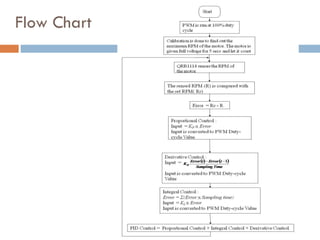
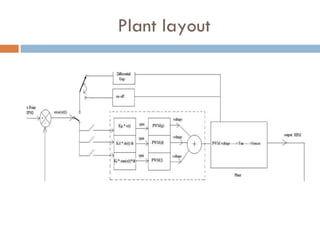
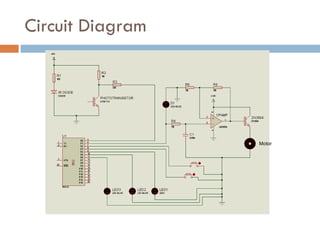
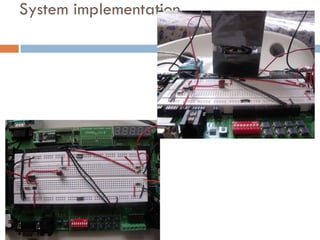
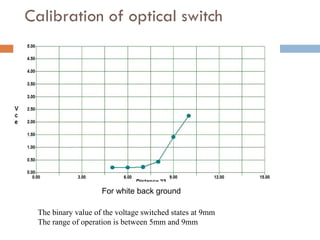
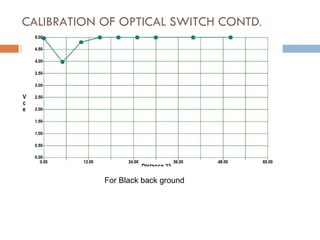
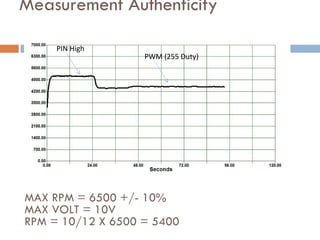
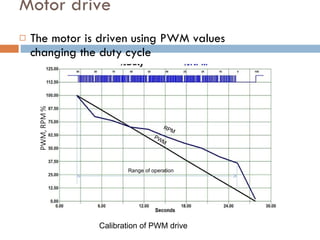
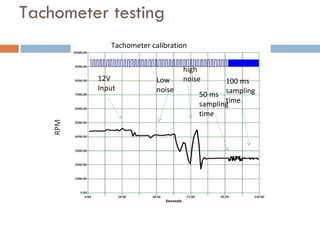
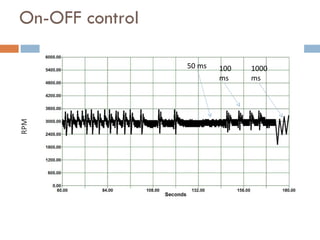
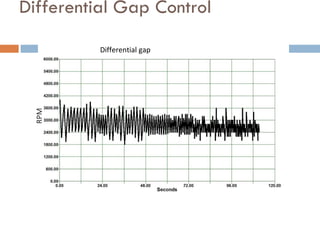
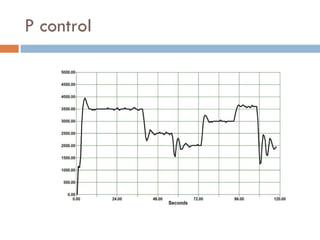
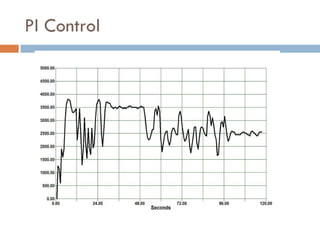
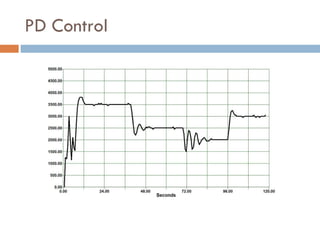
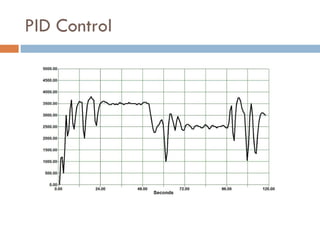
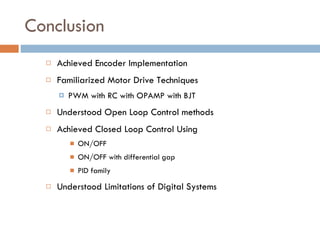
The document outlines a lab project focused on the implementation and calibration of a DC motor speed control system, including the integration of digital sensors and actuators. It details the use of various control schemes (on-off, P, PI, PD, PID) and the calibration of components such as optical switches and tachometers. The project concludes with insights into encoder design, motor drive techniques, and the limitations of digital systems.
![IMPLEMENTATION OF A DC MOTOR SPEED CONTROL MAE 576 [MECHATRONICS] LAB-3 GROUP E Chembrammel Elavunkal Srinivasan Vishwajeet University at Buffalo, Mechatronics, Spring 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt3-100514031851-phpapp01/75/Lab-3-DC-Motor-Control-1-2048.jpg)