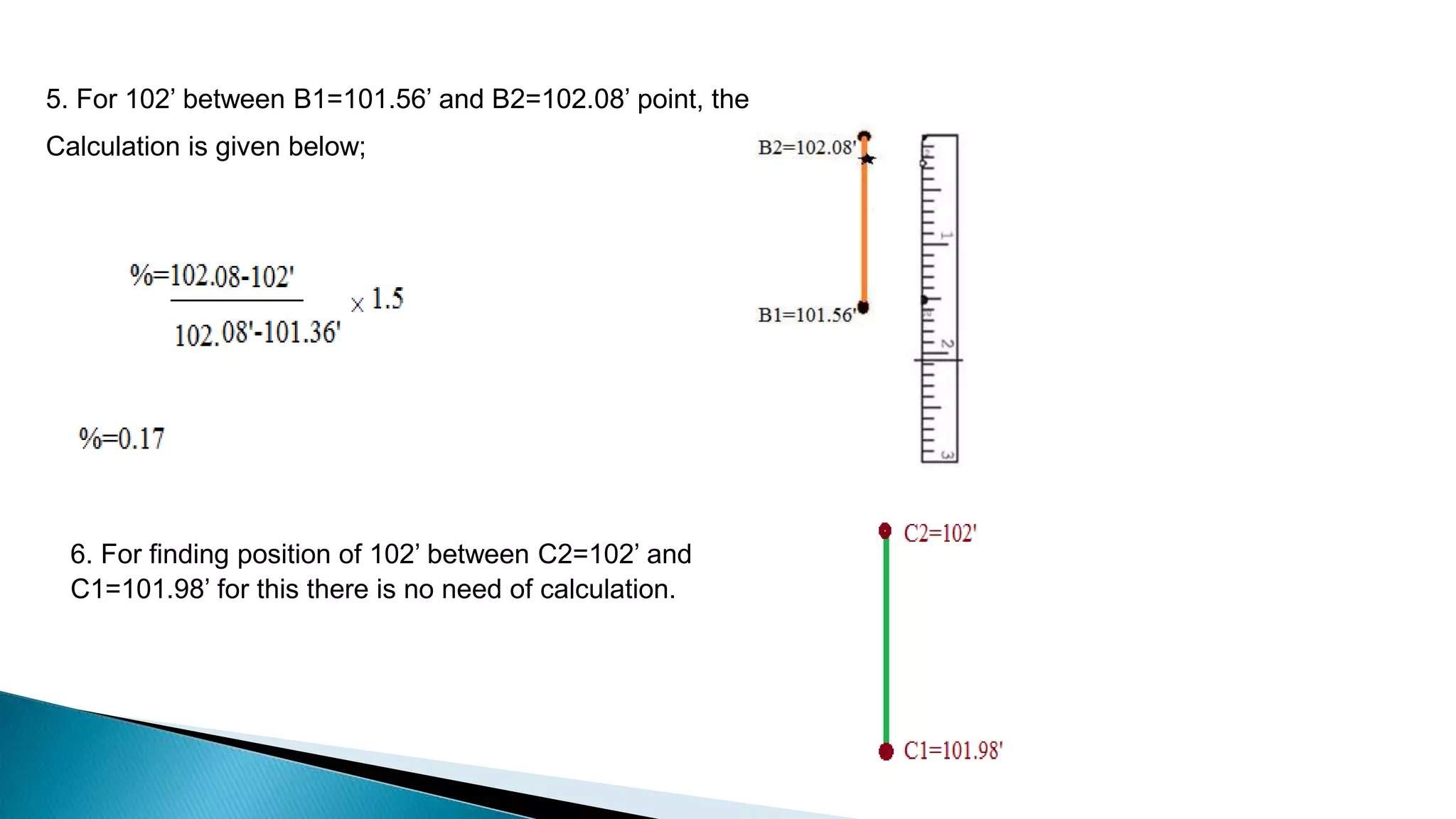
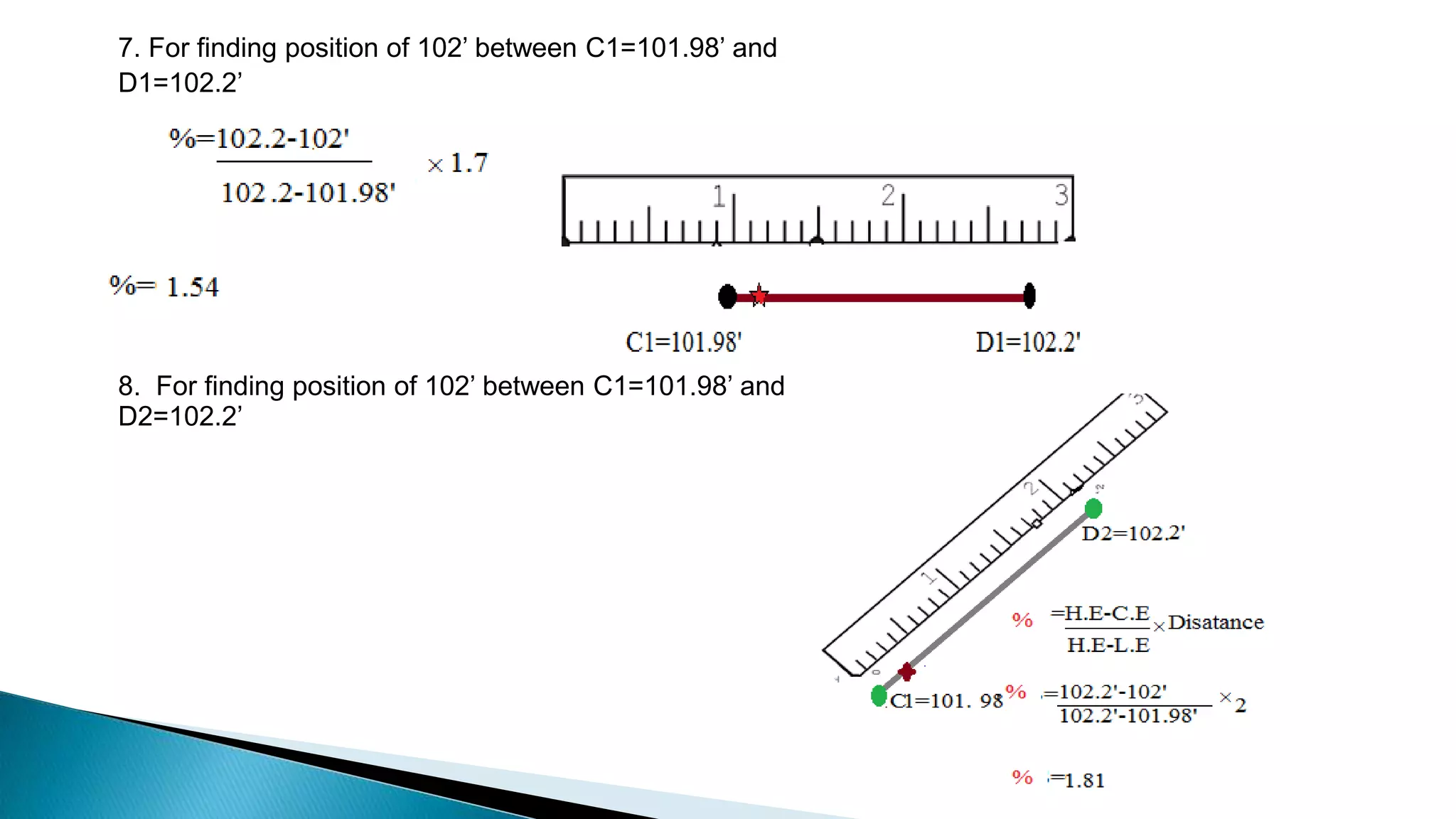
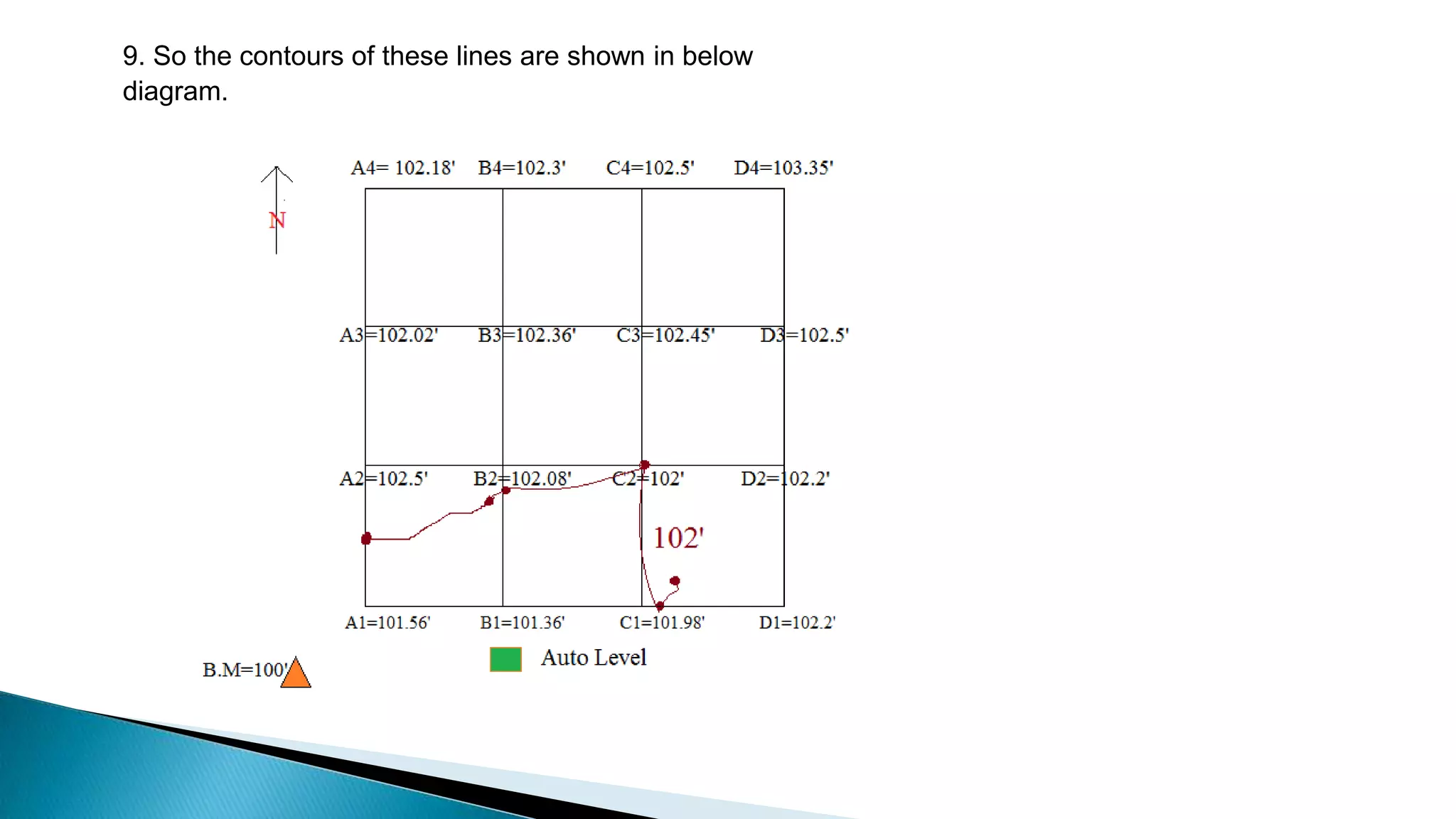
