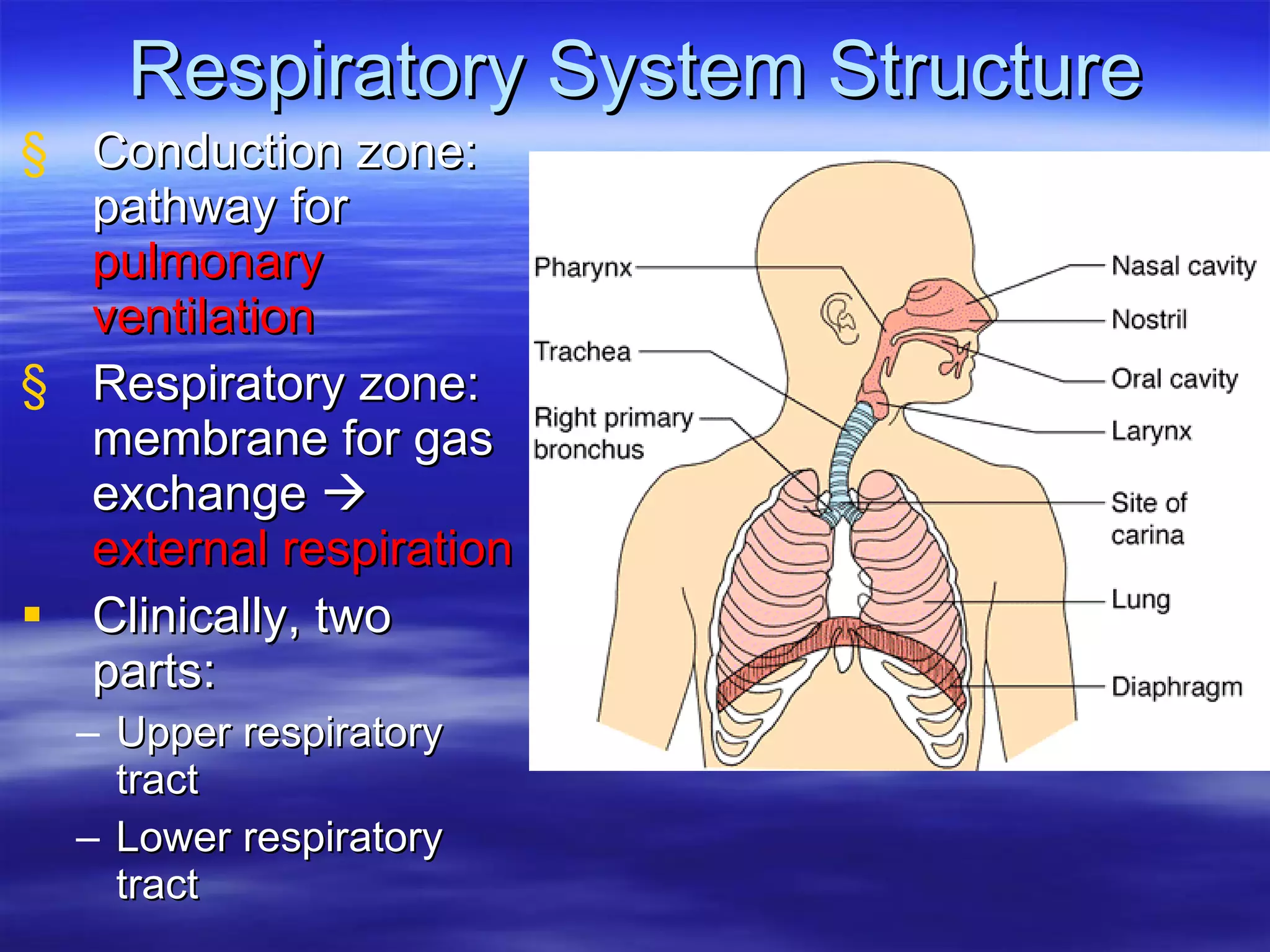
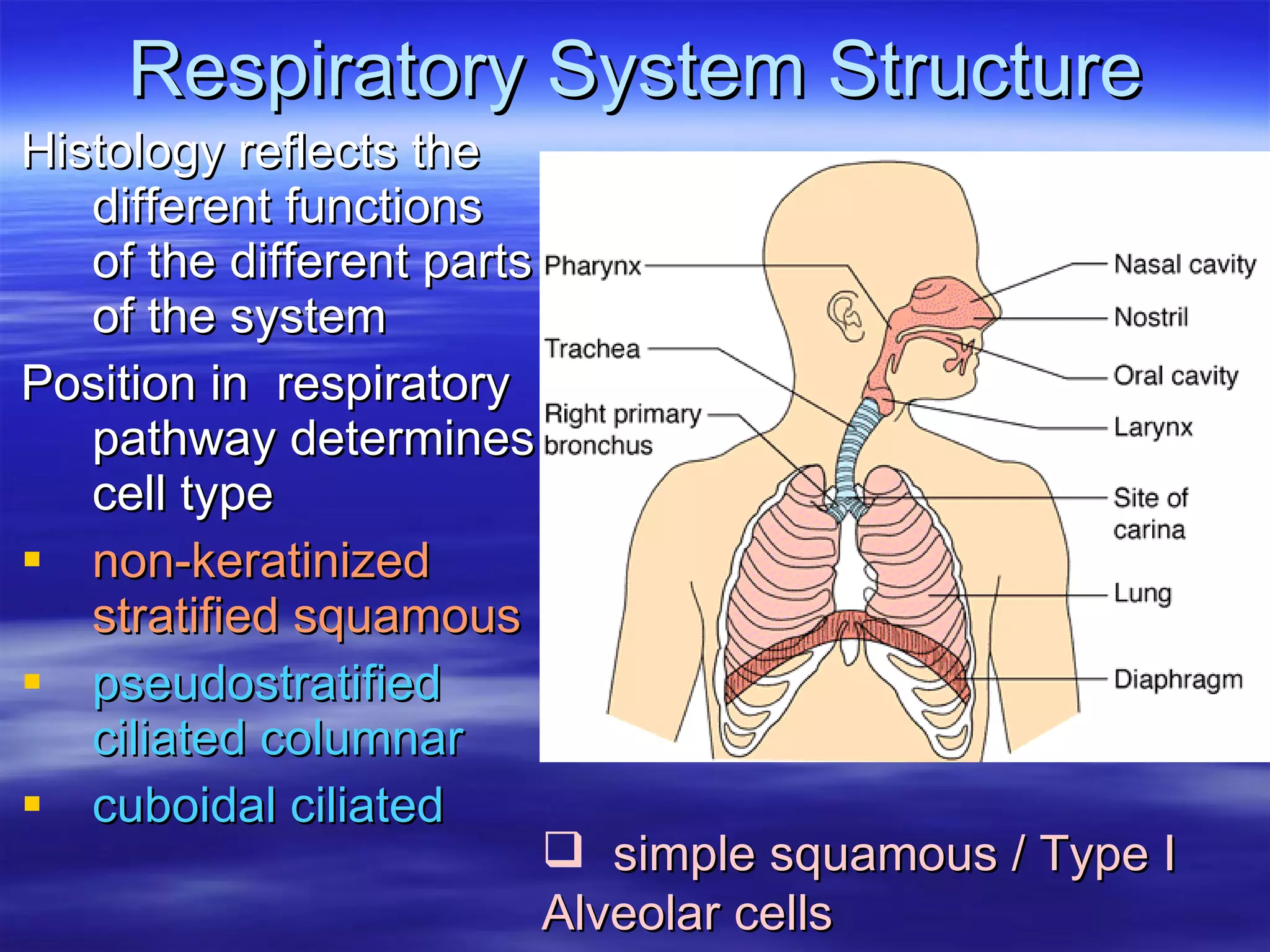
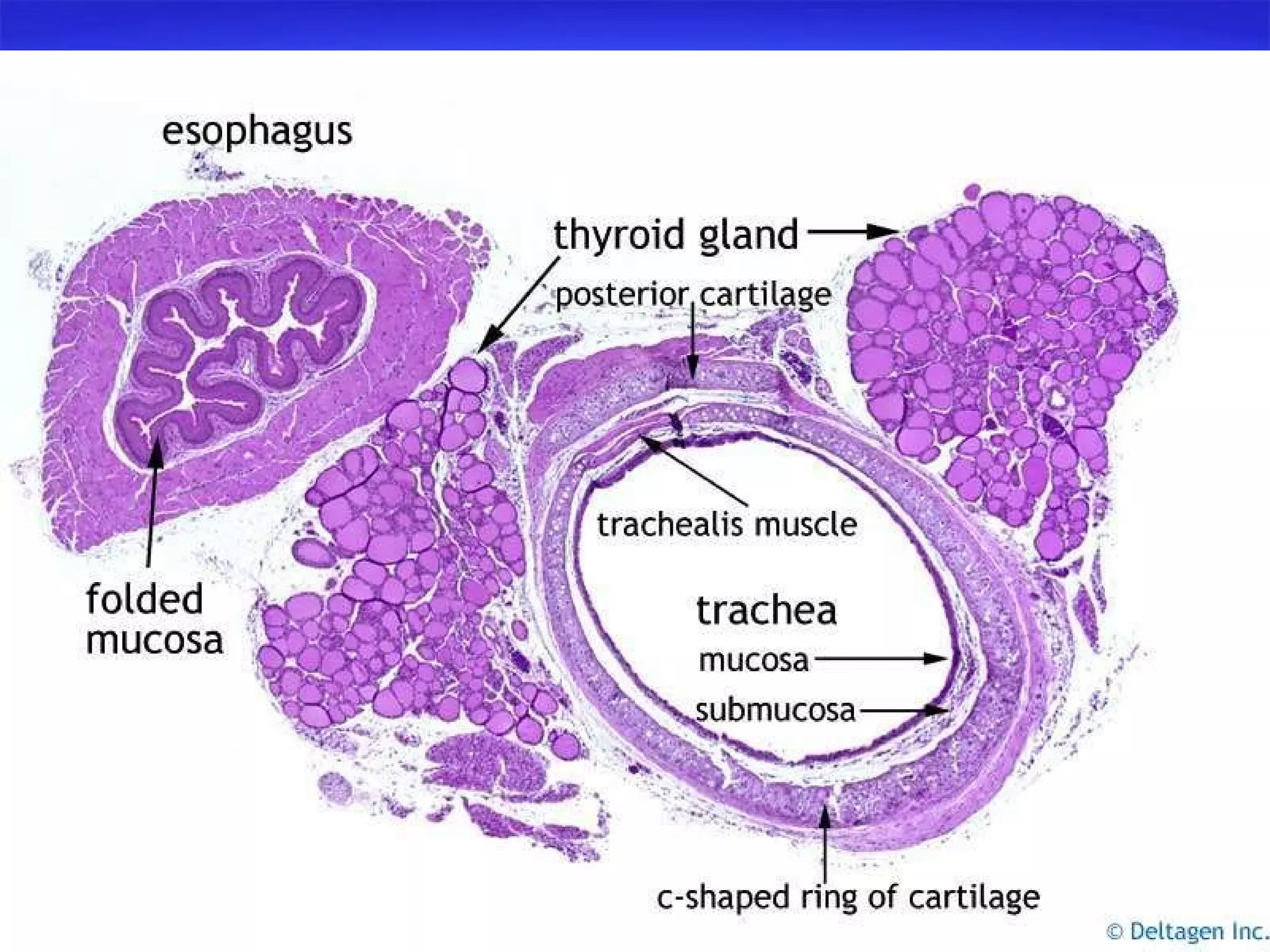
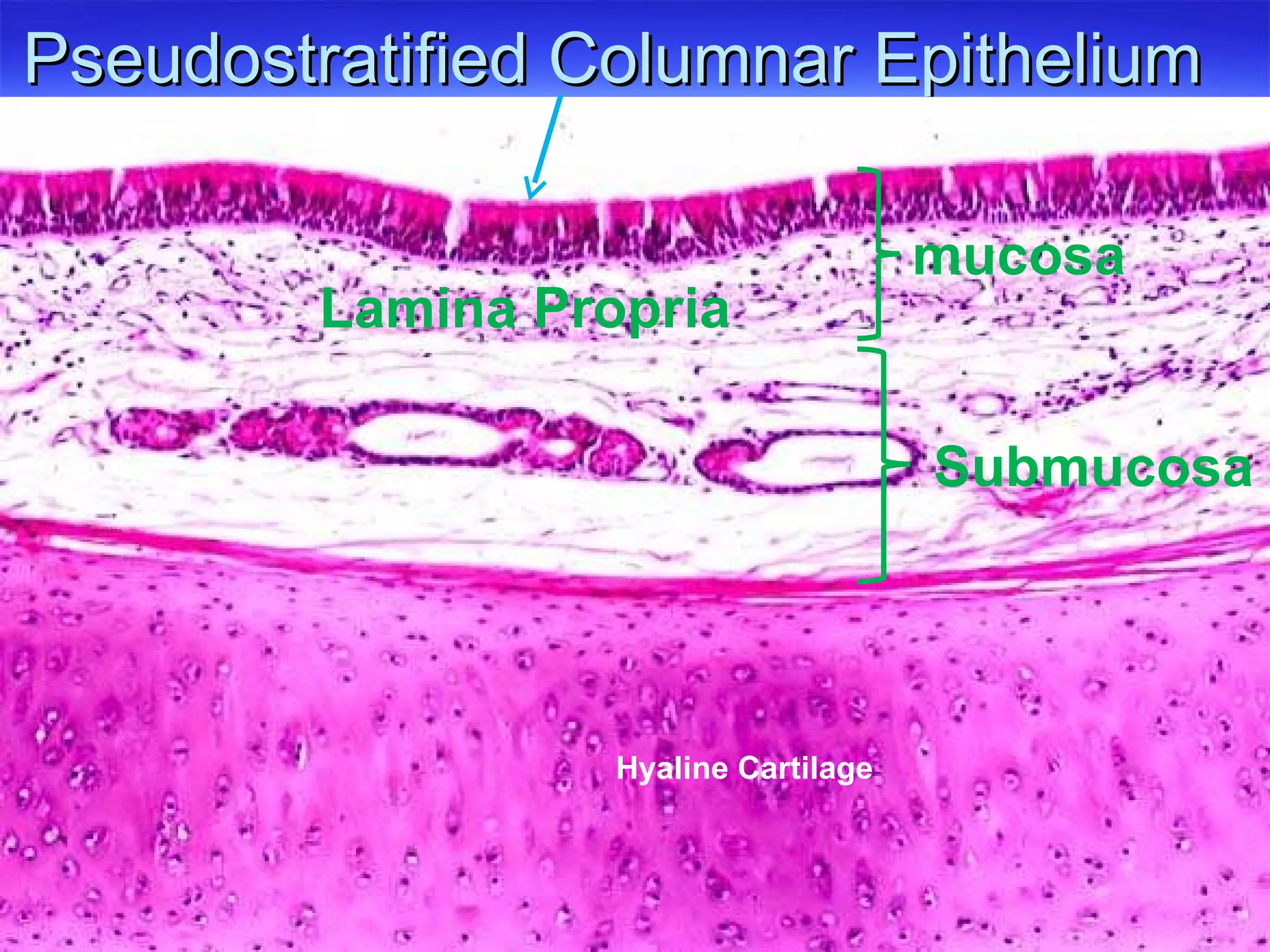
