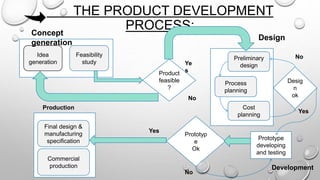
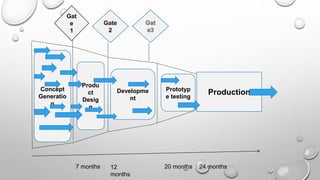
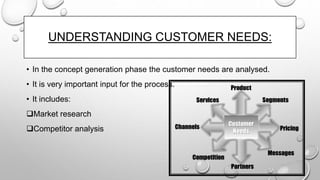
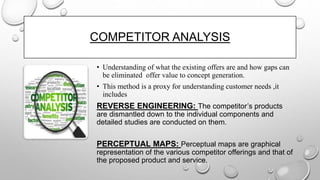
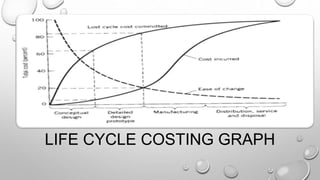
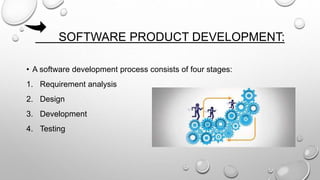
The document discusses the product development process. It describes the key stages as concept generation, design, development, and production. It also discusses tools and techniques used in product development like quality function deployment, value engineering, design for manufacturability, and mass customization. Performance measures to assess the effectiveness of the process are also outlined. Management accounting tools like life cycle costing and target costing help control product costs throughout the development cycle.