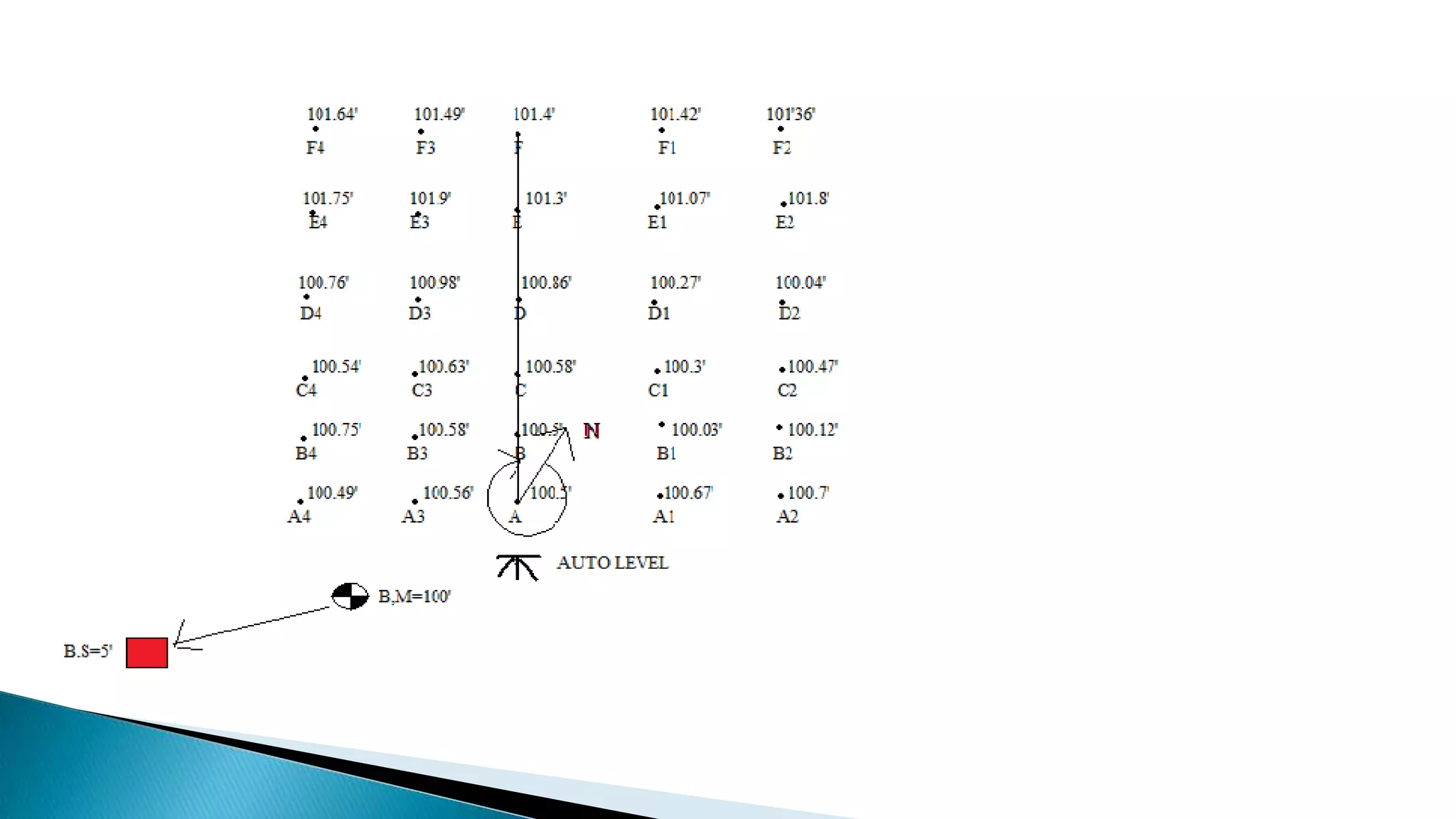
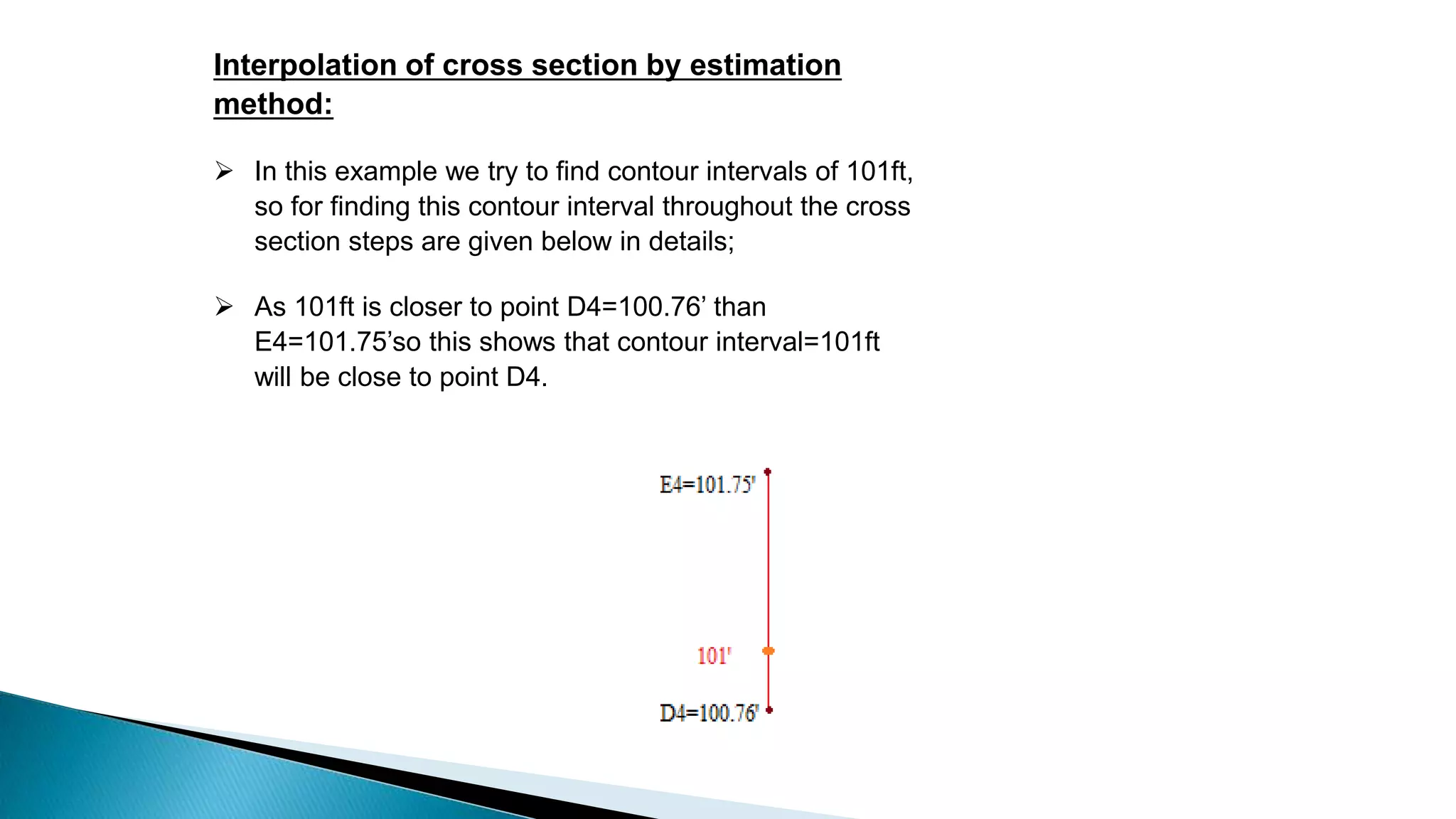
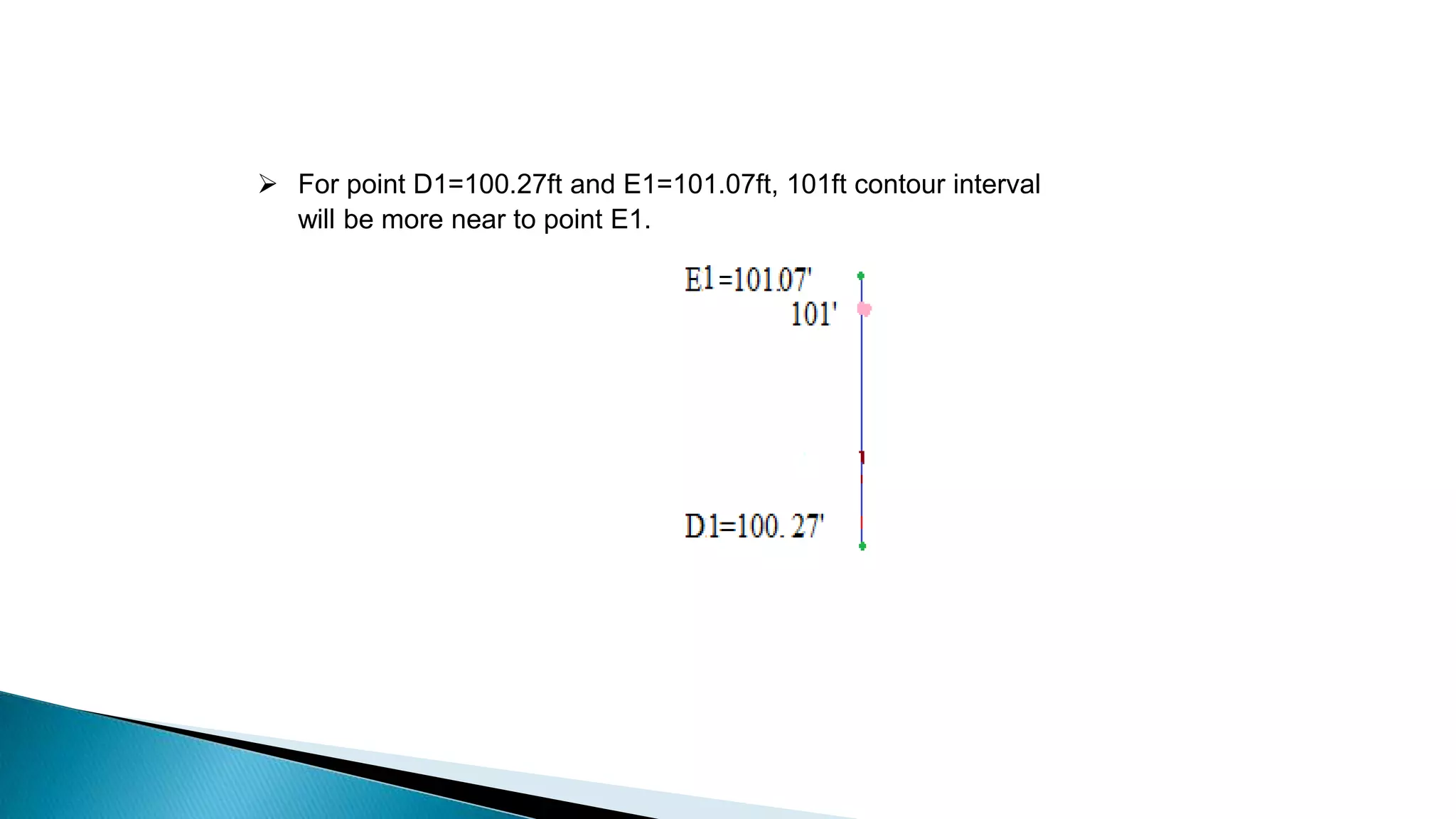
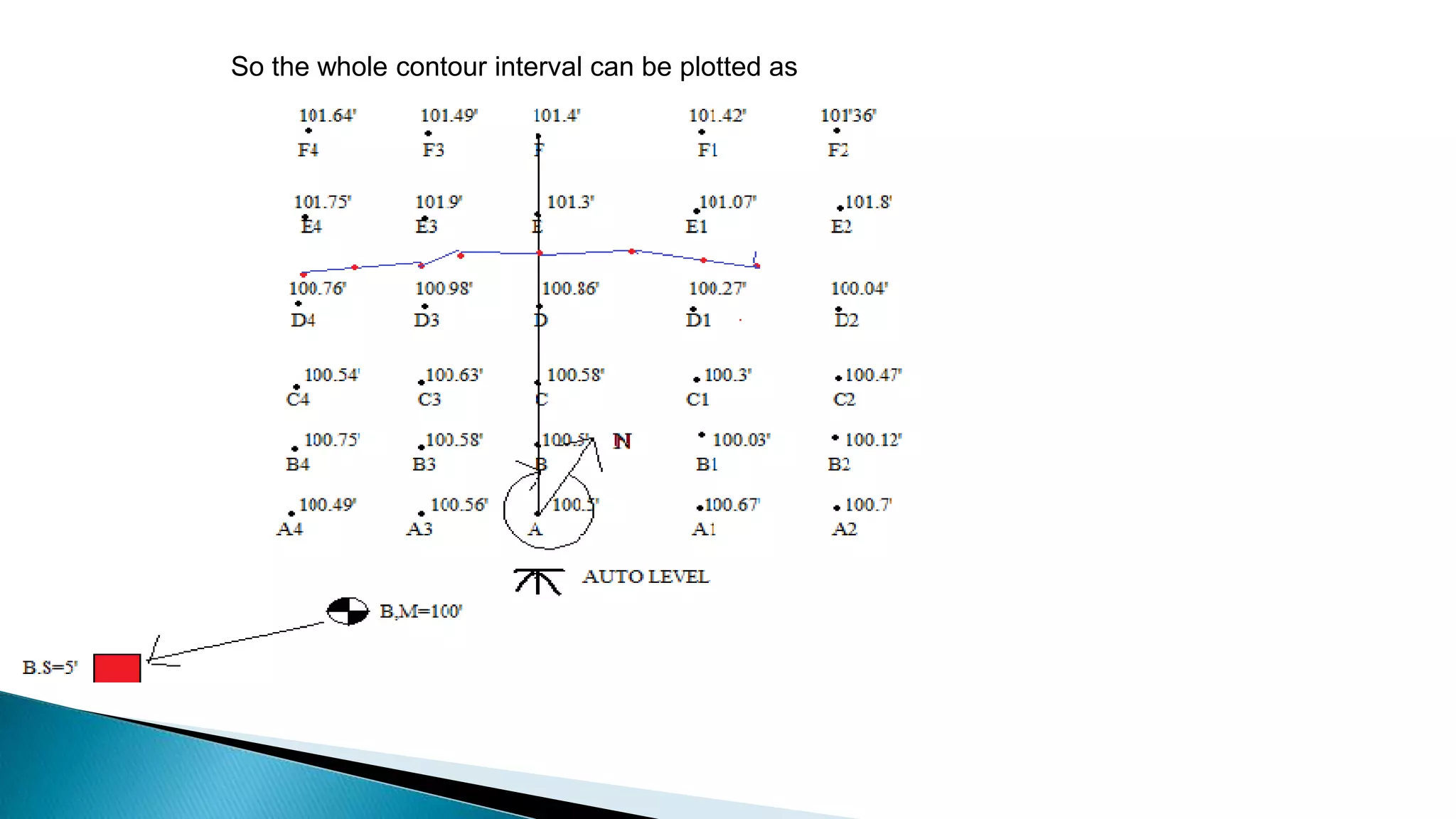