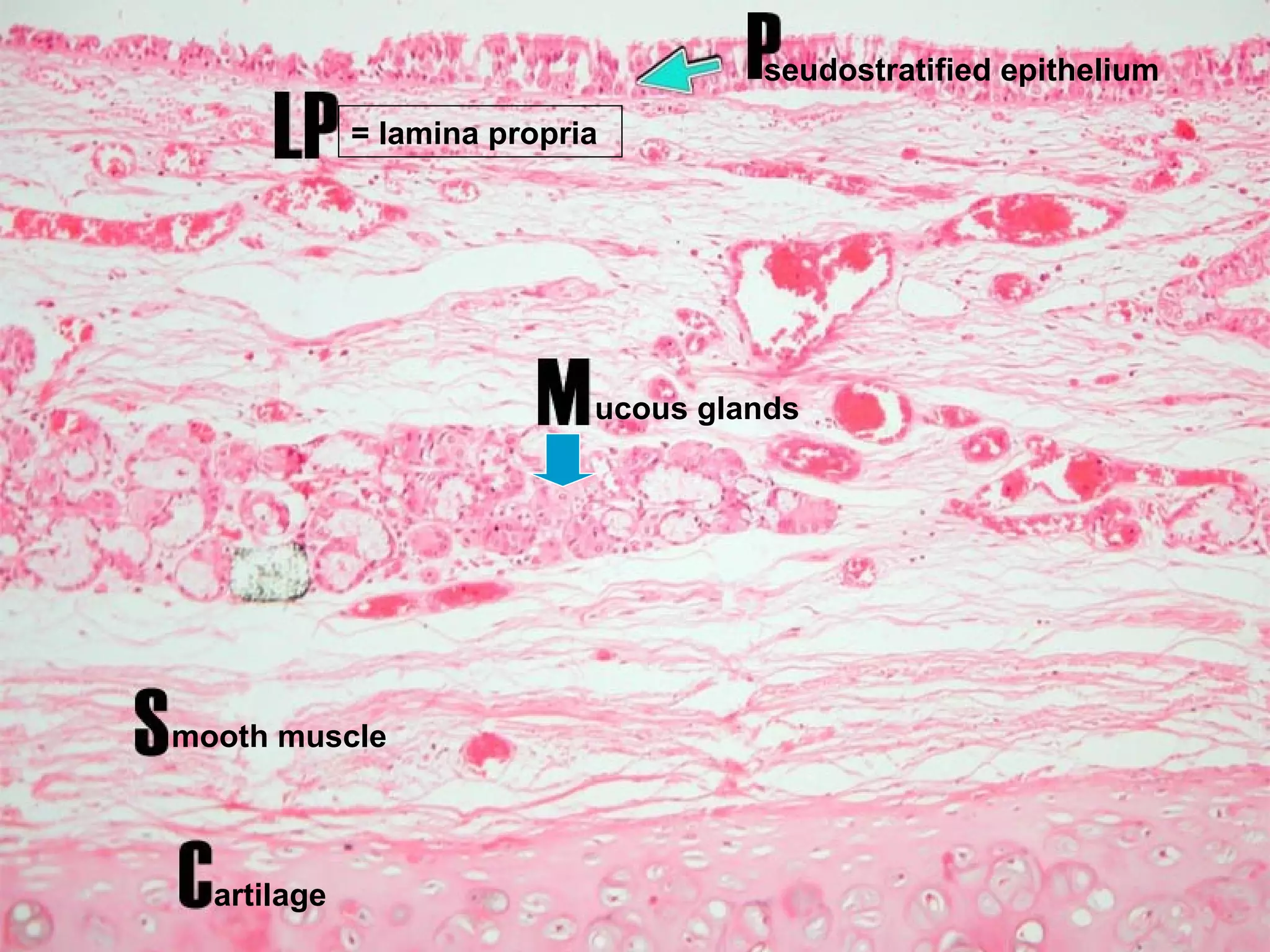
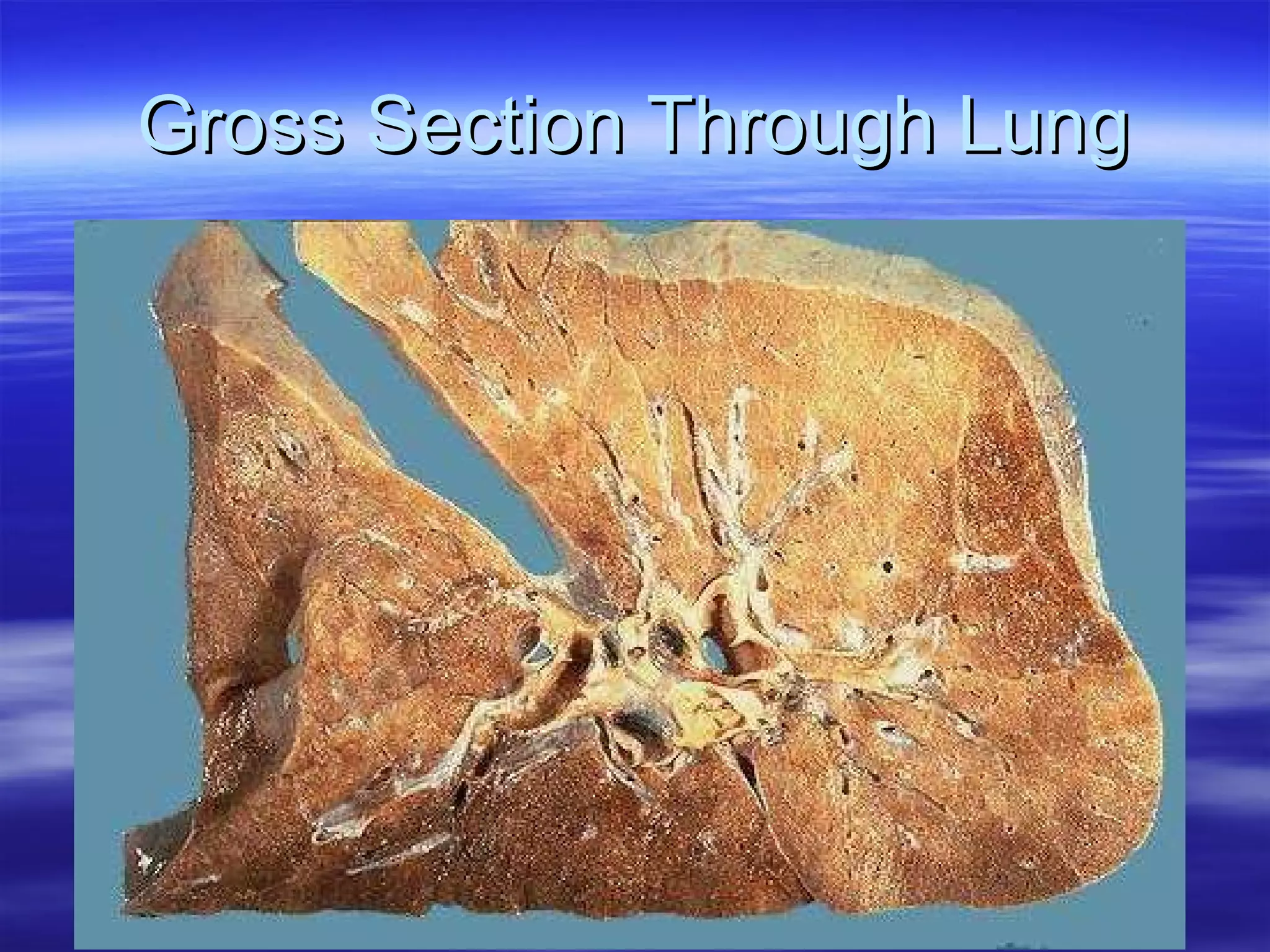
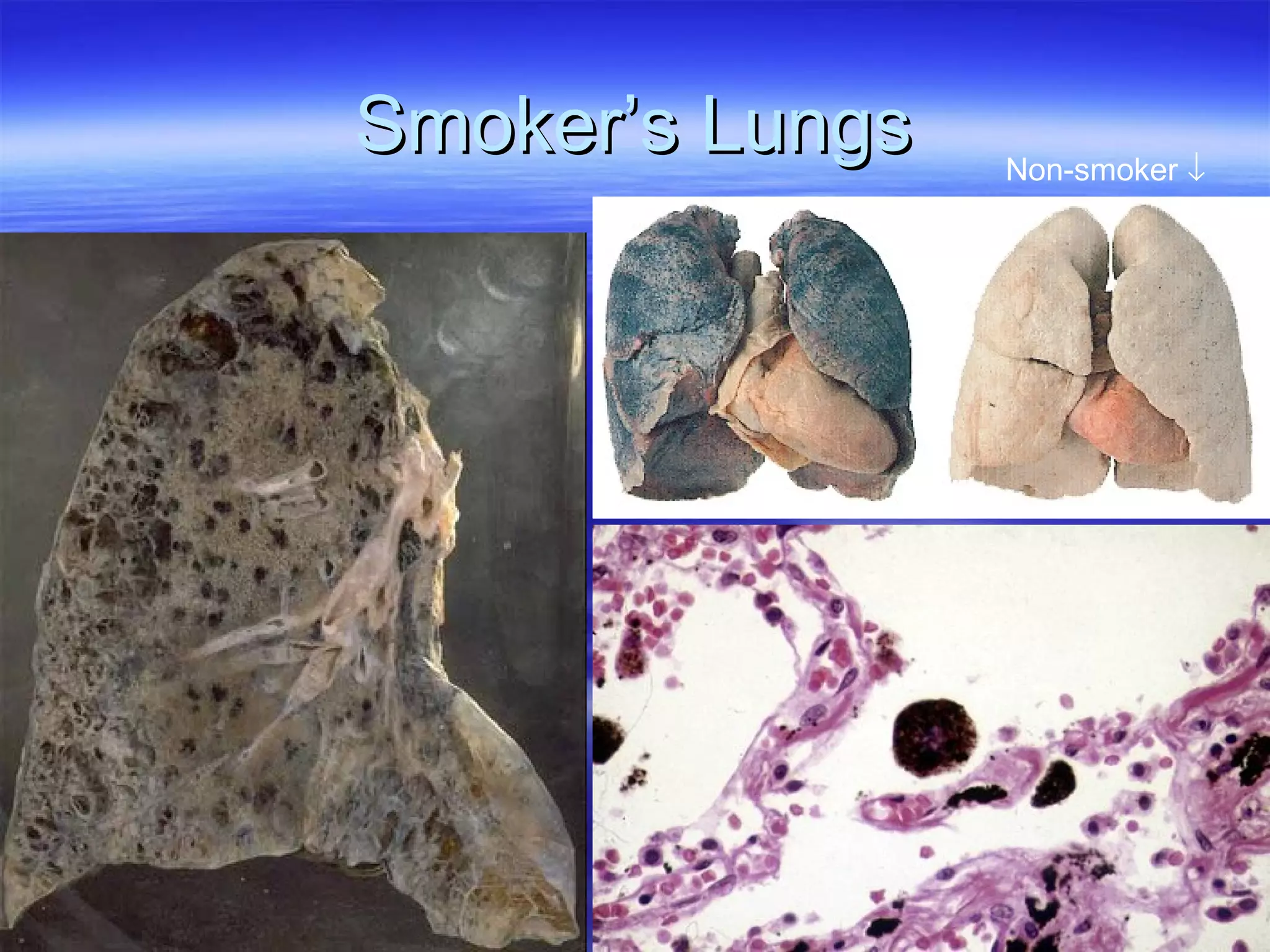
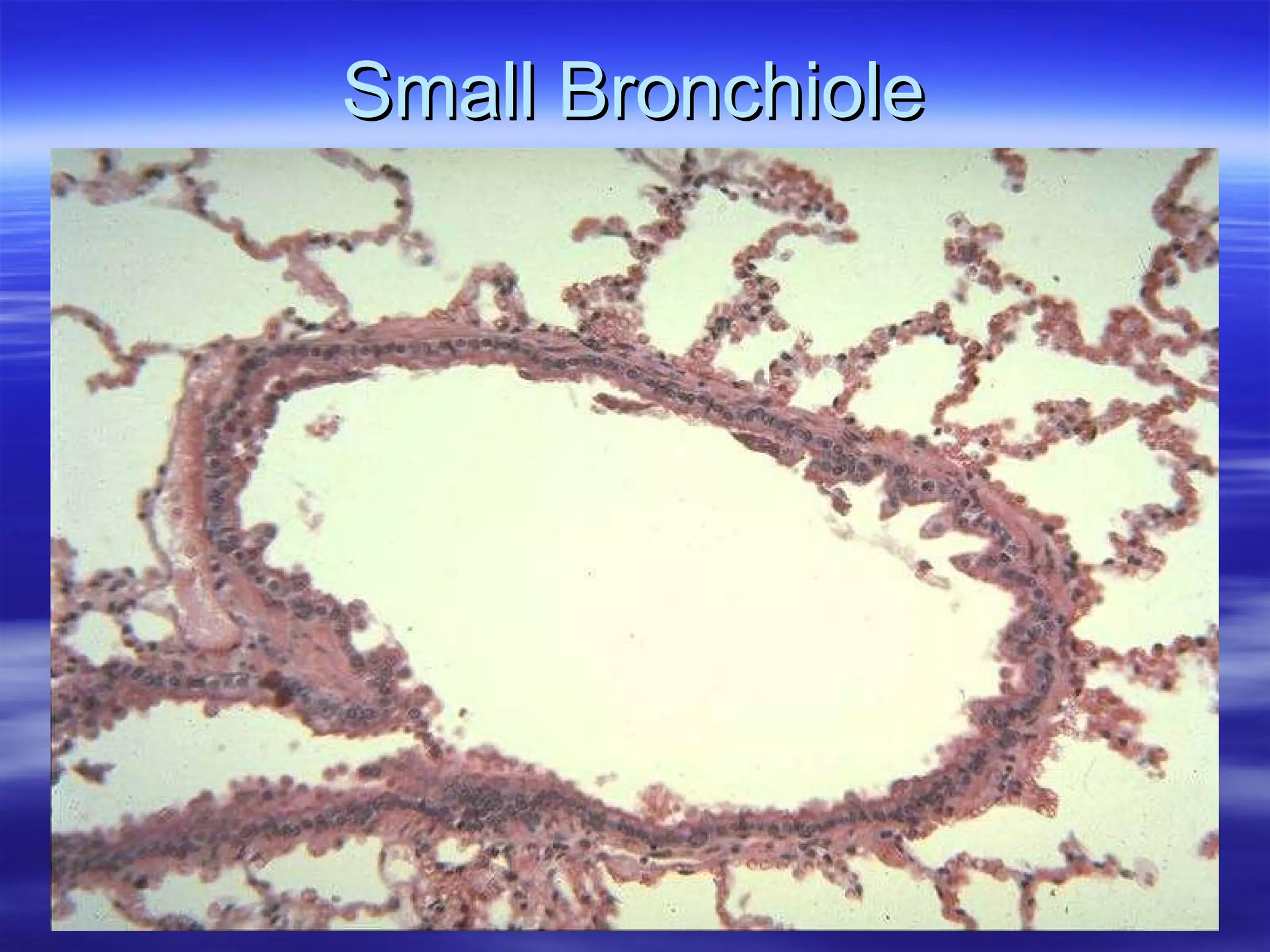
