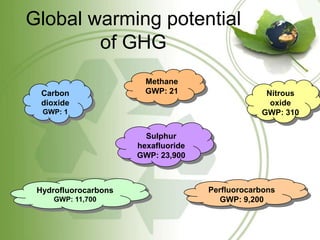
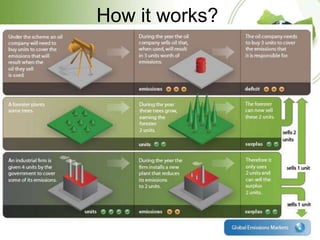
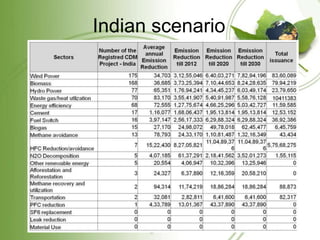
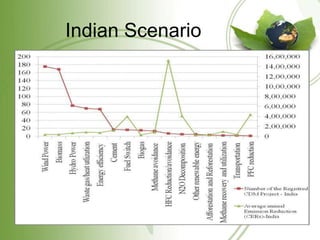
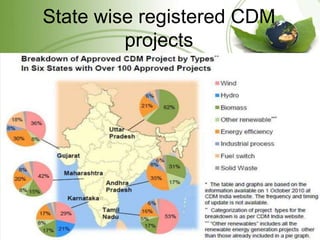
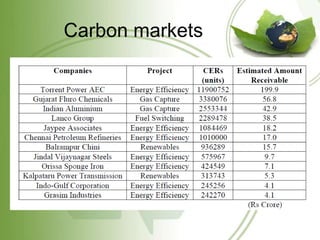
The document discusses the Kyoto Protocol's impact on India, covering global warming, emissions reduction mechanisms, and India's role in these frameworks. It details the history and objectives of the Kyoto Protocol, as well as India's initiatives like the National Action Plan and various carbon trading projects. Additionally, it addresses current affairs related to climate talks and global implications of climate change.