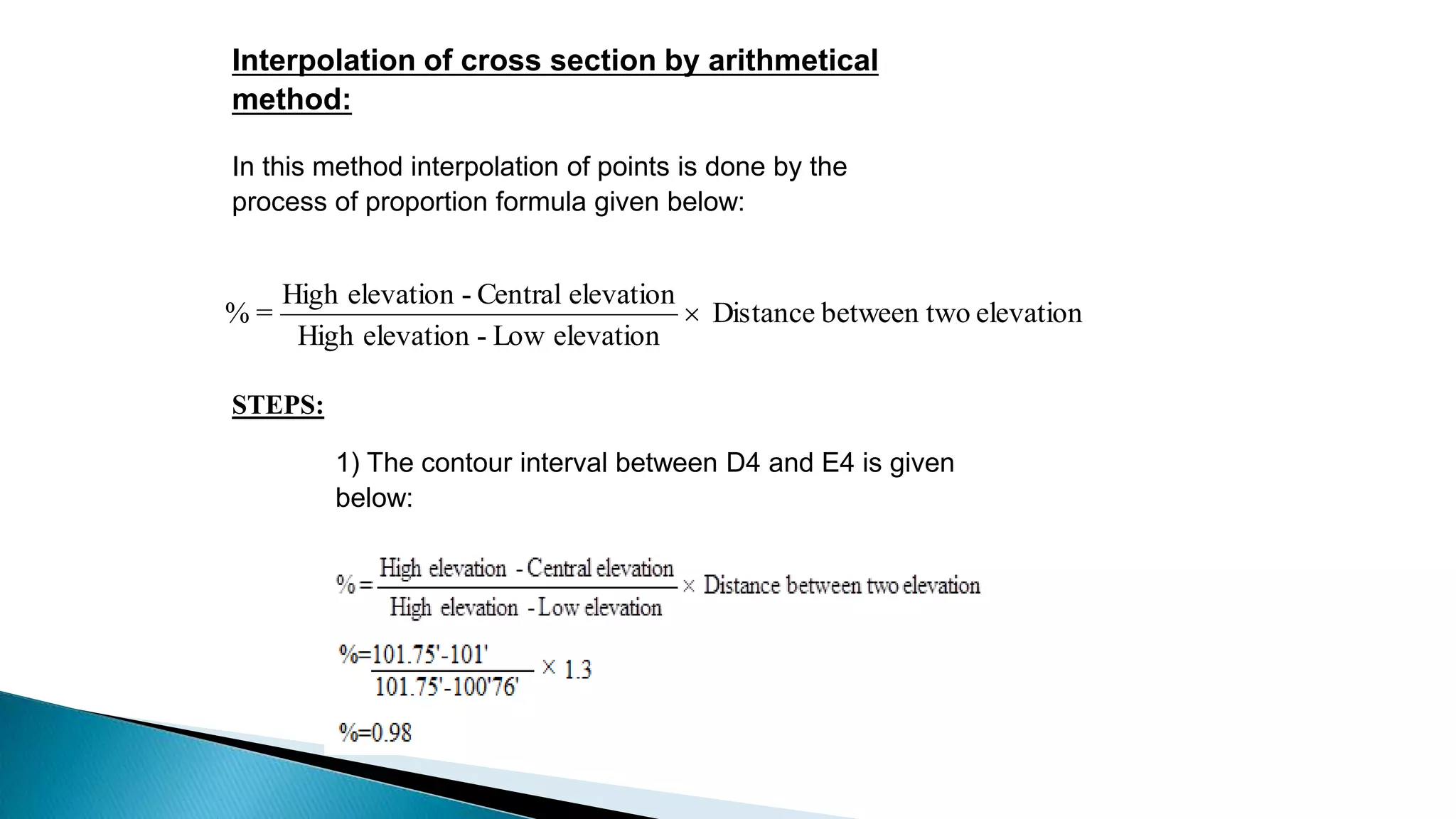
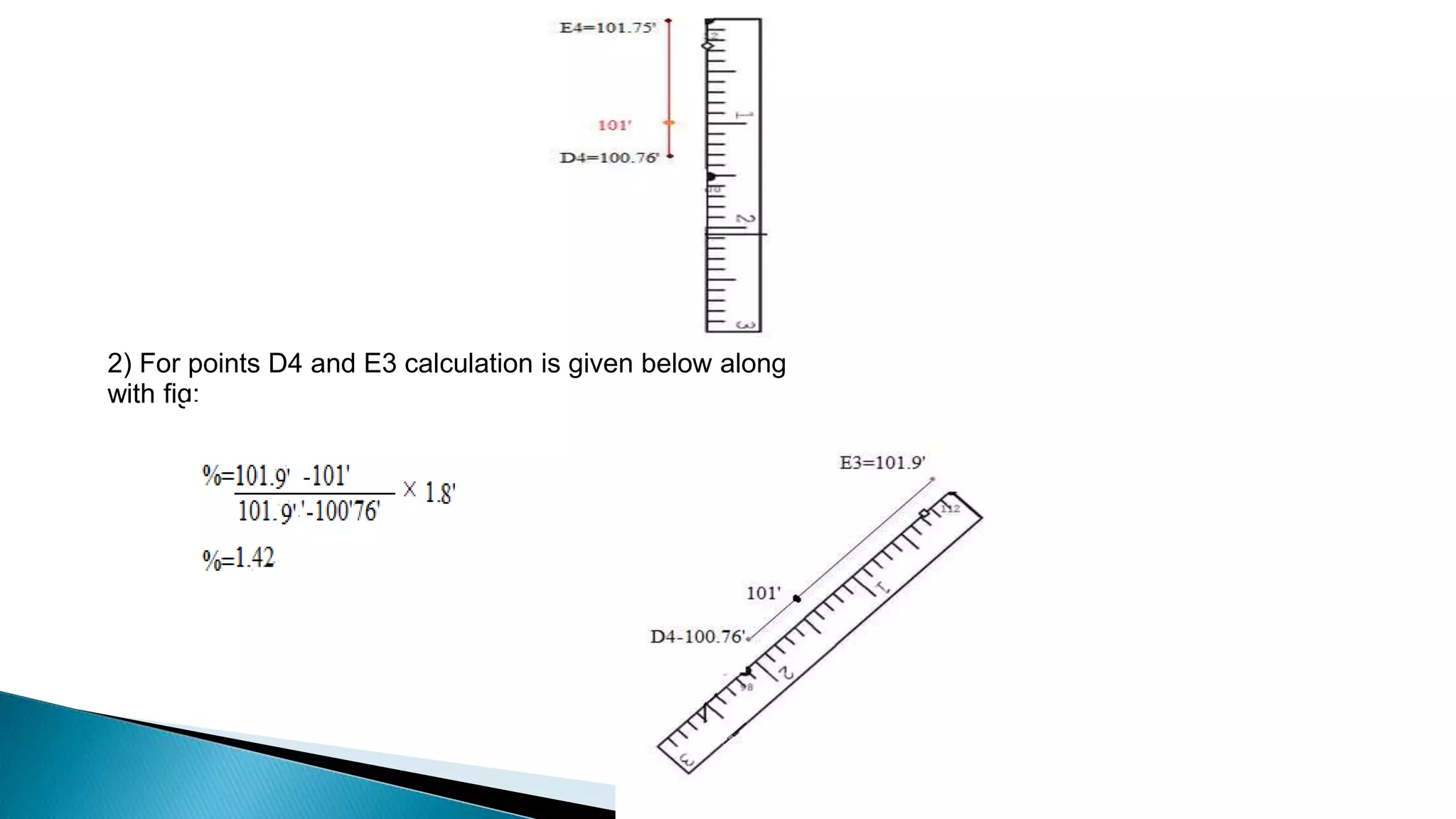
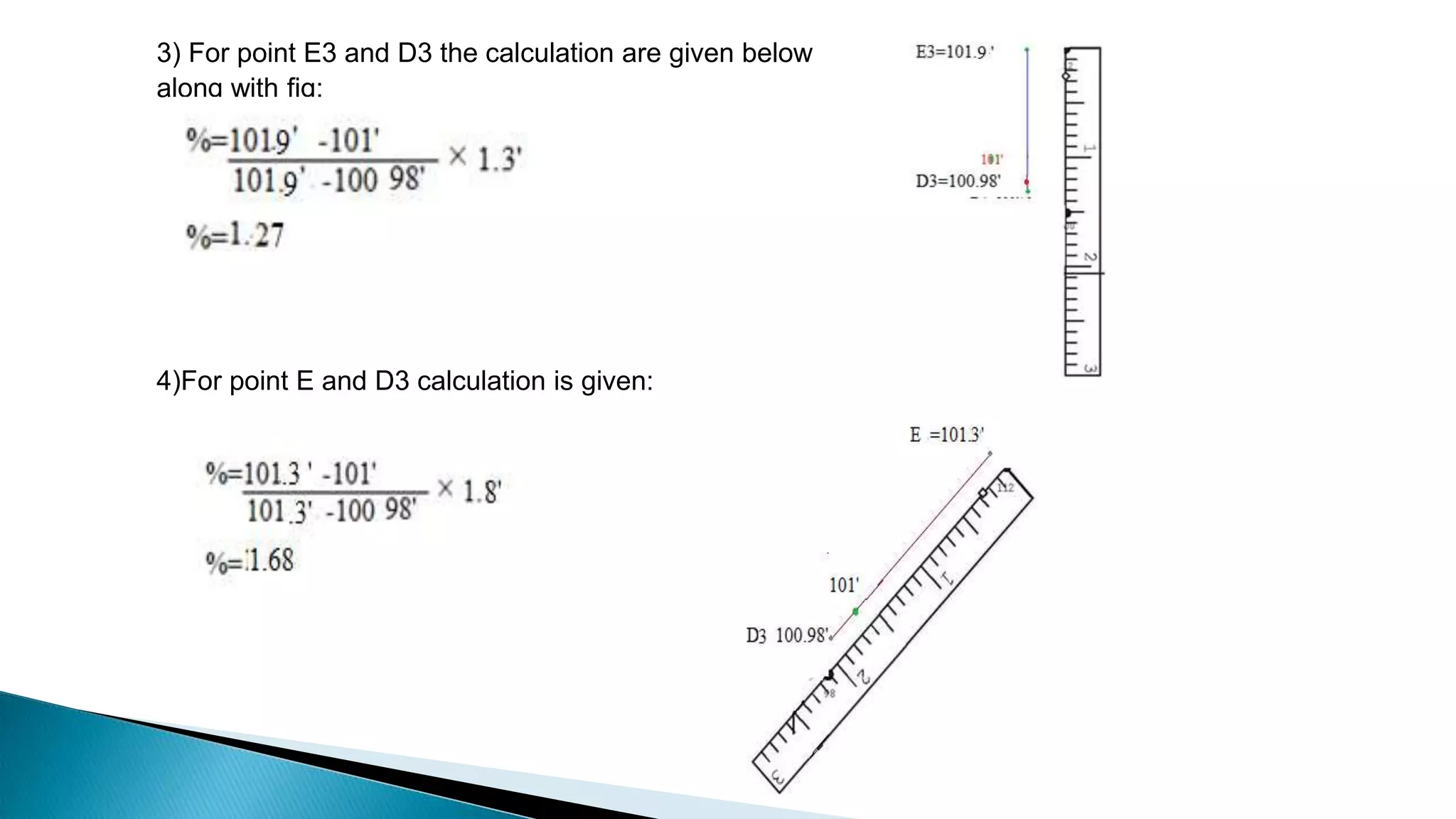