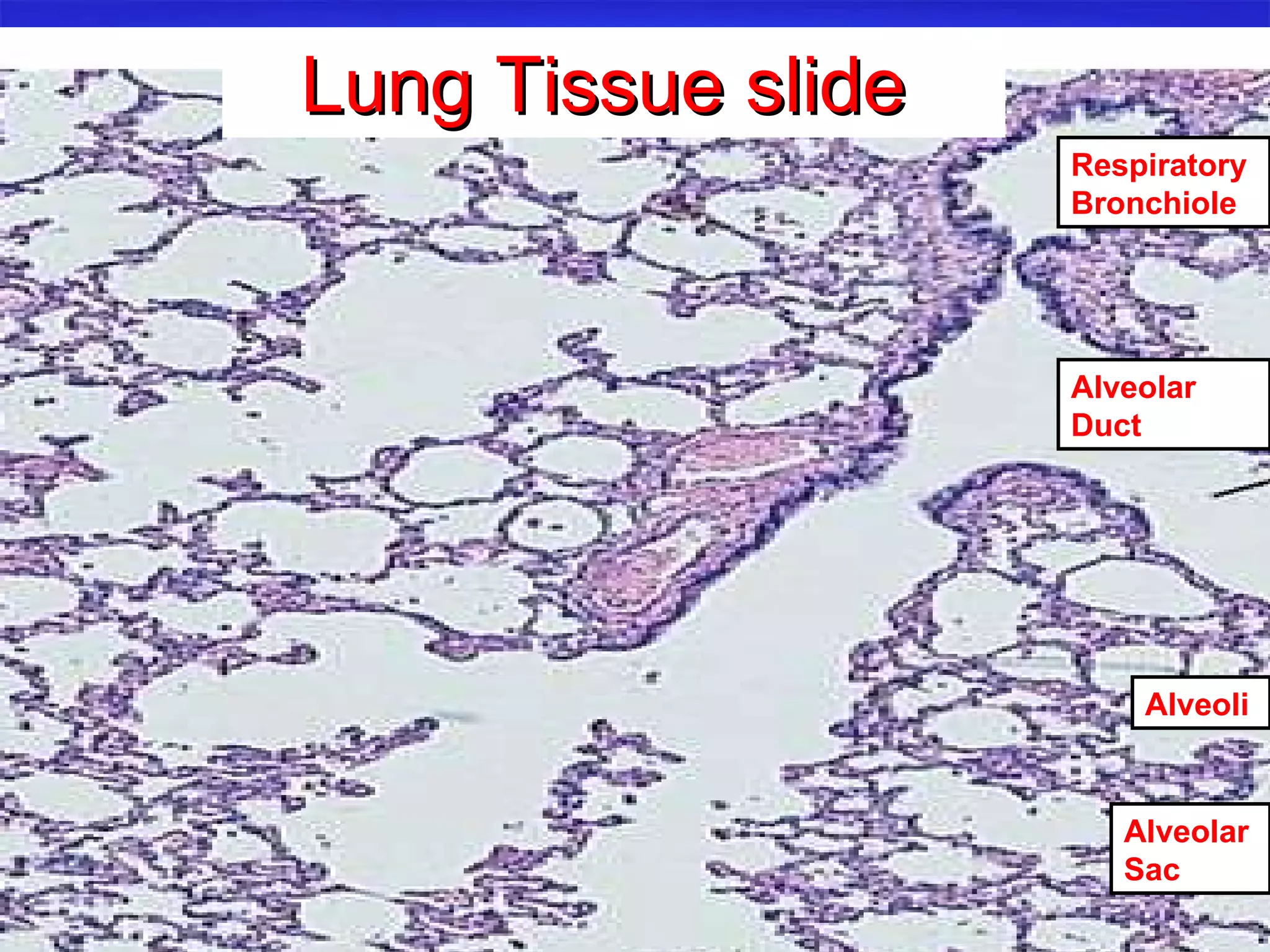
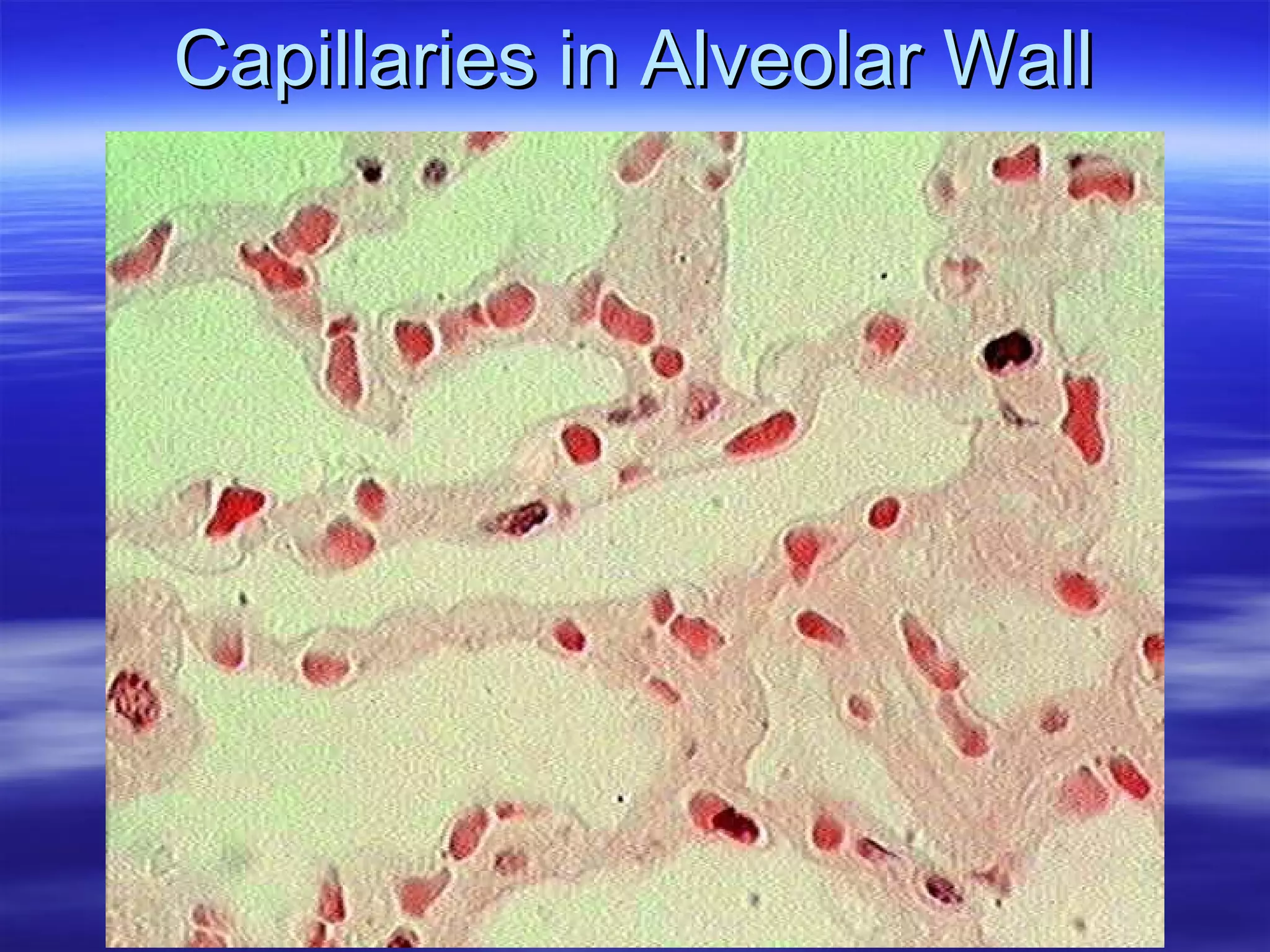
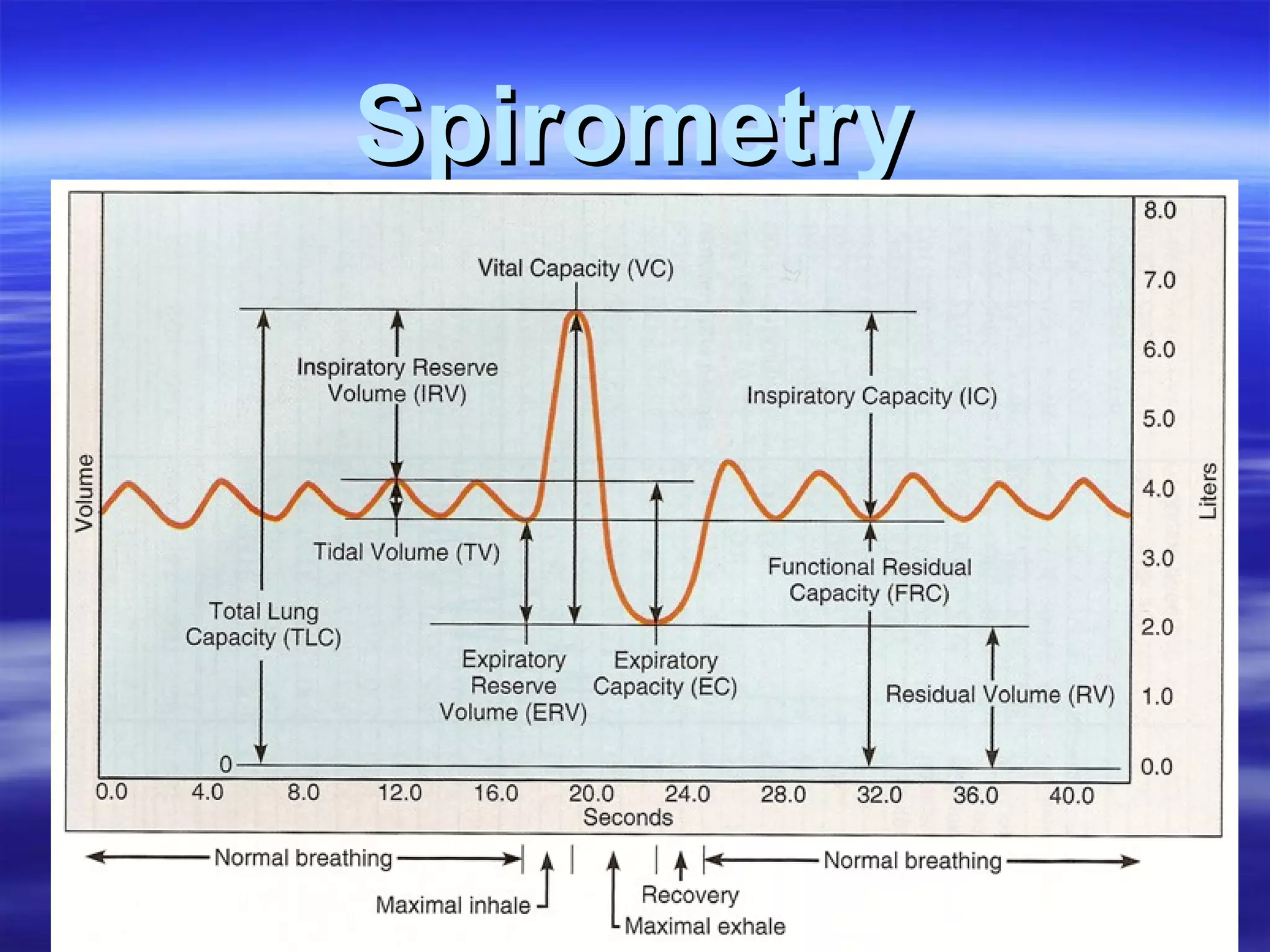
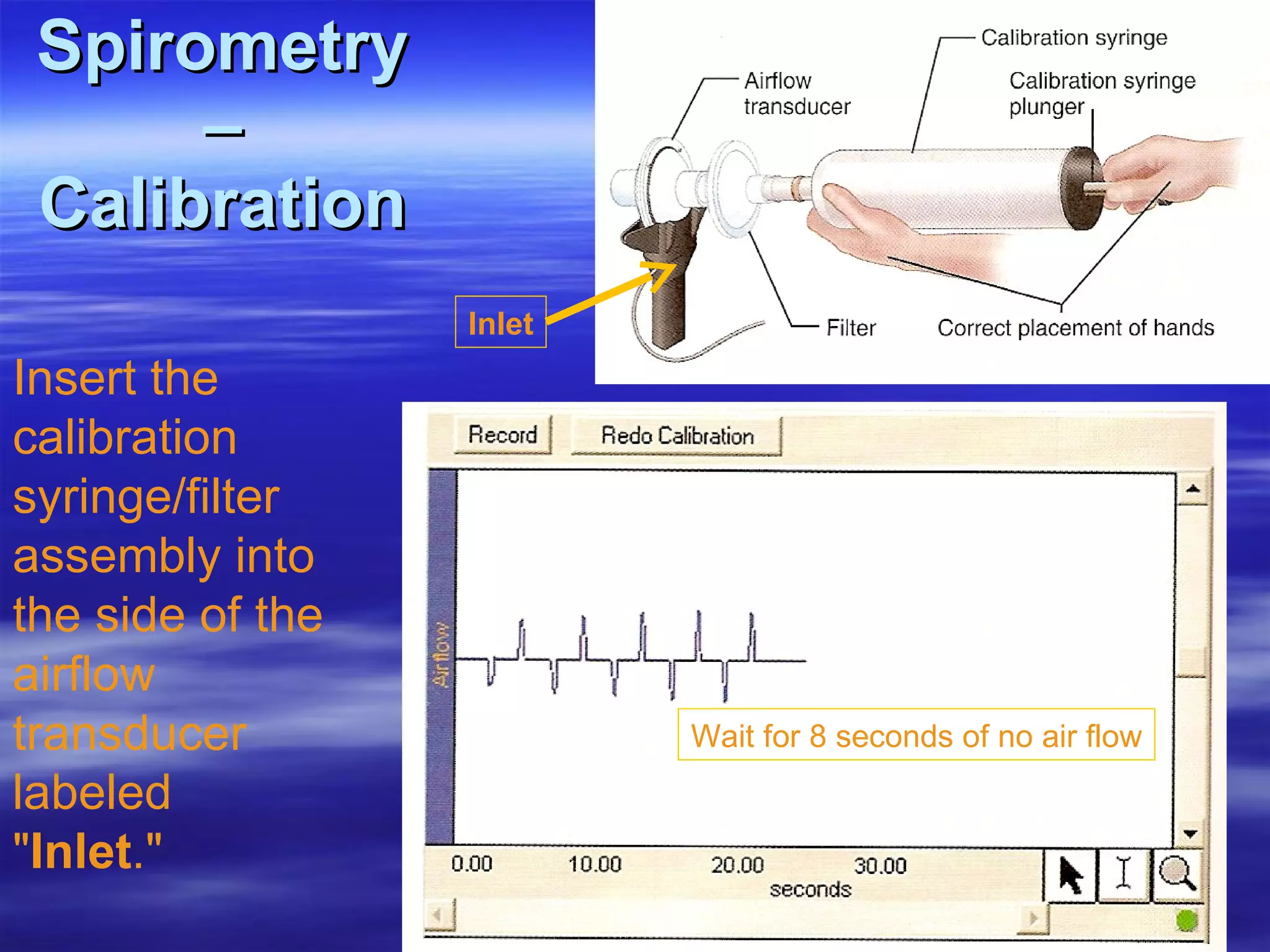
