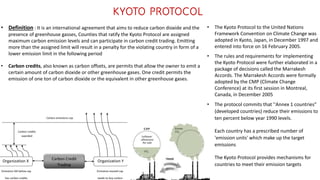
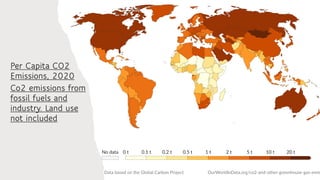
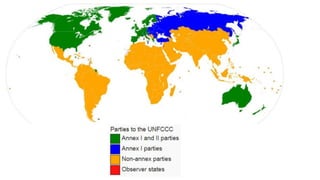
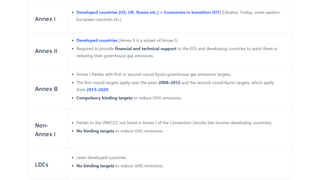
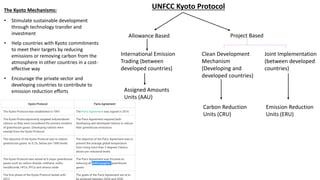
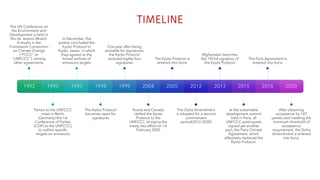
The Kyoto Protocol, adopted in December 1997 and entered into force in February 2005, is an international agreement aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particularly for Annex I (developed) countries, to 10% below 1990 levels. It includes mechanisms for emissions trading and project-based credits like the Clean Development Mechanism, allowing developed countries to invest in developing nations to meet their emission targets. The protocol was eventually succeeded by the Paris Agreement, which was adopted in 2015 and entered into force in 2016.