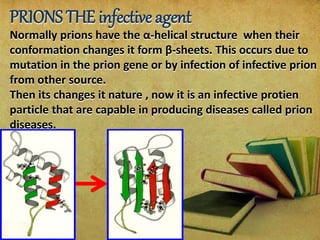
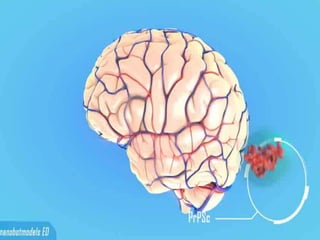
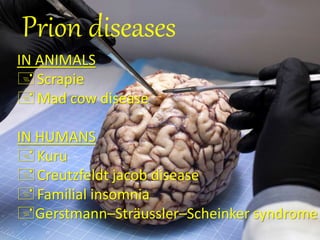
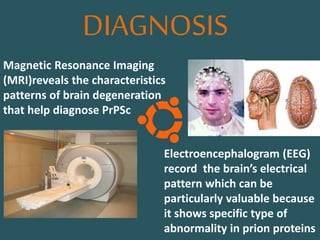
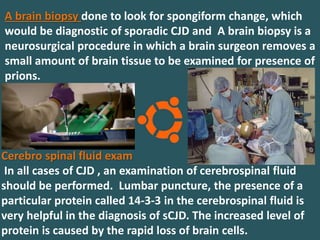
Prions are abnormal protein particles that can cause neurodegenerative diseases. They have a normal function in the body but can transform into an infectious form. When this happens, they induce other normal prion proteins to adopt the abnormal shape. Common prion diseases include scrapie in sheep, mad cow disease, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans. There are currently no effective treatments for prion diseases, so prevention and diagnosis are important.