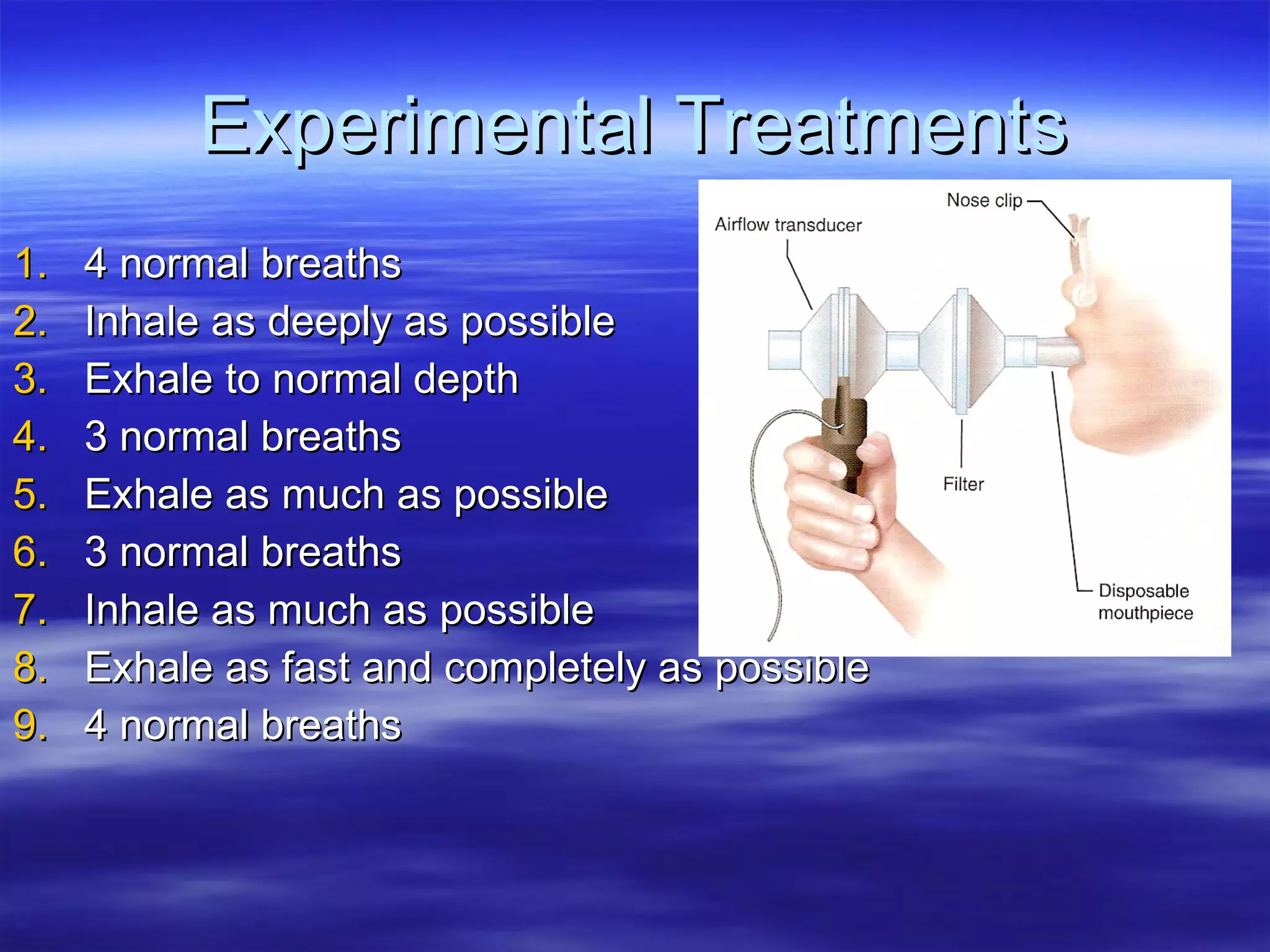
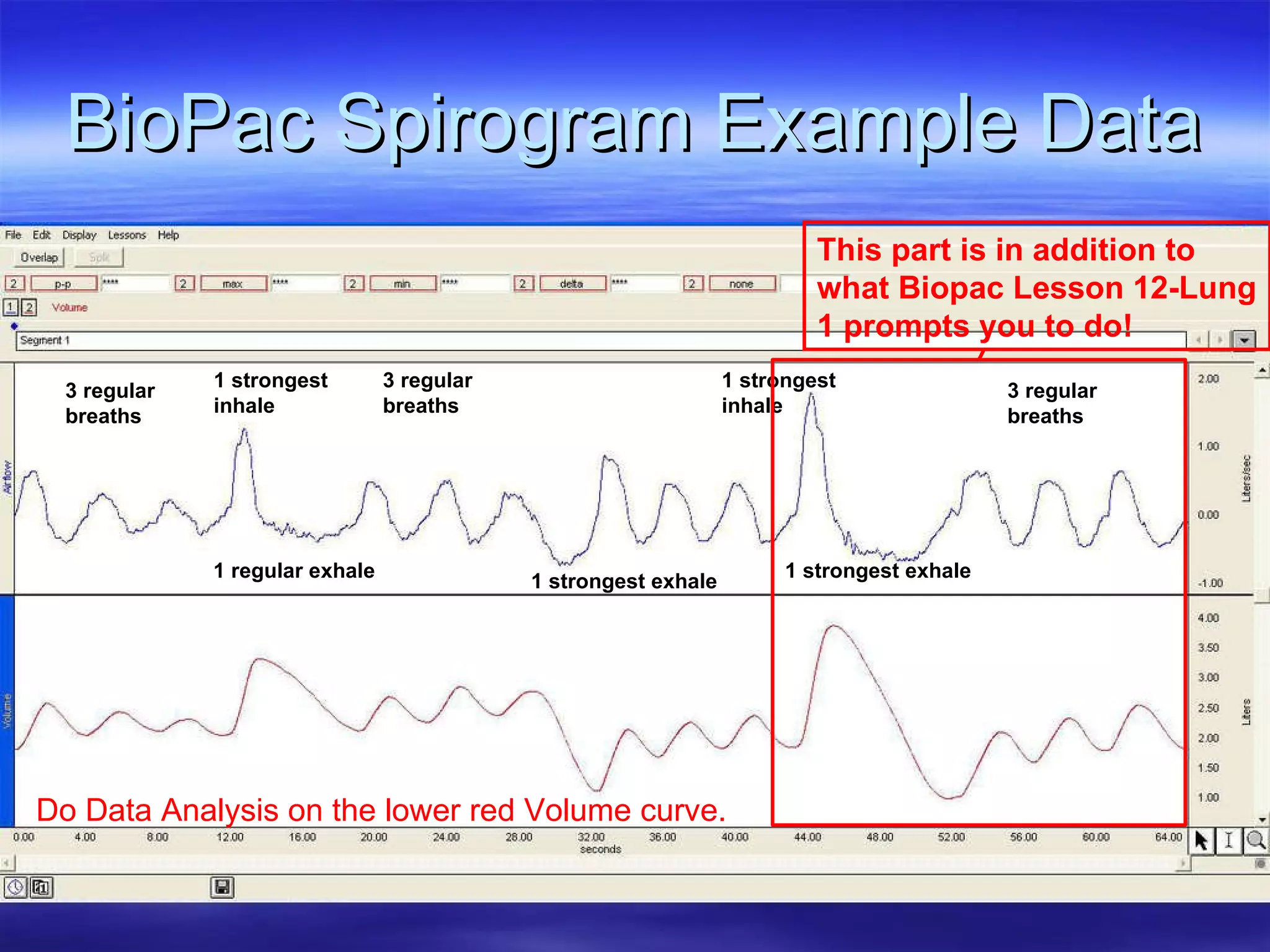
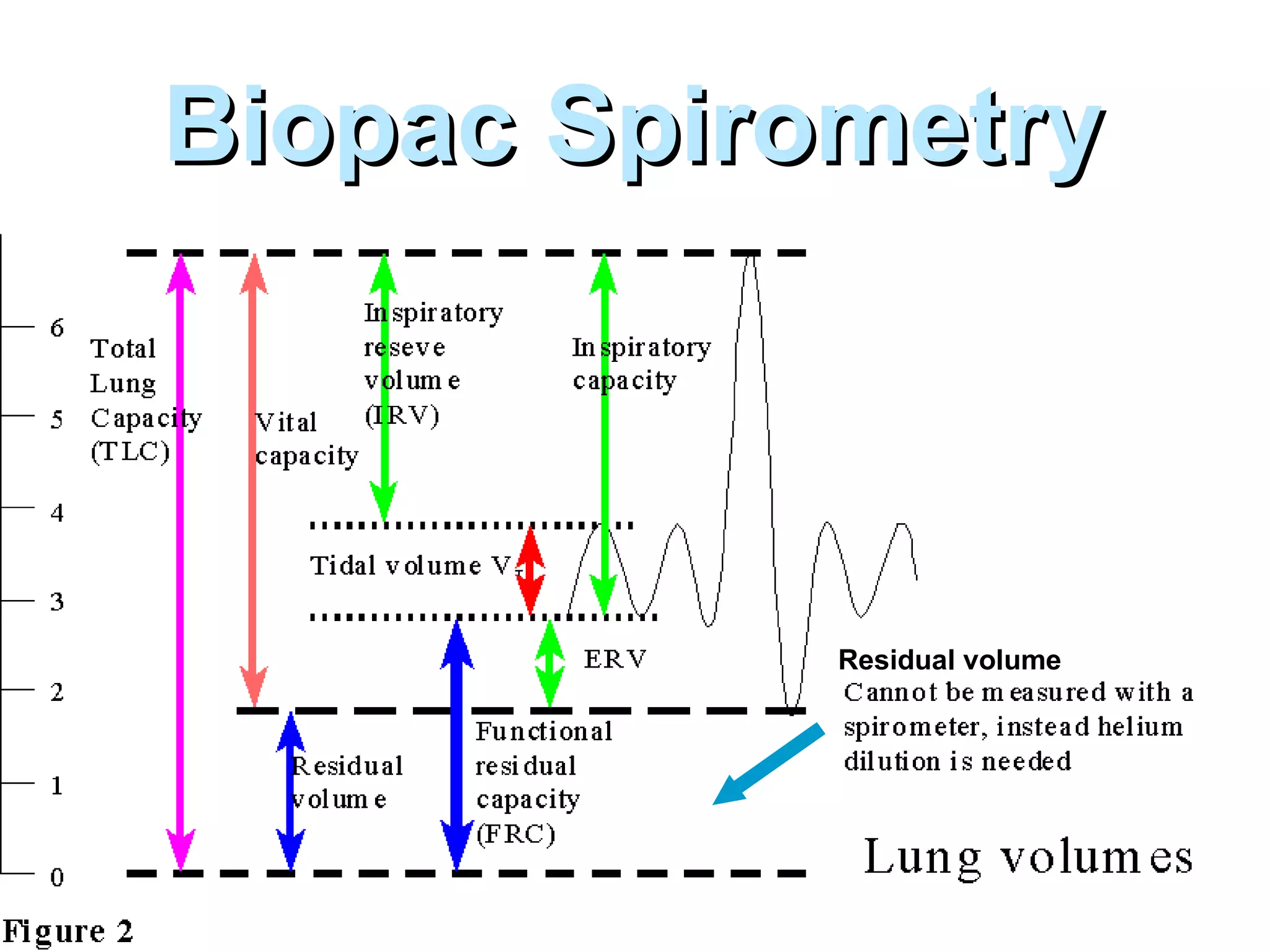
