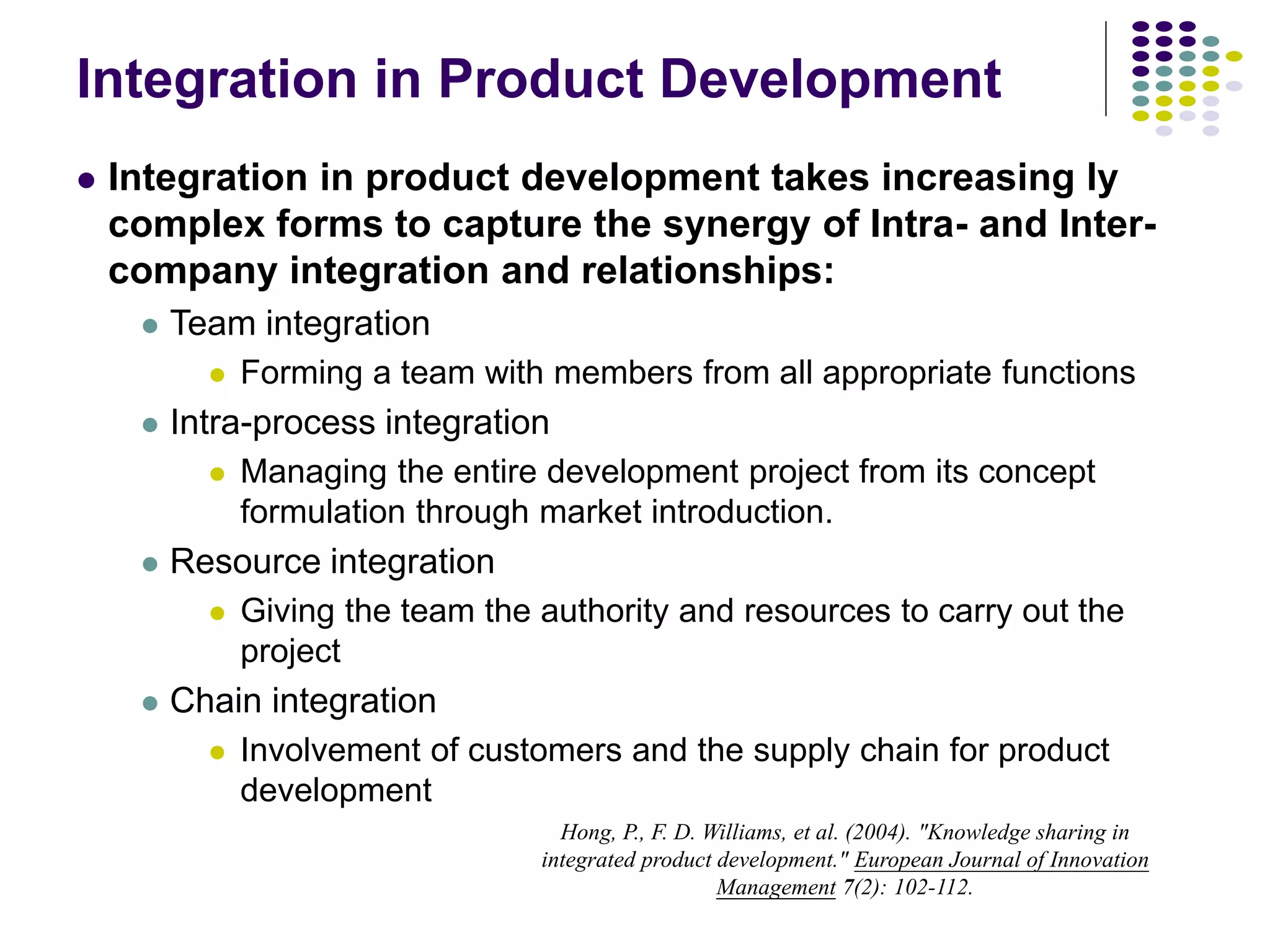
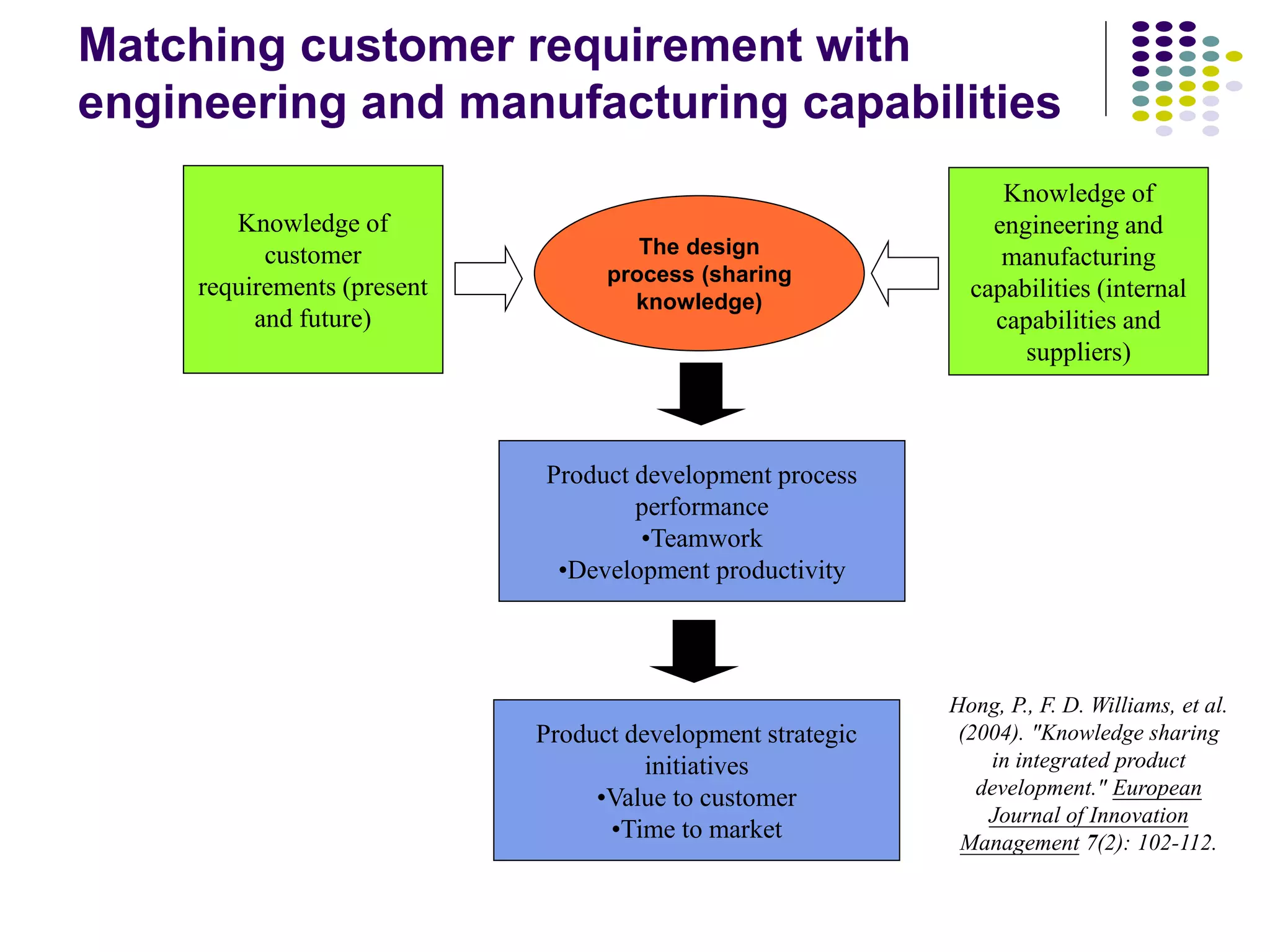
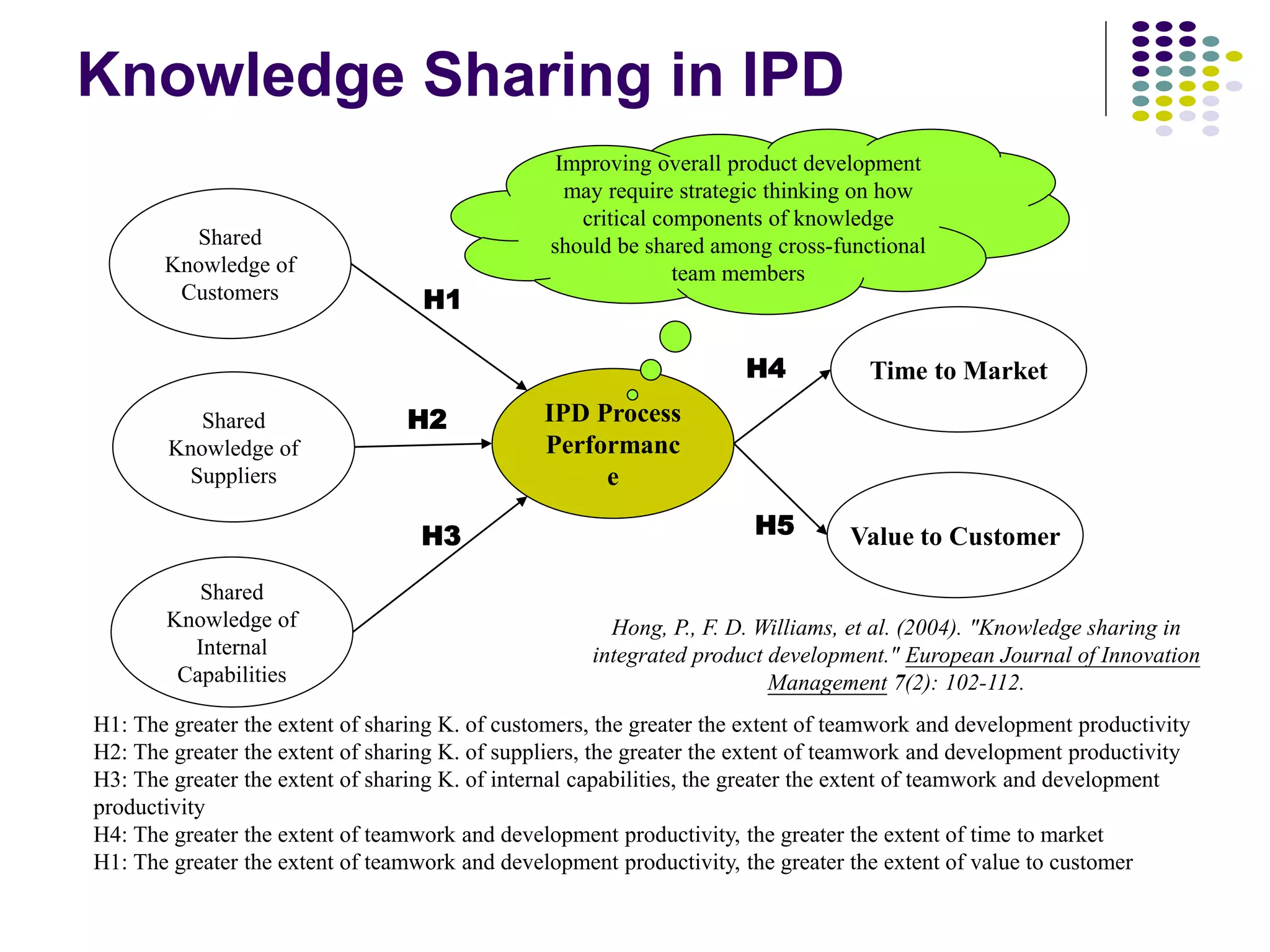
The document discusses the complexities of knowledge sharing in integrated product development (IPD) and the various forms of integration, including team and resource integration. It highlights the importance of sharing knowledge among team members regarding customer needs, internal design and manufacturing capabilities, and suppliers' capabilities, which impacts teamwork, productivity, and time to market. The study emphasizes that effective knowledge sharing and teamwork can lead to improved product development performance and greater value for customers.