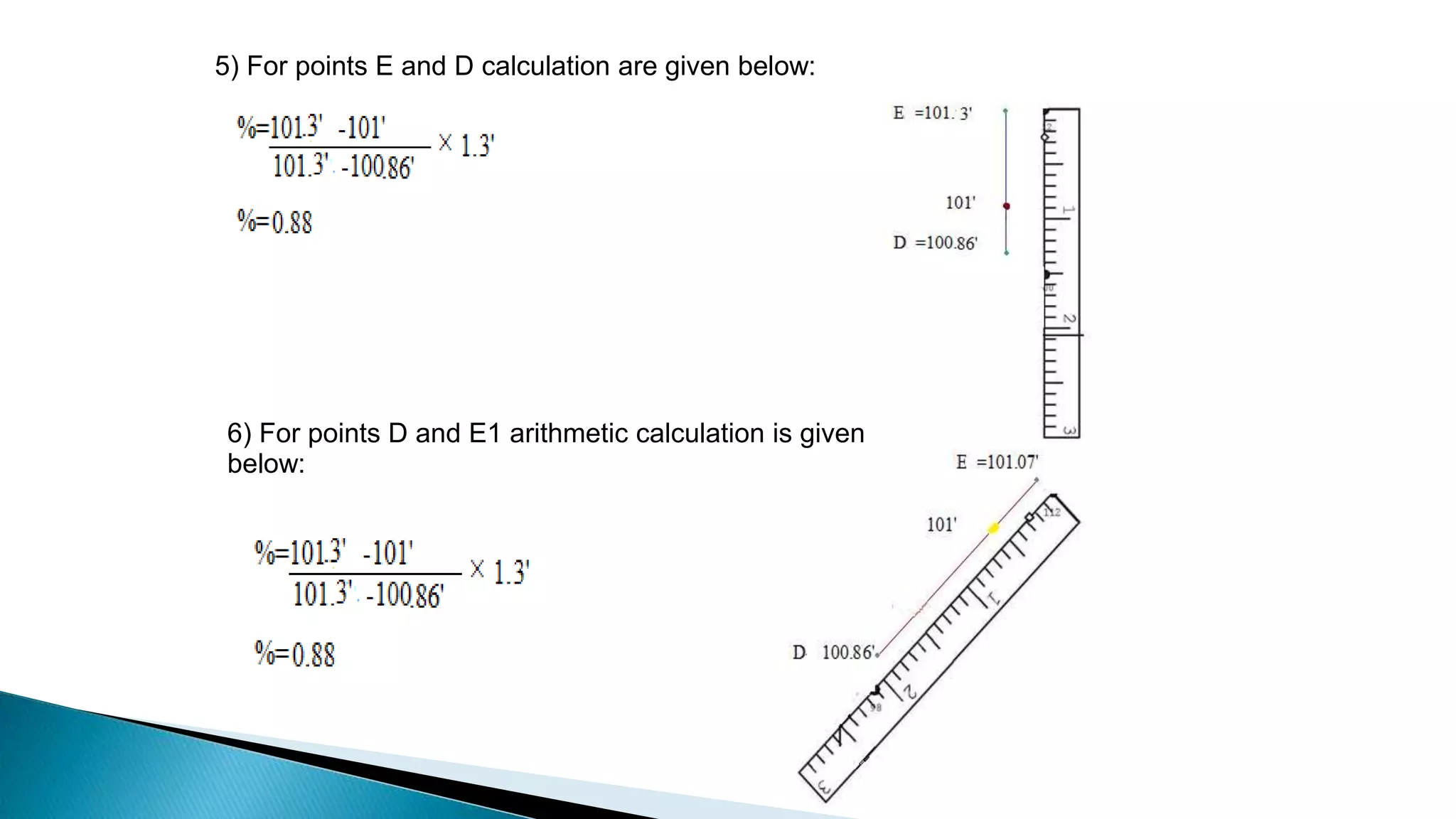
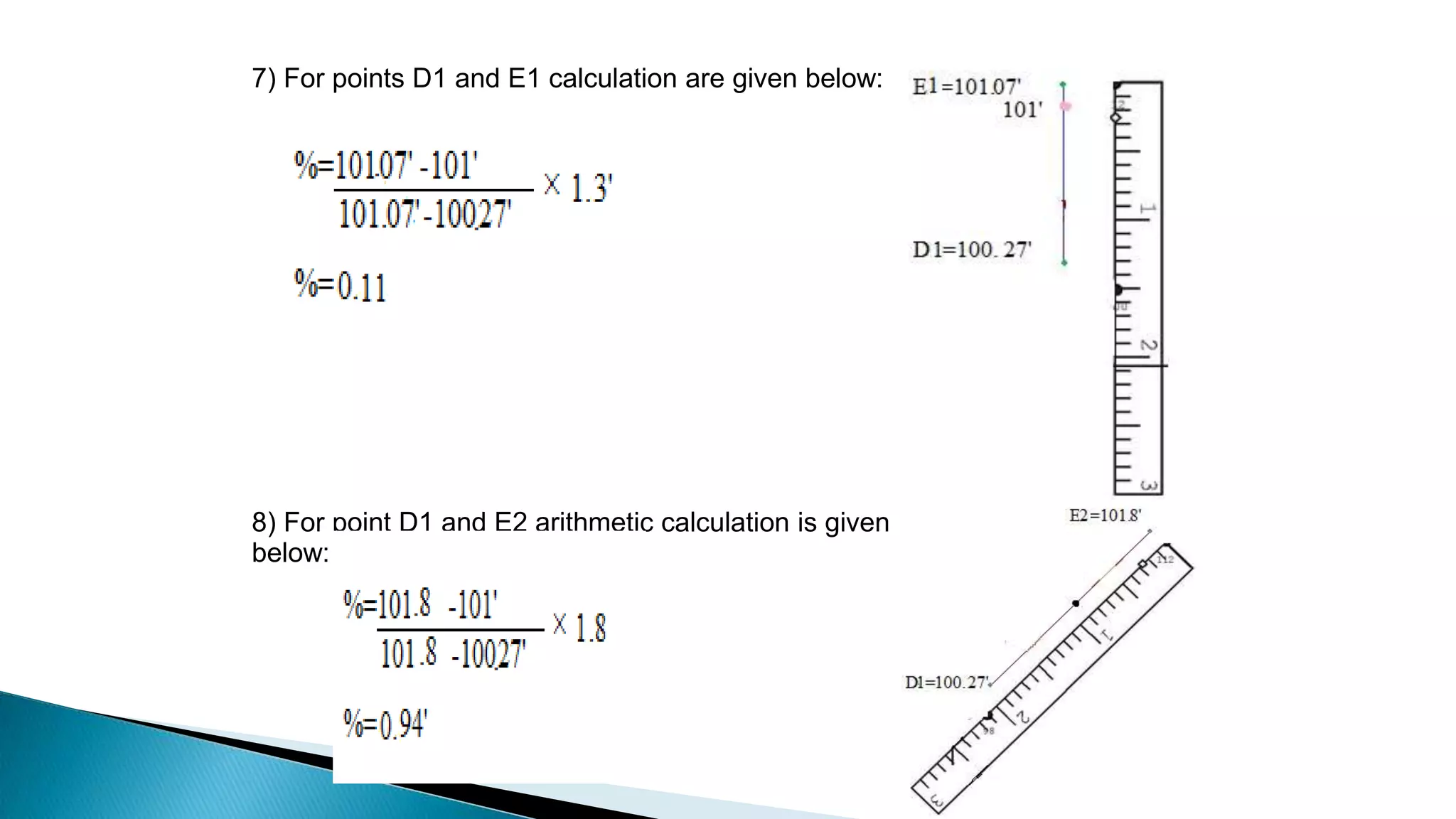
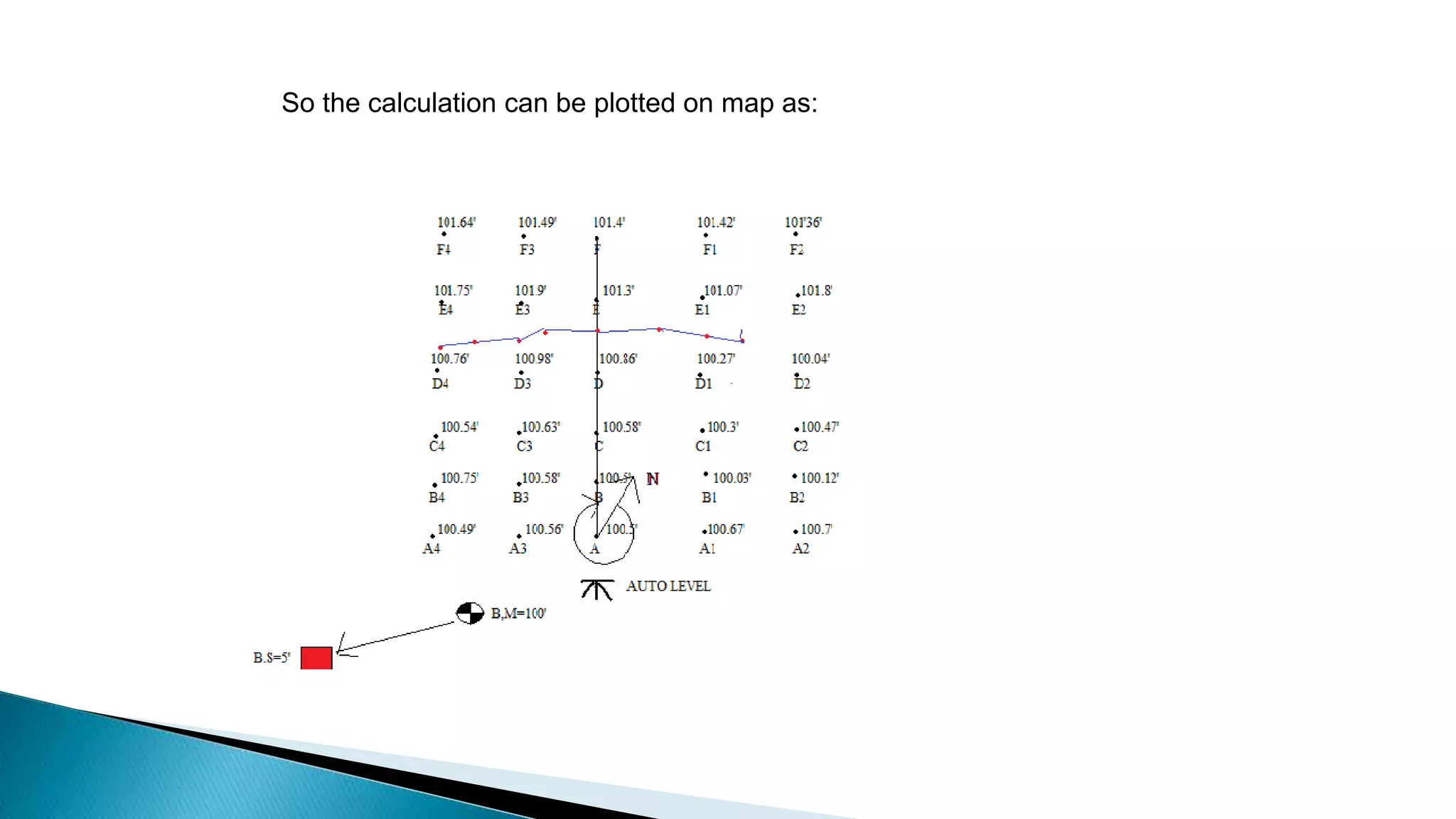
This document describes various methods for contour mapping, including both direct and indirect methods. It focuses on explaining the indirect grid or square method, cross section method, tachometric method, and radial lines method in detail. For each method, it provides an example to illustrate the procedure, including taking spot levels, determining reduced levels, and interpolating contour lines either by estimation or arithmetical calculation. It emphasizes that the indirect or interpolation methods are quicker, more economical and less laborious than direct methods of contour mapping.