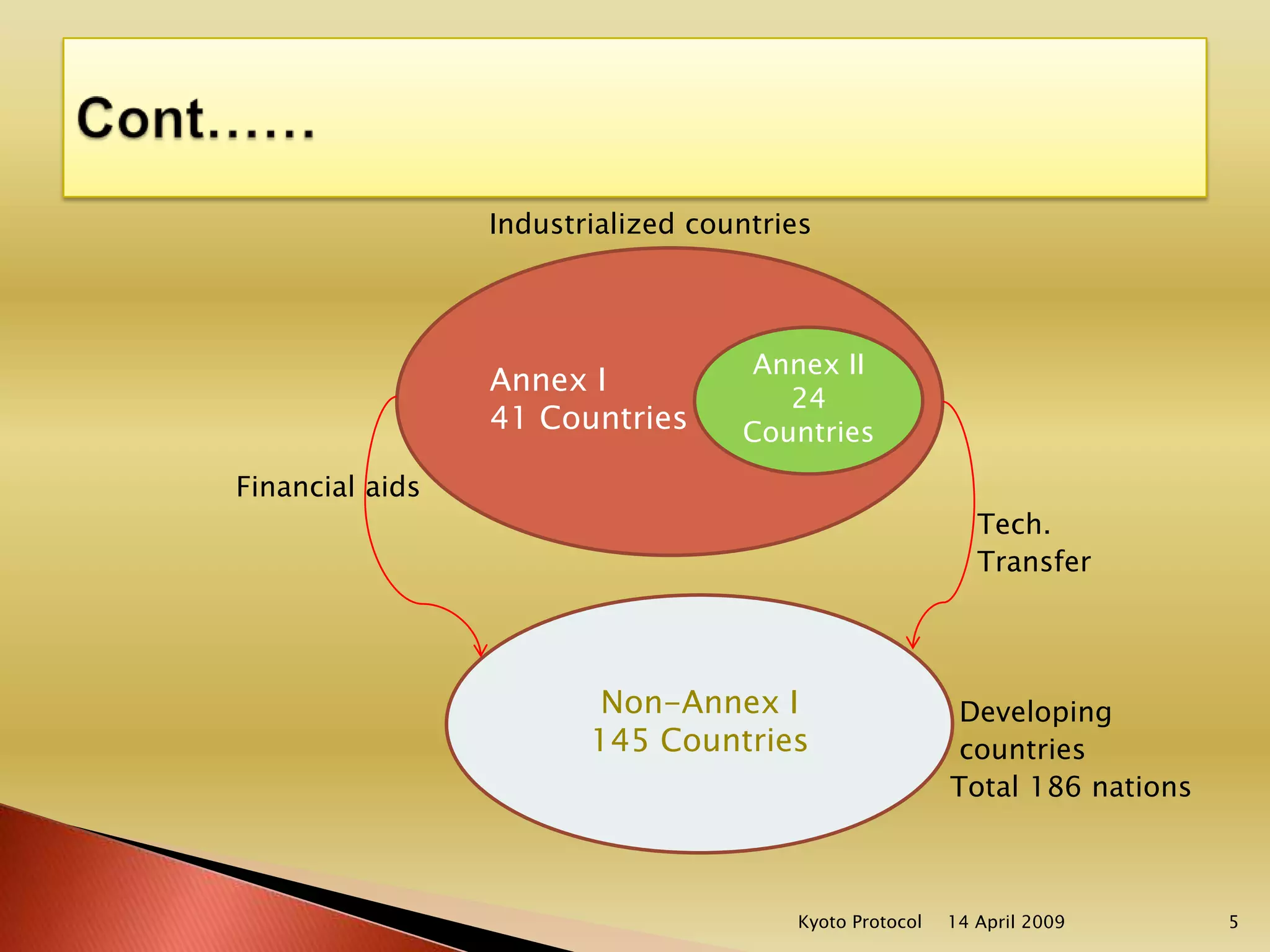
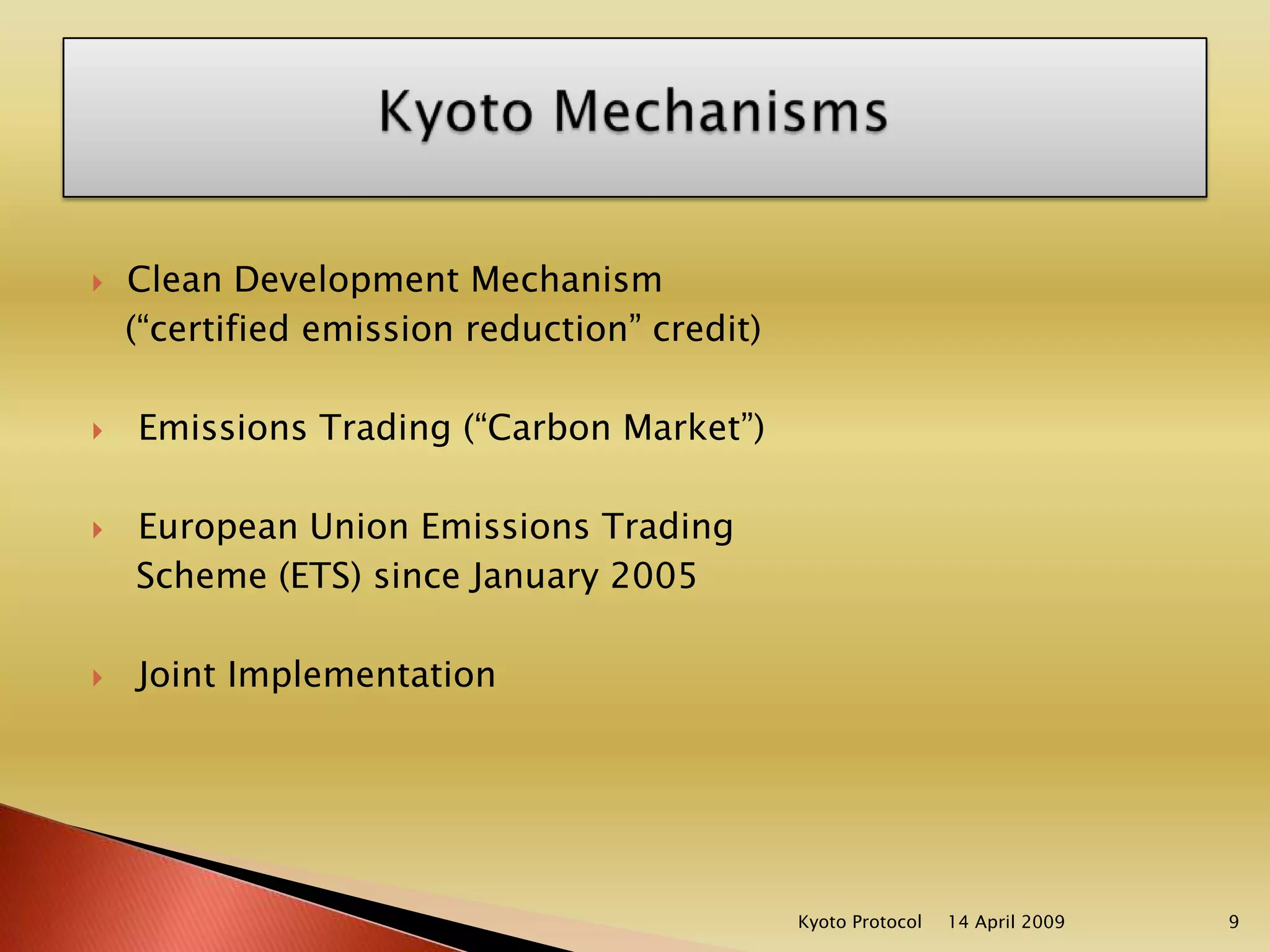
This document discusses India's involvement with the Kyoto Protocol and the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM). It explains that the Kyoto Protocol aims to reduce emissions of six greenhouse gases. It divides countries into three categories - Annex I countries have emission reduction commitments, Annex II countries provide financial and technological support, and non-Annex I developing countries have no commitments. The CDM allows projects in developing countries to earn certified emissions reductions credits that can be used by Annex I countries to meet their targets. India has many registered CDM projects and could earn billions of euros from carbon credits. The document concludes that India will be a major player in the CDM market in the near future.