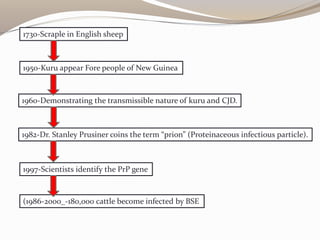
Kuru is a rare prion disease found among people in New Guinea who practiced cannibalism by eating the brains of deceased people as part of a funeral ritual. It was the first human prion disease transmitted to chimpanzees and recognized as both a neurodegenerative disease and transmissible infectious agent. Kuru is caused by an infectious prion protein found in contaminated human brain tissue and has an incubation period of 10-50 years, ultimately causing brain changes and symptoms like tremors, difficulty walking and swallowing, and malnutrition.