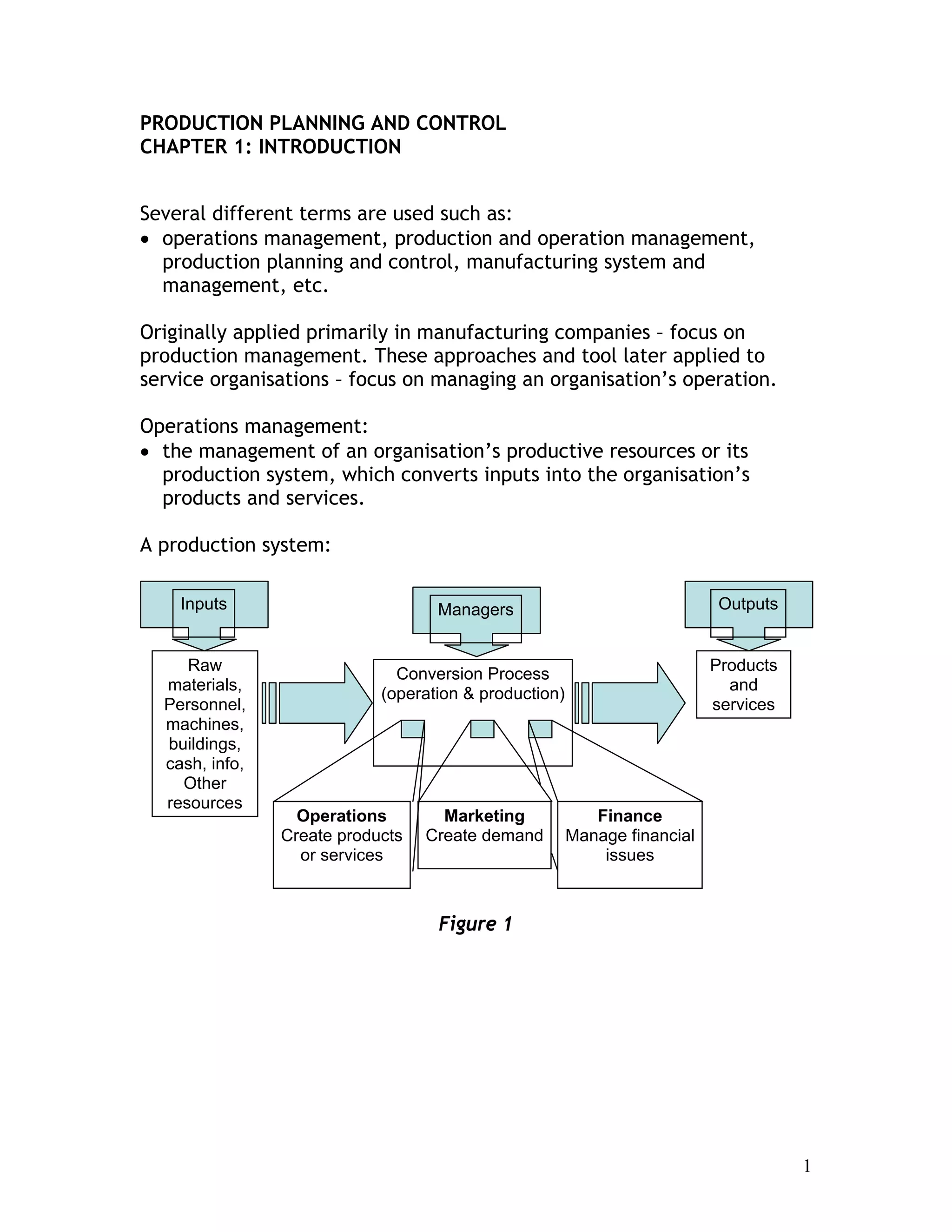
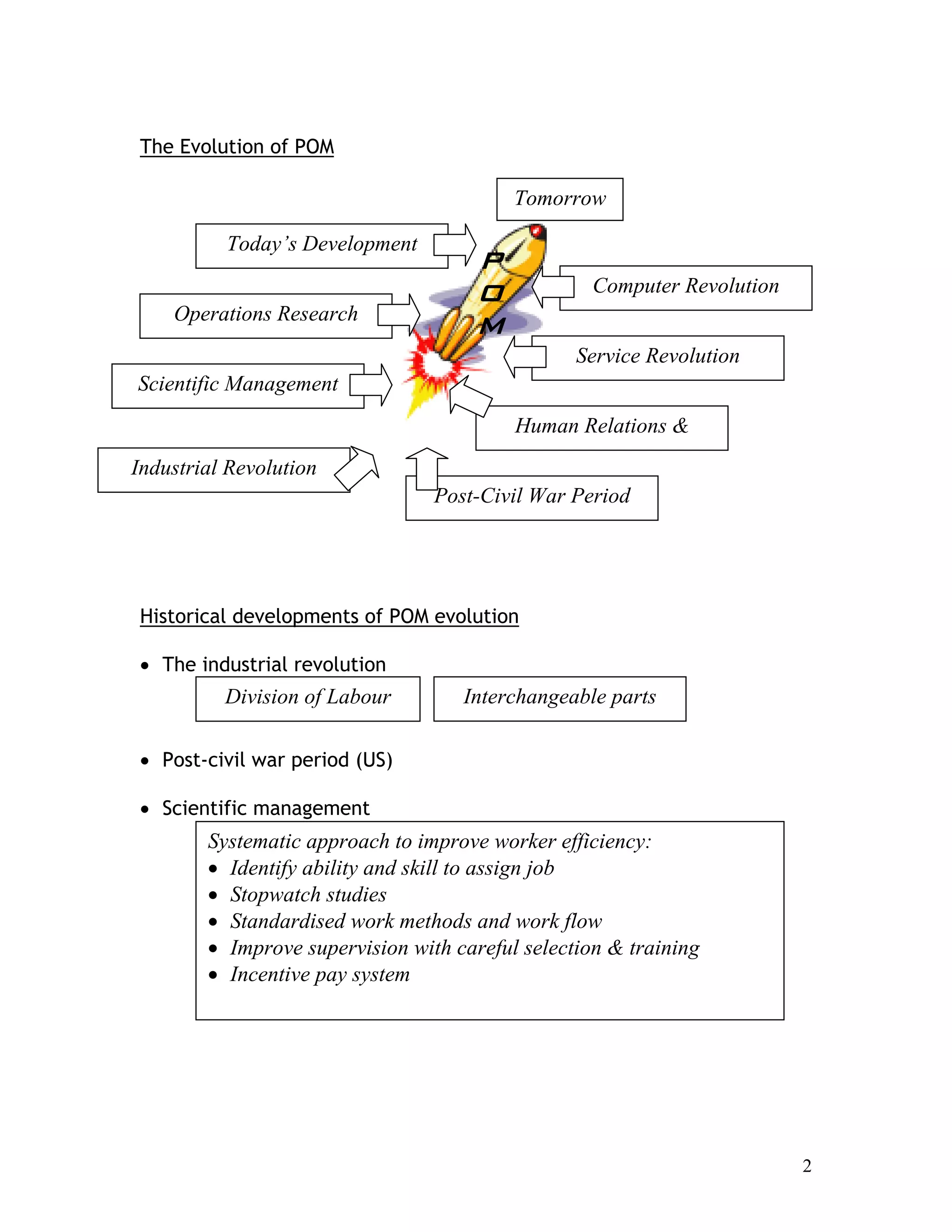
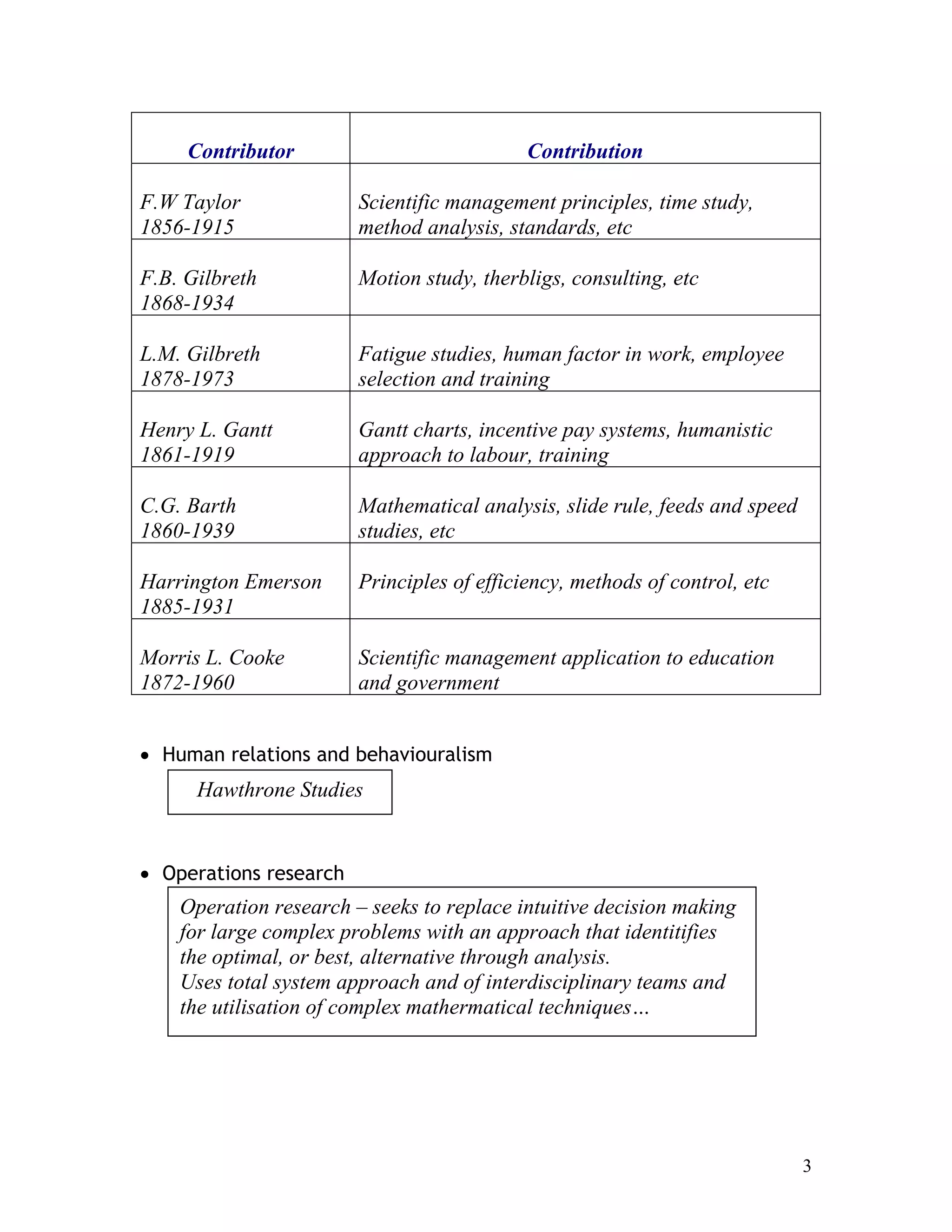
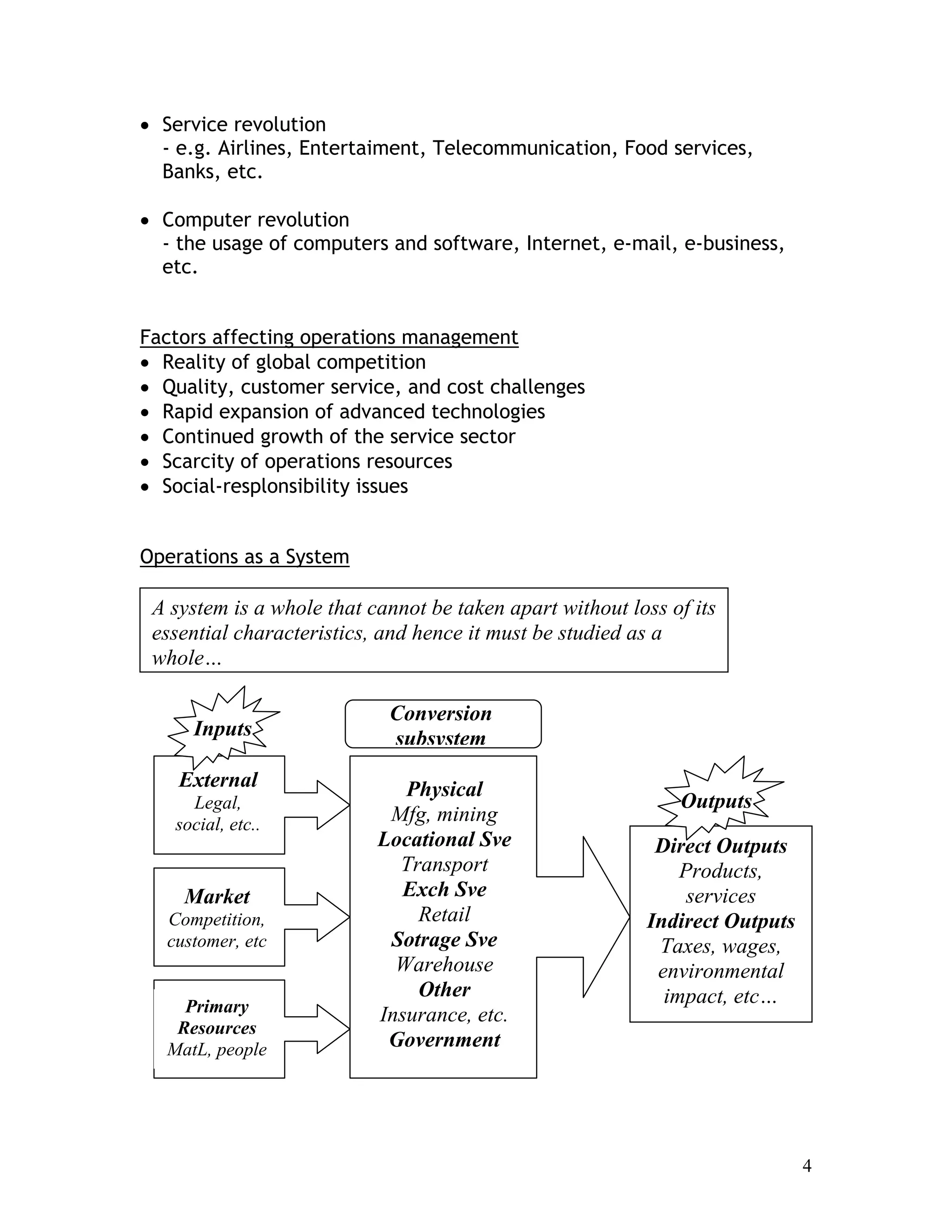
This document provides an introduction to production planning and control (POM). It discusses key terms in POM like operations management. POM focuses on managing an organization's production system to convert inputs into products and services. The evolution of POM is then summarized, from the industrial revolution to developments in scientific management, human relations, operations research, and computer technology. Influential contributors to the development of POM concepts are also listed.
![5
Decision making in POM
Assignment 1
Find at least three (3) entry-level jobs (in Malaysia) at three (3) different
companies which are related to the production and operations
management function. Describe the jobs and how they are related to the
production and operation management. Describe the companies,
mentioning what type of prodcution system they are, primary inputs,
conversion subsystem and outputs. You could search for the jobs at
Jobstreet (www.jobstreet.com) or JobsDB (www.jobsdb.com).
[][][]
Strategic
Decision
Operating
Decision
Control
Decision
Decisions about products, processes, and
facilities. These decisions are of strategic
importance and have long-term significance for
the organisation
Decisions about planning production to meet
demand. These decisions are necessary if the
ongoing production of goods and services is to
satisfy the demands of the market and provide
profit for the company
Decisions about planning and controlling
operations. These decisions concern with the
day-to-day activities of workers, quality of
products and service, production and overhead
costs, and maintenance of equipment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l2-130507022655-phpapp01/75/L2-5-2048.jpg)