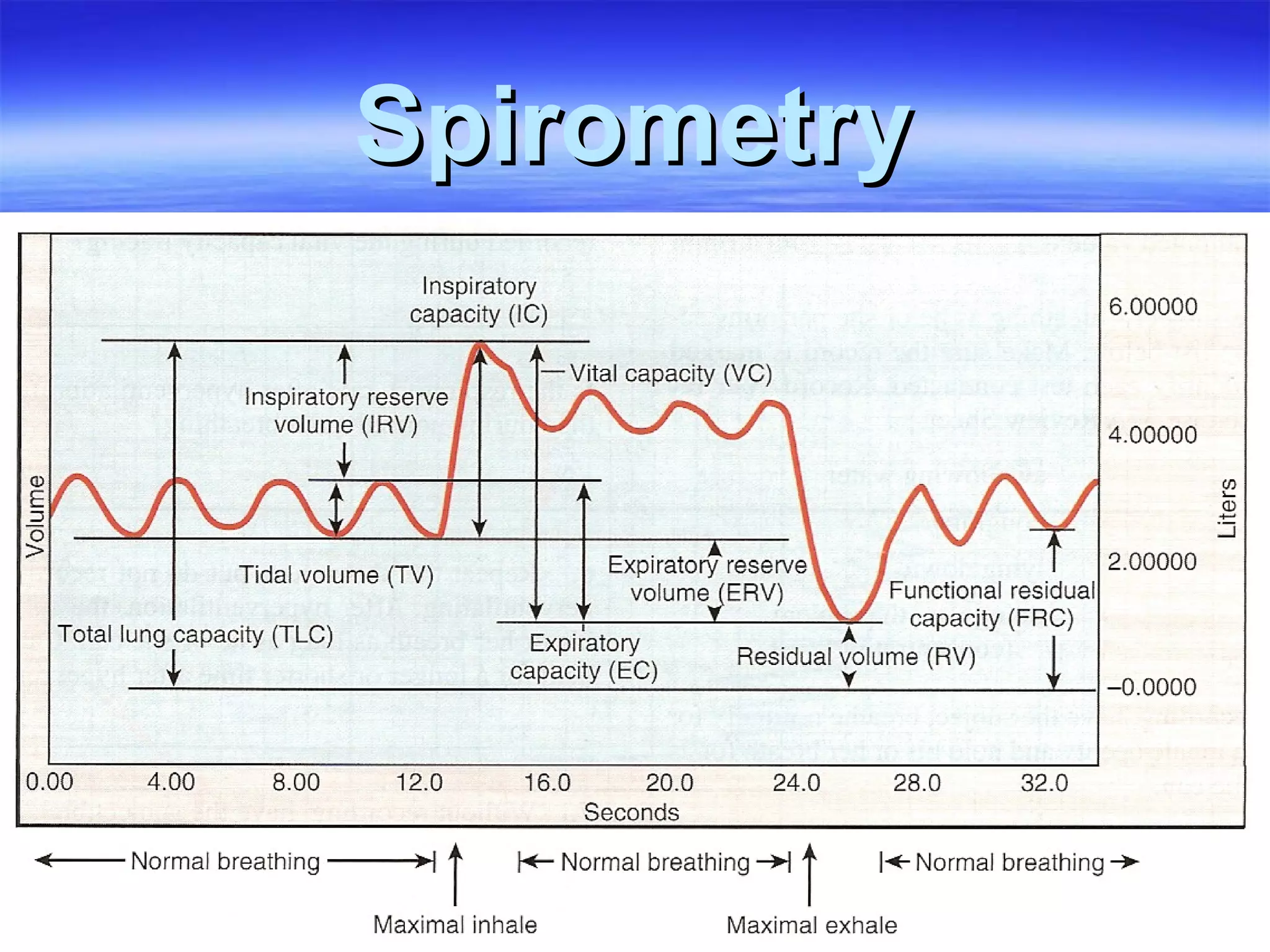
The document summarizes a lab on the respiratory system and spirometry. It describes the parts of the respiratory system including the conduction zone for ventilation and respiratory zone for gas exchange. It examines histology samples of different parts of the respiratory system and how the structure relates to function. The document then discusses spirometry and how it is used to measure lung volumes and capacities like tidal volume, vital capacity, and residual volume. Procedures for calibrating and performing spirometry tests on the Biopac system are provided along with an example spirogram.